Международный эндокринологический журнал Том 15, №4, 2019
Вернуться к номеру
Cтан антиоксидантної, прооксидантної та ендотеліальної систем у пацієнтів із хронічною критичною ішемією нижніх кінцівок та високим ризиком розвитку реперфузійно-реоксигенаційних ускладнень
Авторы: Колотило О.Б.
Вищий державний навчальний заклад України «Буковинський державний медичний університет», м. Чернівці, Україна
Рубрики: Эндокринология
Разделы: Клинические исследования
Версия для печати
Актуальність. Облітеруючий атеросклероз магістральних периферичних судин становить понад 20 % випадків від усієї серцево-судинної патології, тобто відзначається у 3 % від загальної кількості населення. Незважаючи на великий досвід виконання оперативних втручань на артеріях, 3-річна спроможність стегново-підколінних шунтів не перевищує 80 %. Частота реоклюзії судин аорто-клубового сегмента становить від 6 до 42 %. Метою дослідження було вивчення особливостей оксидантної, прооксидантної та ендотеліальної систем у пацієнтів із хронічною критичною ішемією нижніх кінцівок. Матеріали та методи. В основу роботи покладено аналіз комплексного обстеження та хірургічного лікування 220 хворих на облітеруючий атеросклероз аорти та магістральних артерій нижніх кінцівок. Хворі були розподілені на дві групи за об’ємом операційної реваскуляризації аорто-стегно-підколінного сегмента. Операційне втручання в першій групі пацієнтів включало одномоментну реконструкцію аорто-стегнового та стегно-підколінного сегментів, у пацієнтів другої групи реконструкцію вказаних сегментів було виконано у два етапи. Активність складових прооксидантно-антиоксидантної системи визначали за допомогою спектрофотометричних методів. Результати. Дослідження активності процесів вільнорадикального окислення вказують, що процеси, які відбуваються в тканинах нижніх кінцівок, через вплив на них вільних радикалів кисню не лише активують вільнорадикальні процеси, але й можуть потенціювати процеси ушкоджувального впливу на клітини тканин і передусім на ендотеліальну систему. Висновки. Ризик розвитку реперфузійних ускладнень у післяопераційному періоді в пацієнтів підтверджується високим рівнем запальної відповіді. При реваскуляризації відбувається руйнування, відшарування ендотеліальних клітин, розширення ендотеліальних параклітинних контактів, що сприяє гіперпроникності ендотеліального моношару.
Актуальность. Облитерирующий атеросклероз магистральных периферических сосудов составляет более 20 % случаев всей сердечно-сосудистой патологии, то есть свыше 3 % общей численности населения. Несмотря на большой опыт выполнения оперативных вмешательств на артериях, 3-летняя способность бедренно-подколенных шунтов не превышает 80 %. Частота реокклюзии сосудов аорто-подвздошного сегмента составляет от 6 до 42 %. Целью исследования было изучение особенностей оксидантной, прооксидантной и эндотелиальной систем у пациентов с хронической критической ишемией нижних конечностей. Материалы и методы. В основу работы положен анализ комплексного обследования и хирургического лечения 220 больных облитерирующим атеросклерозом аорты и магистральных артерий нижних конечностей. Больные были распределены на две группы по объему операционной реваскуляризации аорто-бедренно-подколенного сегмента. Операционное вмешательство в первой группе пациентов включало одномоментную реконструкцию аорто-бедренного и бедренно-подколенного сегментов, у пациентов второй группы реконструкция указанных сегментов выполнена в два этапа. Активность составляющих прооксидантно-антиоксидантной системы определяли с помощью спектрофотометрического метода. Результаты. Исследование активности процессов свободного радикального окисления указывает на то, что процессы, происходящие в тканях нижних конечностей, из-за влияния на них свободных радикалов кислорода не только активируют свободнорадикальные процессы, но и могут усиливать процессы повреждающего воздействия на клетки тканей и прежде всего на эндотелиальную систему. Выводы. Риск развития реперфузионных осложнений в послеоперационном периоде у пациентов подтверждается высоким уровнем воспалительного ответа. При реваскуляризации происходит разрушение, отслоение эндотелиальных клеток, расширение эндотелиальных параклеточных контактов, что способствует гиперпроницаемости эндотелиального слоя.
Background. Obliterating atherosclerosis of the peripheral arterial vessels accounts for more than 20 % of cases of cardiovascular pathology, that is more than in 3 % of the total population. Despite the large experience of performing operative arterial interventions, the 3-year ability of the femoral subcutaneous shunts does not exceed 80 %. The frequency of re-occlusion of iliac arteries is from 6 to 42 %. The purpose of the research was to study the features of the oxidant, pro-oxidant and endothelial systems in patients with chronic critical lower limb ischemia. Materials and methods. The work is based on the analysis of complex examination and surgical treatment of 220 patients with obliterating atherosclerosis of aorta and main arteries of the lower extremities. The patients were divided into two groups in terms of volume of surgical revascularization of femoropopliteal arteries. In the first group of patients, operative intervention included one-stage reconstruction of the aorta-femoral and femoropopliteal segments, in patients of the second group, the reconstruction of the indicated segments was performed in two stages. The activity of the components of the prooxidant-antioxidant system was determined using spectrophotometric methods. Results. Investigations of the activity of free-radical oxidation demonstrated that the processes involving the tissues of the lower limbs, due to the influence of oxygen free radicals on them, not only activate free radical processes, but can also enhance the processes of damaging effects on the tissue cells and, moreover, on the endothelial system. Conclusions. The risk of reperfusion complications in the postoperative period in patients is confirmed by the high level of the inflammatory response. When revascularization occurs, the destruction, detachment of endothelial cells, the spread of endothelial cell-cell contacts contributes to increase of penetration of the endothelial layer.
реперфузійно-реоксигенаційний синдром; антиоксидантна система; прооксидантна система; ендотеліальна система; критична ішемія; реваскуляризація
реперфузионно-реоксигенационный синдром; антиоксидантная система; прооксидантная система; эндотелиальная система; критическая ишемия; реваскуляризация
reperfusion and reoxygenation syndrome; antioxidant system; pro-oxidant system; endothelial system; critical ischemia; revascularization
Вступ
Матеріали та методи
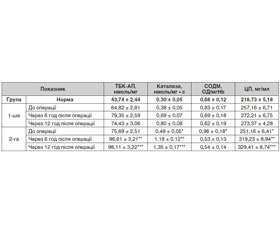
Результати
Обговорення
Висновки
- Rosenfield K, Jaff MR, White CJ, et al. Trial of a paclitaxel-coated balloon for femoropopliteal artery disease. N Engl J Med. 2015 Jul 9;373(2):145-53. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1406235.
- Ryden L, Grant PJ, Anker SD, et al. ESC Guidelines on diabetes, prediabetes, and cardiovascular diseases developed in collaboration with the EASD: the Task Force on diabetes, pre-diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and developed in collaboration with the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD). Eur Heart J. 2013 Oct;34(39):3035-87. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/eht108.
- Sabatine MS, Giugliano RP, Keech AC, et al. Evolocumab and clinical outcomes in patients with cardiovascular disease. N Engl J Med. 2017 May 4;376(18):1713-1722. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1615664.
- Santistevan JR. Acute Limb Ischemia: An Emergency Medicine Approach. Emerg Med Clin North Am. 2017 Nov;35(4):889-909. doi: 10.1016/j.emc.2017.07.006.
- Schmit K, Dolor RJ, Jones WS, et al. Comparative effectiveness review of antiplatelet agents in peripheral artery disease. J Am Heart Assoc. 2014 Dec 4;3(6):e001330. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.113.001330.
- Schultz MJ, Dunser MW, Dondorp AM, et al. Current challenges in the management of sepsis in ICUs in resource-poor settings and suggestions for the future. Intensive Care Med. 2017 May;43(5):612-624. doi: 10.1007/s00134-017-4750-z.
- Seymour CW, Liu VX, Iwashyna TJ, et al. Assessment of clinical criteria for sepsis: for the third international consensus definitions for sepsis and septic shock (Sepsis-3). JAMA. 2016 Feb 23;315(8):762-74. doi: 10.1001/jama.2016.0288.
- Shammas NW. Epidemiology, classification, and modifiable risk factors of peripheral arterial disease. Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2007;3(2):229-34. doi: 10.2147/vhrm.2007.3.2.229.
- Shammas NW, Radaideh Q. A Combined Radial and Pedal Access to Treat a Flush Chronic Total Occlusion of the Superficial Femoral Artery in a Critical Limb Ischemia Patient. Open J Cardiovasc Surg. 2019 Mar 10;11:1179065219834523. doi: 10.1177/1179065219834523.
- Sigvant B, Lundin F, Wahlberg E. The risk of disease progression in peripheral arterial disease is higher than expected: a meta-analysis of mortality and disease progression in peripheral arterial disease. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2016 Mar;51(3):395-403. doi: 10.1016/j.ejvs.2015.10.022.
- Aboyans V, Ricco JB, Bartelink MEL, et al. 2017 ESC Guidelines on the Diagnosis and Treatment of Peripheral Arterial Diseases, in collaboration with the European Society for Vascular Surgery (ESVS): Document covering atherosclerotic disease of extracranial carotid and vertebral, mesenteric, renal, upper and lower extremity arteriesEndorsed by: the European Stroke Organization (ESO)The Task Force for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Peripheral Arterial Diseases of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and of the European Society for Vascular Surgery (ESVS). Eur Heart J. 2018 Mar 1;39(9):763-816. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehx095.
- Strobl FF, Brechtel K, Schmehl J, et al. Twelve-month results of a randomized trial comparing mono with dual antiplatelet therapy in endovascularly treated patients with peripheral artery disease. J Endovasc Ther. 2013 Oct;20(5):699-706. doi: 10.1583/13-4275MR.1.
- Sultan S, Chua BY, Hamada N, Hynes N. Preoperative vascular screening in the presence of aortic, carotid and peripheral pathology for patients undergoing their first arterial intervention: 18 month follow-up. Int Angiol. 2013 Jun;32(3):281-90.
- Teague HL, Ahlman MA, Alavi A, et al. Unraveling Vascular Inflammation: From Immunology to Imaging. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2017 Sep 12;70(11):1403-1412. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2017.07.750.
- European Stroke Organisation, Tendera M, Aboyans V, et al. ESC Guidelines on the diagnosis and treatment of peripheral artery diseases: Document covering atherosclerotic disease of extracranial carotid and vertebral, mesenteric, renal, upper and lower extremity arteries: the Task Force on the Diagnosis and Treatment of Peripheral Artery Diseases of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Eur Heart J. 2011 Nov;32(22):2851-906. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehr211.
- Teraa M, Conte MS, Moll FL, Verhaar MC. Critical limb ischemia: current trends and future directions. J Am Heart Assoc. 2016 Feb 23;5(2). pii: e002938. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.115.002938.
- van de Weijer MA, Vonken EJ, de Vries JP, Moll FL, Vos JA, de Borst GJ. Technical and clinical success and long-term durability of endovascular treatment for atherosclerotic aortic arch branch origin obstruction: evaluation of 144 procedures. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2015 Jul;50(1):13-20. doi: 10.1016/j.ejvs.2015.03.058.
- Vemulapalli S, Dolor RJ, Hasselblad V, et al. Comparative effectiveness of medical therapy, supervised exercise, and revascularization for patients with intermittent claudication: a network meta-analysis. Clin Cardiol. 2015 Jun;38(6):378-86. doi: 10.1002/clc.22406.
- Vincent JL, Marshall JC, Namendys-Silva SA, et al. Assessment of the worldwide burden of critical illness: the Intensive Care Over Nations (ICON) audit. Lancet Respir Med. 2014 May;2(5):380-6. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(14)70061-X.
- Zeller T, Tepe G. Treatment of acute limb ischemia with focus on endovascular techniques. Vasa. 2009 May;38(2):123-33. doi: 10.1024/0301-1526.38.2.123.

/330-1.jpg)
/331-1.jpg)