Журнал «Здоровье ребенка» 4 (55) 2014
Вернуться к номеру
The peculiarities of treatment of chronic gastritis which are associated with herpesviruses in children
Авторы: A. Y. Abaturov, N. I. Leonenko - State Institution "Dnipropetrovsk Medical Academy, Ministry of Health of Ukraine»; State Institution "Institute of Gastroenterology NAMS of Ukraine"
Рубрики: Педиатрия/Неонатология
Разделы: Клинические исследования
Версия для печати
Introduction
Active study of Helicobacter pylori revealed many facts of it`s involvement in the pathogenesis of diseases of the stomach. Current epidemiological studies indicate a high prevalence of H. pylori infection among children and adults. Along with the significance of Helicobacter pylori in gastroduodenal pathology, as competing etiological factor today is considered to be a specific intracellular infection. The exceptional role in the affection of the stomach and duodenum is given to infectious agents, including viruses of herpes family. There had been accumulated data on the possible role of cytomegalovirus infection, Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) in the development of gastritis in children. One of the most common of the herpesvirus family is an EBV virus. The structure of the genome and biological properties - it is a gamma herpesvirus, herpesvirus classification - pathogenic to humans, EBV - herpesvirus type IV or HHV-4 (human herpesvirus type 4) [1].
The complications of etiological structure of gastroduodenal diseases in children and identifying of the new pathogens had caused a change in the approach to therapy. Therefore, the relevant issue today is the optimal differential approach to the primary diagnosis, requires the development of new effective treatment for this pathology [2, 3]. In the study discusses problems of treatment of chronic Epstein-Barr virus infection, more attention is paid to interferon-α, in some cases with interferon inducers. Interferon is used to generate virus status of natural killer cells, increase phagocytic activity of monocytes, increase number of lymphocytes, which contributes to a full immune response and improves the prognosis. One of the promising areas of modern pharmacology is developing of liposomal drugs that have a number of obvious advantages: protecting body cells from the toxic effect of drugs, prolongation of the action of a drug injected to the organism, promoting the manifestation of targeted specificity by selective permeation from blood into the tissues, change of pharmacokinetics, improving the pharmacological efficacy, resolution for creating the water-soluble form of drug substances row, increasing their bioavailability [4-6]. These characteristics of the drug led to the study of it`s efficacy in the treatment of children with chronic gastritis, associated with intracellular viral infection.
Objective: To study the clinical efficacy of the use of recombinant interferon-α2 in children with chronic gastritis, associated with intracellular viral infection.
Materials and methods
There had been 50 children observed aged from 6 to 17 years with chronic gastritis, associated with intracellular viral infection in the exacerbation stage, who had been passing the examination and treatment in municipal children's gastroenterology department of SI "City Children`s Clinical Hospital #1" of Dnipropetrovsk Regional Council" of the city of Dnepropetrovsk.
Children who were under observation had been divided randomly into 2 groups (26 and 24). The main group consisted of 26 children in whom treatment had been carried out according to unified clinical protocols of medical care for children with diseases of the digestive system : in the case of chronic hyperacid gastritis - H2-histamine receptor blockers or inhibitor of H+-K+- ATPh-ase, antacids, prokinetics, cytoprotectors. To the complex therapy there had been included liposomal drug of recombinant α- interferon (Lipoferon, Vector-Medica, Russia), 500 IU per day during 14 days. The comparison group involved 24 patients who had been recieving symptomatic therapy.
All sick children along with clarifying the complaints and disease history, physical examination, laboratory examination (general clinical examination of blood, urine and excrement, biochemical hepatogram) had been performed endoscopic examination of the esophagus, stomach, duodenum (Pentax FG-15W, Japan) defining the acid- and secretory functions, abdomen cavity ultrasound, specific immunoglobulins IgM, IgG to CMV, IgM antibodies to capsid antigen (VCA) EBV, IgG to the early antigen (EA) EBV, IgG to nuclear antigen (EBNA) EBV. DNA of CMV and EBV viruses were determined in the biopsy of the gastric mucosa (the gastric mucosa) and gastric juice by PCR method (test system "AmplySens", Russia).
The criterion for the presence of EBV- associated infection or evidence of exposure to EBV in the past are the specific serological markers. Hence, in the acute phase of the disease or during exacerbations of chronic process there appear in the serum the specific IgM- antibodies to viral capsid antigen (IgM-VCA-EBV), which disappear usually within four to six weeks. In the acute phase, there are determined the early surface IgG- antibodies (IgG-EA-EBV), which are markers of active viral replication. Within recovery, they disappear. After two or three months after acute EBV- infection there are detected in serum the IgG- antibodies to nuclear antigen (IgG-EBNA-EBV); their production persists throughout all life long.
As the efficacy criteria there were considered the terms of curing and relief of pain and dyspeptic syndromes, dynamics of general condition, the average bed-day and frequency of relapse within a year after treatment cessation.
The duration of treatment was 2 weeks with efficiency control at 7-th and 14-th days of therapy. Monitoring the presence of herpesvirus infections had been carried out in 6 months and one year after treatment cessation.
Statistical analysis of the data was performed using statistical software "Statgraf", "Matstat". Reliability of differences was assessed using Student t-test (data with normal distribution) and Mann–Whitney`s test (if distribution other than normal).
For the survey there had been obtained voluntary informed written consent of the patients` parents.
Results and discussion
Boys in the I-st group of children made up 60.0 % in the II-d group - 57.1 %, girls - respectively 40.0, 32.9 %. The mean age of patients was 12 years.
The clinical picture at the most of patients before treatment had been dominated by pain, dyspeptic and asthenic-vegetative syndromes.
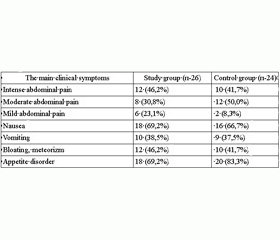
The main clinical symptoms are presented in Table 1.
Table 1
Clinical manifestations of chronic gastritis associated with herpesvirus
Clinical peculiarities of gastroduodenal pathology course associated with Epstein-Barr virus and cytomegalovirus in children are characterized by seasonality of exacerbations (spring and autumn) in the background or after SARS, resistant asthenic-vegetative disorders. Joining of herpesvirus infections in patients significantly worsens the prognosis of gastroduodenal diseases. Analysis of patients' complaints showed that most of the patients experienced painsyndrome (100 %). The most common location of pain was observed in the epigastric and pyloroduodenal zone with equal frequency in children of different age groups. Pain syndrome was often combined with diarrhea and asthenic-vegetative syndromes. Dyspeptic syndrome was characterized by disorder of appetite, nausea, vomiting, heartburn, flatulence. Almost all pediatric patients had been determined a clear association of pain syndrome with food intake. Asthenic-vegetative syndrome manifested by the vegetative instability, irritability, fatigue, headache.
Comparing of the dynamics of clinical manifestations at 7-th and 14-th days after the treatment start, it had been found that during treatment with combination therapy with inclusion of liposomal drug of recombinant α- interferon there had appeared a faster regression of intensity of the disease`s main syndromes, resulting in that an average bed-day was 12.5 versus 15.5 days in the comparison group, the incidence of relapse during the first year after treatment had been significantly lower in contrast to patients of a comparison group: 2.4 versus 35.6 %.
Efficiency of successful eradication of viral infection had been being controlled at 6 months and 1 year after the end of antiviral therapy by determining the DNA virus Epstein-Barr virus and cytomegalovirus DNA in gastric juice and gastric mucosa biopsy. In children of the main group within a year after treatment cessation there were not revealed the DNA virus Epstein-Barr virus and cytomegalovirus DNA.
Conclusions
1. Detection of DNA of Epstein-Barr virus and cytomegalovirus`s DNA in gastric juice and (or) in the lining of the stomach mucosa evidence of active viral replication in the stomach, and is the indication for inclusion of an antiviral drug in the treatment regimen.
2. We had proven the safety and efficacy of oral liposomal recombinant interferon alfa-2b through more rapid reduction of pain, dyspeptic and asthenic-vegetative syndromes, resulting in reduced patient's bed-days quantity and decreased frequency of relapses.

/45_g/45_gl.jpg)