Журнал «Здоровье ребенка» Том 15, №4, 2020
Вернуться к номеру
Роль однонуклеотидного поліморфізму TLR4 у розвитку неалкогольної жирової хвороби печінки в дітей
Авторы: Степанов Ю.М., Завгородня Н.Ю., Грабовська О.І., Кленіна І.А., Татарчук О.М.
ДУ «Інститут гастроентерології НАМН України», м. Дніпро, Україна
Рубрики: Педиатрия/Неонатология
Разделы: Клинические исследования
Версия для печати
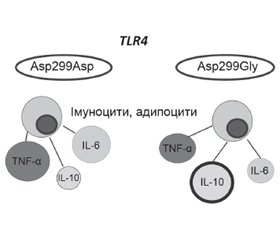
Актуальність. Прогресування неалкогольної жирової хвороби печінки (НАЖХП) від простого стеатозу до стеатогепатиту відбувається в генетично схильних індивідуумів внаслідок порушення імунного гомеостазу й розвитку системної і локальної запальної відповіді. Несинонімічні однонуклеотидні поліморфізми гена TLR4, змінюючи просторову структуру протеїну і, ймовірно, чутливість рецептора до його лігандів, обумовлюють певні функціональні аберації, що можуть впливати на характер й активність запалення. Мета дослідження: вивчити асоціацію SNP Asp299Gly rs4986790 гена TLR4 зі структурними змінами печінки, показниками вродженого імунітету та вуглеводного обміну в дітей із НАЖХП. Матеріали та методи. Під спостереженням перебували 76 дітей із надмірною вагою та ожирінням віком від 9 до 17 років. Наявність стеатозу печінки визначалась за допомогою транзієнтної еластометрії. За наявністю стеатозу печінки діти були розподілені на 2 групи, за наявністю SNP Asp299Gly (rs4986790) гена TLR4 кожна з груп розподілена на 2 підгрупи: діти з нормальним (Asp299Asp) та поліморфним (Asp299Gly) варіантами гена TLR4. Вміст інсуліну, IL-6, IL-10, TNF-α в сироватці крові визначали імуноферментним методом, розраховували індекс HOMA-IR. Результати. Частота виявлення SNP Asp299Gly rs4986790 гена TLR4 у гетерозиготному стані серед обстежених дітей становила 15,8 %, у дітей із НАЖХП — 20,0 %, у дітей без стеатозу — 11,1 % (р > 0,05). Значущих відмінностей показників жорсткості та ступеня жирової інфільтрації печінки пацієнтів з AA та AG генотипами SNP rs4986790 гена TLR4 не знайдено (р > 0,05). У дітей із НАЖХП із варіантом Asp299Gly гена TLR4 рівень IL-10 був вірогідно вищим порівняно з хворими з варіантом Asp299Asp гена TLR4. У той же час у дітей із варіантом Asp299Asp без стеатозу печінки спостерігався вірогідно вищий рівень IL-6 (р < 0,05) порівняно з особами з поліморфним варіантом Asp299Gly гена TLR4. Виявлений прямий кореляційний зв’язок помірної сили між варіантом Asp299Gly гена TLR4 та рівнем IL-10 (r = 0,459, p < 0,05). У дітей із варіантом Asp299Asp гена TLR4, хворих на НАЖХП, відзначалися вищі значення HOMA-IR порівняно з хворими з варіантом Asp299Gly гена TLR4 (р > 0,05). Виявлений прямий кореляційний зв’язок між рівнем ІL-6 та інсуліном (r = 0,398; р < 0,01), індексом HOMA-IR (r = 0,364; р < 0,05) у дітей, хворих на НАЖХП. Висновки. Діти з SNP Asp299Gly TLR4, хворі на НАЖХП, характеризуються вірогідно вищим рівнем продукції IL-10 та нижчими рівнями інсуліну та HOMA-IR, що може свідчити про протективні властивості SNP Asp299Gly rs4986790 гена TLR4 щодо розвитку й прогресування НАЖХП.
Актуальность. Прогрессирование неалкогольной жировой болезни пчени (НАЖБП) от простого стеатоза до стеатогепатита происходит у генетически предрасположенных индивидуумов вследствие нарушения иммунного гомеостаза и развития системного и локального воспалительного ответа. Несинонимические однонуклеотидные полиморфизмы гена TLR4, изменяя пространственную структуру и, вероятно, чувствительность рецептора к его лигандам, обусловливают определенные функциональные аберрации, которые могут влиять на характер и активность воспаления. Цель исследования: изучить ассоциации SNP Asp299Gly rs4986790 гена TLR4 со структурными изменениями печени, показателями врожденного иммунитета и углеводного обмена у детей с НАЖБП. Материалы и методы. Под наблюдением находились 76 детей с избыточным весом и ожирением в возрасте от 9 до 17 лет. Наличие стеатоза печени определялось с помощью транзиентной эластометрии. По наличию стеатоза печени дети были разделены на 2 группы, по наличию SNP Asp299Gly (rs4986790) гена TLR4 каждая из групп разделена на 2 подгруппы: дети с нормальным (Asp299Asp) и полиморфным (Asp299Gly) вариантами гена TLR4. Содержание инсулина, IL-6, IL-10, TNF-α в сыворотке крови определяли иммуноферментным методом, рассчитывали индекс HOMA-IR. Результаты. Частота выявления SNP Asp299Gly rs4986790 гена TLR4 в гетерозиготном состоянии среди обследованных детей составила 15,8 %, у детей с НАЖБП — 20,0 %, у детей без стеатоза — 11,1 % (р > 0,05). Значимых различий показателей жесткости и степени жировой инфильтрации печени пациентов с AA и AG генотипами SNP rs4986790 гена TLR4 не найдено (р > 0,05). У детей с НАЖБП с вариантом Asp299Gly гена TLR4 уровень IL-10 был достоверно выше по сравнению с больными с вариантом Asp299Asp гена TLR4. В то же время у детей с вариантом Asp299Asp без стеатоза печени наблюдался достоверно более высокий уровень IL-6 (р < 0,05) по сравнению с лицами с полиморфным вариантом Asp299Gly гена TLR4. Обнаружена прямая корреляционная связь умеренной силы между вариантом Asp299Gly гена TLR4 и уровнем IL-10 (r = 0,459, p < 0,05). У детей с вариантом Asp299Asp гена TLR4, больных НАЖБП, отмечались более высокие значения HOMA-IR по сравнению с больными с вариантом Asp299Gly гена TLR4 (р > 0,05). Обнаружена прямая корреляционная связь между уровнем IL-6 и инсулином (r = 0,398; р < 0,01), индексом HOMA-IR (r = 0,364; р < 0,05) у детей, больных НАЖБП. Выводы. Дети с НАЖБП и SNP Asp299Gly гена TLR4 характеризуются достоверно более высоким уровнем продукции IL-10 и низкими уровнями инсулина и HOMA-IR, что может свидетельствовать о протективных свойствах SNP Asp299Gly rs4986790 гена TLR4 в развитии и прогрессировании НАЖБП.
Background. The TLR4 non-synonymous single nucleotide polymorphism (SNPs) changes the spatial structure and, probably, the sensitivity of the receptor to its ligands, determines the certain functional aberrations that can affect the nature and activity of inflammation. The purpose of the study was to examine the associations of the SNP Asp299Gly rs4986790 of the TLR4 gene with liver structural changes, innate immunity, and carbohydrate metabolism parameters in children with NAFLD. Materials and methods. The study included 76 children with overweight and obesity aged 9 to 17 years. The presence of liver steatosis was determined using transient elastometry. According to the presence of liver steatosis, the children were divided into 2 groups; following the presence of SNP Asp299Gly (rs4986790) of the TLR4 gene, each group was divided into two subgroups: children with normal (Asp299Asp) and polymorphic (Asp299Gly) variants of the TLR4 gene. The blood serum content of insulin, IL-6, IL-10, TNF-α was determined by enzyme immunoassay, the HOMA-IR index was calculated. Results. The SNP Asp299Gly rs4986790 of the TLR4 gene detection rate in the heterozygous state among all children was 15.8 %, in children with NAFLD — 20.0 %, and in children without steatosis — 11.1 % (p > 0.05). Significant differences in the stiffness and degree of fatty liver in patients with AA and AG SNP rs4986790 genotypes were not found (p > 0.05). In children with NAFLD with the Asp299Gly variant of the TLR4 gene, the level of IL-10 was significantly higher compared to patients with the Asp299Asp variant of the TLR4 gene. At the same time, in children with the Asp299Asp variant without liver steatosis, a significantly higher level of IL-6 concentration was observed (p < 0.05) compared with individuals with the TLR4 gene Asp299Gly polymorphic variant. A moderate direct correlation was found between the Asp299Gly variant of the TLR4 gene and IL-10 level (r = 0.459, p < 0.05). In children with the Asp299Asp variant of the TLR4 gene with NAFLD, higher HOMA-IR values were observed compared to patients with the Asp299Asp variant of the TLR4 gene (p > 0.05). A direct correlation was found between the level of IL-6 and insulin (r = 0.398; p < 0.01), the HOMA-IR index (r = 0.364; p < 0.05) in children with NAFLD. Conclusions. Children with NAFLD and SNP Asp299Gly rs4986790 TLR4 are characterized by significantly higher levels of IL-10 production and lower levels of insulin and HOMA-IR, which may indicate the protective properties of the SNP Asp299Gly rs4986790 TLR4 in the NAFLD development and progression.
однонуклеотидний поліморфізм; toll-подібний рецептор 4; неалкогольна жирова хвороба печінки; діти
однонуклеотидный полиморфизм; toll-подобный рецептор 4; неалкогольная жировая болезнь печени; дети
single nucleotide polymorphism; toll-like receptor 4; non-alcoholic fatty liver disease; children
Вступ
Матеріали та методи
Результати
Обговорення
/12.jpg)
/13.jpg)
Висновки
- Nobili V., Alisi A., Valenti L., Miele L., Feldstein A.E., Alkhouri N. NAFLD in children: new genes, new diagnostic modalities and new drugs. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019. 16(9) Р. 517-530. doi: 10.1038/s41575-019-0169-z.
- Fitzpatrick E. Understanding susceptibility and targeting treatment in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in children; moving the fulcrum. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2019. 78(3). Р. 362-371. doi: 10.1017/S0029665118002914.
- Степанов Ю.М., Абатуров О.Є., Завгородня Н.Ю., Скирда І.Ю. Неалкогольна жирова хвороба печінки у дітей: сучасний погляд на можливості діагностики та лікування (частина I). Гастроентерологія. 2015. № 2(56). С. 99-107.
- Takaki A., Kawai D., Yamamoto K. Molecular mechanisms and new treatment strategies for non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014. 15(5). Р. 7352-7379. Published 2014, Apr 29. doi: 10.3390/ijms15057352.
- Stepanov Yu.M., Zavhorodnia N.Yu., Lukianenko O.Yu., Zygalo E.V., Yagmur V.B. Association of small intestinal bacterial overgrowth and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in children. Gastroenterologìa. 2019. 53(4). Р. 266-272. doi: 10.22141/2308-2097.53.3.2019.182406.
- Arbour N.C., Lorenz E., Schutte B.C. et al. TLR4 mutations are associated with endotoxin hyporesponsiveness in humans. Nat. Genet. 2000. 25(2). Р. 187-191. doi: 10.1038/76048.
- García-Bermúdez M., López-Mejías R., González-Juanatey C. et al. Lack of association between TLR4 rs4986790 polymorphism and risk of cardiovascular disease in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. DNA Cell. Biol. 2012. 31(7). Р. 1214-1220. doi: 10.1089/dna.2011.1582.
- Agnese D.M., Calvano J.E., Hahm S.J. et al. Human toll-like receptor 4 mutations but not CD14 polymorphisms are associated with an increased risk of gram-negative infections. J. Infect. Dis. 2002. 186(10). Р. 1522-1525. doi: 10.1086/344893.
- Lorenz E., Mira J.P., Frees K.L., Schwartz D.A. Relevance of mutations in the TLR4 receptor in patients with gram-negative septic shock. Arch. Intern. Med. 2002. 162(9). Р. 1028-1032. doi: 10.1001/archinte.162.9.1028.
- Vidyant S., Chatterjee A., Dhole T.N. A single-nucleotide polymorphism in TLR4 is linked with the risk of HIV-1 infection. Br. J. Biomed. Sci. 2019. 76(2). Р. 59-63. doi: 10.1080/09674845.2018.1559486.
- Sellers R.M., Payne J.B., Yu F., LeVan T.D., Walker C., Mikuls T.R. TLR4 Asp299Gly polymorphism may be protective against chronic periodontitis. J. Periodontal. Res. 2016. 51(2). Р. 203-211. doi: 10.1111/jre.12299.
- Moaaz M., Youssry S., Moaz A., Abdelrahman M. Study of Toll-Like Receptor 4 Gene Polymorphisms in Colorectal Cancer: Correlation with Clinicopathological Features. Immunol Invest. 2020. 49(5). Р. 571-584. doi: 10.1080/08820139.2020.1716787.
- Абатуров О.Є., Герасименко О.М., Шликова О.А., Кайдашев І.П. Генетичний поліморфізм ASP299GLY гена ТОЛ-подібного рецептора 4 у дітей з хелікобактерною інфекцією. Здоровье ребенка. 2013. № 6(49). С. 14-18.
- Дубинська Г.М., Сизова Л.М., Коваль Т.І., Шликова О.А. Поширеність поліморфізму гену TLR4 Asp299Gly серед хворих на хронічний гепатит С в Полтавській області. Актуальні проблеми сучасної медицини. 2015. Т. 15. Вип. 1. С. 81-84.
- Сизова Л.М. Особливості клініко-лабораторних характеристик хронічного гепатиту C у хворих із поліморфізмом Asp299Gly гену TLR4 та Gln11Leu гену TLR7. Актуальні проблеми сучасної медицини. 2016. Т. 16. Вип. 4(1). С. 183-188.
- Kiechl S., Lorenz E., Reindl M. et al. Toll-like receptor 4 polymorphisms and atherogenesis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002. 347(3). Р. 185-192. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa012673.
- Lee Y.H., Bae S.C., Song G.G. Meta-analysis demonstrates association between TLR polymorphisms and rheumatoid arthritis. Genet. Mol. Res. 2013. 12(1). Р. 328-334. Published 2013, Feb 7. doi: 10.4238/2013.February.7.2.
- Lee Y.H., Bae S.C., Kim J.H., Song G.G. Toll-like receptor polymorphisms and rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic review. Rheumatol. Int. 2014. 34(1). Р. 111-116. doi: 10.1007/s00296-013-2666-7.
- Hajjar A.M., Ernst R.K., Yi J., Yam C.S., Miller S.I. Expression level of human TLR4 rather than sequence is the key determinant of LPS responsiveness. PLoS One. 2017. 12(10). e0186308. Published 2017, Oct 11. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0186308.
- Wood M.J., Powell L.W., Dixon J.L., Subramaniam V.N., Ramm G.A. Transforming growth factor-β and toll-like receptor-4 polymorphisms are not associated with fibrosis in haemochromatosis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2013. 19(48). Р. 9366-9376. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i48.9366.
- Ferwerda B., McCall M.B., Alonso S. et al. TLR4 polymorphisms, infectious diseases, and evolutionary pressure during migration of modern humans. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA. 2007. 104(42). Р. 16645-16650. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0704828104.
- Kapil S., Duseja A., Sharma B.K. et al. Genetic polymorphism in CD14 gene, a co-receptor of TLR4 associated with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016. 22(42). Р. 9346-9355. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i42.9346.
- Kiziltas S., Ata P., Colak Y. et al. TLR4 gene polymorphism in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in comparison to healthy controls. Metab. Syndr. Relat. Disord. 2014. 12(3). Р. 165-170. doi: 10.1089/met.2013.0120.
- Miura K., Ishioka M., Iijima K. The Roles of the Gut Microbiota and Toll-like Receptors in Obesity and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. J. Obes. Metab. Syndr. 2017. 26(2). Р. 86-96. doi: 10.7570/jomes.2017.26.2.86.
- Абатуров О.Є., Герасименко О.М. Модуляція активності TLR4 епітеліоцитів слизової оболонки шлунка при хелікобактерній інфекції. Современная педиатрия. 2009. № 6(28). С. 141-146.
- Bessone F., Razori M.V., Roma M.G. Molecular pathways of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease development and progression. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2019. 76(1). Р. 99-128. doi: 10.1007/s00018-018-2947-0.
- Jin C., Henao-Mejia J., Flavell R.A. Innate immune receptors: key regulators of metabolic disease progression. Cell. Metab. 2013. 17(6). Р. 873-882. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2013.05.011.
- Steinhardt A.P., Aranguren F., Tellechea M.L. et al. A functional nonsynonymous toll-like receptor 4 gene polymorphism is associated with metabolic syndrome, surrogates of insulin resistance, and syndromes of lipid accumulation. Metabolism. 2010. 59(5). Р. 711-717. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2009.09.015.
- Chang W.W., Zhang L., Jin Y.L., Yao Y.S. Toll-like receptor 4 gene Asp299Gly and Thr399Ile polymorphisms in type 2 diabetes mellitus: A meta-analysis of 15,059 subjects: Need for clarification of data in a recent meta-analysis. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2015. 110(3). Р. 31-32. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2015.08.001.
- Weyrich P., Staiger H., Stančáková A. et al. The D299G/T399I Toll-like receptor 4 variant associates with body and liver fat: results from the TULIP and METSIM Studies. PLoS One. 2010. 5(11). e13980. Published 2010, Nov 15. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0013980.

/10.jpg)
/10_2.jpg)
/11_2.jpg)
/11.jpg)
/12_2.jpg)