Международный эндокринологический журнал Том 17, №3, 2021
Вернуться к номеру
Глікемічний контроль та ефективність спостереження при синдромі діабетичної стопи
Авторы: Ayten Guner Atayoglu(1), Ali Timucin Atayoglu(2), Rahime Ozgur(3), Hammad Khan(4)
(1) — Ataturk Family Health Center, Istanbul Provincial Directorate of Health Admininstration, Istanbul, Turkiye
(2) — Istanbul Medipol University, International School of Medicine, Department of Family Medicine, Istanbul, Turkiye
(3) — Gaziosmanpasa Taksim Training & Research Hospital, Department of Internal Medicine, Istanbul, Turkiye
(4) — University of California Davis School of Medicine, Department of Psychiatry & Behavioral Science,
Sacramento, California, USA
Рубрики: Эндокринология
Разделы: Клинические исследования
Версия для печати
Актуальність. Хронічні ускладнення цукрового діабету (ЦД) є наслідком широкого спектра патогенезу захворювання. Кореляція між рівнем цукру в крові та хронічними ускладненнями була продемонстрована в різних дослідженнях. Навчання пацієнтів, управління факторами ризику та інші профілактичні заходи є найважливішими елементами зменшення частоти ускладнень ЦД, зокрема синдрому діабетичної стопи (СДС). Мета дослідження — оцінити рівень знань та ставлення до догляду за ногами серед хворих на цукровий діабет, а також встановити кореляцію між глікемічним контролем та розвитком СДС. Матеріали та методи. Проведене описове перехресне дослідження хворих на цукровий діабет, які зверталися за амбулаторною медичною допомогою. Проведений аналіз даних, зібраних за допомогою опитувань пацієнтів, клінічної оцінки, консультацій суміжних спеціалістів та визначення рівня глікованого гемоглобіну (HbA1c) у сироватці крові. У дослідження включені 90 пацієнтів із діагнозом ЦД. Результати. Із 90 хворих на ЦД, включених у дослідження, під спостереженням перебували 42 (46,7 %) жінки та 48 (53,3 %) чоловіків. Серед учасників дослідження число осіб, які повідомили про щоденне самооцінювання стану ніг (наявність ран, тріщин та зміни кольору шкіри), було вірогідно вищим (68,9 %), ніж тих, хто повідомив, що не проводив оцінку щодня (31,1 %). Майже в половини учасників діагностований СДС (n = 43; 47,7 %), при цьому рівні HbA1c у пацієнтів із СДС були вірогідно вищими порівняно з показниками HbA1c у пацієнтів без СДС (p < 0,05). Висновки. У дослідженні був виявлений високий рівень захворюваності на СДС із позитивною та статистично значущою кореляцією між рівнем HbA1c та наявністю СДС. Проведене дослідження підкреслює важливість ретельного моніторингу, навчання та дотримання рекомендацій лікарів з огляду на ризик серйозних ускладнень ЦД, зокрема СДС, при незадовільно контрольованому ЦД.
Background. The chronic complications of diabetes mellitus (DM) result from a wide variety of effects of disease. The correlation between blood sugar level and chronic complications has been demonstrated in various studies. Patient education, risk factor management, and other preventative measures are critical elements in reducing the incidence of diabetes complications such as Diabetic Foot Syndrome (DFS). We purposed to evaluate knowledge and attitudes towards foot care amongst patients with diabetes mellitus; in addition, we investigated the correlation between glycemic control and DFS. Materials and methods. This was a descriptive cross-sectional evaluation of patients who were diagnosed with diabetes mellitus seeking outpatient medical care with data being collected through patient surveys, clinical evaluation, specialty consultation, and biochemical analysis of glycated haemoglobin (HbA1c) serum levels. The population of the study was composed of 90 patients diagnosed with DM. Results. A total of 90 patients, 42 (46.7 %) females and 48 (53.3 %) males were included in the study. The rate of participants who reported completing daily self-evaluations for wounds, cracks, and discoloration on the feet was significantly higher (68.9 %) than those who reported not evaluating on a daily basis (31.1 %). Almost half of the participants were diagnosed with DFS (n = 43; 47.7 %) with the HbA1c levels of patients with DFS being significantly higher compared to the HbA1c levels of patients without DFS (p < 0.05). Conclusions. As a high incidence of DFS was found with a positive and statistically significant correlation between the HbA1c level and DFS presence, our study highlights the importance of close monitoring, education, and treatment given the risk of serious complications of DM such as DFS in setting of poorly controlled DM.
цукровий діабет; синдром діабетичної стопи; глікемічний контроль; навчання
diabetes mellitus; diabetic foot syndrome; blood glucose control
Introduction
Materials and Methods
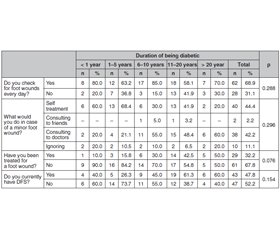
Results
Discussion
Conclusions
- Introduction: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes-2021. Diabetes Care. 2021. 44(Suppl 1). S1-S2. doi: 10.2337/dc21-Sint.
- International Diabetes Federation. IDF Diabetes Atlas. 9th ed. Brussels, Belgium, 2019. Available at: https://www.diabetesatlas.org
- Leroith D., Biessels G.J., Braithwaite S.S. et al. Treatment of Diabetes in Older Adults: An Endocrine Society Clinical Practice Guideline. The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism. 2019. 104(5). 1520-1574. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2019-00198
- Brannick B., Wynn A., Dagogo-Jack S. Prediabetes as a toxic environment for the initiation of microvascular and macrovascular complications. Experimental Biology and Medicine. 2016 [cited 2020 Dec 13]. 241(12). 1323-31. http://journals.sagepub.com/doi/10.1177/1535370216654227
- Hasan R., Firwana B., Elraiyah T. et al. A systematic review and meta-analysis of glycemic control for the prevention of diabetic foot syndrome. J. Vasc. Surg. 2016. 63(2 Suppl.). 22S-28S. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2015.10.005.
- Hazari A., Maiya G.А., Hazari A., Maiya G.A. Pathomechanics of Diabetic Foot Syndrome. In: Clinical Biomechanics and its Implications on Diabetic Foot [Internet]. Springer Singapore. 2020 [cited 2020 Dec 13]. 23-31. Available from: https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-981-15-3681-6_3
- Megallaa M.Н., Ismail A.А., Zeitoun M.Н., Khalifa M.S. Association of diabetic foot ulcers with chronic vascular diabetic complications in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. 2019. 13(2). 1287-1292. doi: 10.1016/j.dsx.2019.01.048.
- Kudlová P., Kočvarová I. Quality of life in patients with diabetic foot ulcers. Cent. Eur. J. Nurs. Midw. 2020. 11(1). 34-42. DOI: 10.15452/cejnm.2020.11.0006.
- Lavery L.А., Oz O.К., Bhavan K., Wukich D.K. Diabetic Foot Syndrome in the Twenty-First Century. Clin. Podiatr. Med. Surg. 2019. 36(3). 355-359. doi: 10.1016/j.cpm.2019.02.002.
- Bahador R.S., Afrazandeh S.S., Ghanbarzehi N., Ebrahimi M. The Impact of Three-month Training Programme on Foot Care and Self-efficacy of Patients with Diabetic Foot Ulcers. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2017. 11(7). IC01-IC04. doi: 10.7860/JCDR/2017/29025.10261.
- Zhang L., Zhang Q. Glycated Plasma Proteins as More Sensitive Markers for Glycemic Control in Type 1 Diabetes. PROTEOMICS Clinical Applications. 2020 [cited 2020 Dec 13]. 14(2). 1900104. https://doi.org/10.1002/prca.201900104
- Chehregosha H., Khamseh M.Е., Malek M., Hosseinpanah F., Ismail-Beigi F. A View Beyond HbA1c: Role of Continuous Glucose Monitoring. Diabetes Ther. 2019. 10(3). 853-863. doi: 10.1007/s13300-019-0619-1.
- Nathan D.М., Balkau B., Bonora E., Borch-Johnsen K., Buse J.В., Colagiuri S. et al. International expert committee report on the role of the A1C assay in the diagnosis of diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2009. 32(7). 1327-1334. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc09-9033
- Syed Soffian S.S., Ahmad S.В., Chan H.К., Soelar S.A., Abu Hassan M.R., Ismail N. Management and glycemic control of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus at primary care level in Kedah, Malaysia: A statewide evaluation. PLoS One. 2019. 14(10). e0223383. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0223383.
- Cavero-Redondo І., Peleteiro B., Álvarez-Bueno C., Rodriguez-Artalejo F., Martínez-Vizcaíno V. Glycated haemoglobin A1c as a risk factor of cardiovascular outcomes and all-cause mortality in diabetic and non-diabetic populations: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ Open. 2017. 7. e015949. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2017-015949.
- Navarro-Peternella F.М., Lopes A.Р.А.Т., de Arruda G.О., Teston E.F., Marcon S.S. Differences between genders in relation to factors associated with risk of diabetic foot in elderly persons: A cross-sectional trial. J. Clin. Transl. Endocrinol. 2016. 6. 30-36. doi: 10.1016/j.jcte.2016.10.001.
- Gökdeniz D., Akgün Şahin Z. Evaluation of Knowledge Levels About Diabetes Foot Care and Self-Care Activities in Diabetic Individuals. The International Journal of Lower Extremity Wounds 2020 [cited 2020 Dec 14]. https://doi.org/10.1177/1534734620926266
- Alonso-Morán E., Orueta J.F., Fraile Esteban J.І. et al. The prevalence of diabetes-related complications and multimorbidity in the population with type 2 diabetes mellitus in the Basque Country. BMC Public Health. 2014. 14. 1059. doi: 10.1186/1471-2458-14-1059.
- Laclé A., Valero-Juan L.F. Diabetes-related lower-extremity amputation incidence and risk factors: a prospective seven-year study in Costa Rica. Rev. Panam. Salud Publica. 2012. 32(3). 192-8. doi: 10.1590/s1020-49892012000900004. PMID: 23183559.
- Kogani M., Mansournia M.А., Doosti-Irani A., Holakouie-Naieni K. Risk factors for amputation in patients with diabetic foot ulcer in southwest Iran: a matched case-control study. Epidemiol. Health. 2015. 37. e2015044. doi: 10.4178/epih/e2015044.
- Chiba Y., Kimbara Y., Kodera R. et al. Risk factors associated with falls in elderly patients with type 2 diabetes. J. Diabetes Complications. 2015. 29(7). 898-902. doi: 10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2015.05.016.
- Yu M.К., Lyles C.R., Bent-Shaw L.A., Young B.A. Sex disparities in diabetes process of care measures and self-care in high-risk patients. J. Diabetes Res. 2013. 2013. 575814. doi: 10.1155/2013/575814.
- Viswanathan V., Shobhana R., Snehalatha C., Seena R., Ramachandran A. Need for education on footcare in diabetic patients in India. J. Assoc. Physicians India. 1999. 47(11). 1083-5. PMID: 10862318.
- Singh S., Jajoo S., Shukla S., Acharya S. Educating patients of diabetes mellitus for diabetic foot care. J. Family Med. Prim. Care. 2020. 9(1). 367-373. doi: 10.4103/jfmpc.jfmpc_861_19.
- Mishra S.С., Chhatbar K.С., Kashikar A., Mehndiratta A. Diabetic foot. BMJ. 2017. 359. doi: https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.j5064.
- Moreno Hernández M.І., Trilla Soler M., Espluga Capdevila A., Mengual Miralles N., Bundó Vidiella M., Juanola Costa J., Aubà Llambrich J. Self care and risk factors of diabetic foot in patients with type II diabetes mellitus. Aten. Primaria. 1997. 20(4). 185-90. (in Spanish). PMID: 9410141.
- Mancini L., Ruotolo V. The diabetic foot: epidemiology. Rays. 1997. 22(4). 511-23. PMID: 9550892.
- van Netten J.J., Lazzarini P.А., Armstrong D.G., Bus S.А., Fitridge R., Harding K. et al. Diabetic Foot Australia guideline on footwear for people with diabetes. J. Foot Ankle Res. 2018. 11. 2. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13047-017-0244-z
- Nicolucci A., Cavaliere D., Scorpiglione N., Carinci F., Capani F., Tognoni G., Benedetti M.M. A comprehensive assessment of the avoidability of long-term complications of diabetes. A case-control study. SID-AMD Italian Study Group for the Implementation of the St. Vincent Declaration. Diabetes Care. 1996. 19(9). 927-33. doi: 10.2337/diacare.19.9.927.
- Haghighatpanah M., Nejad A.S.М., Haghighatpanah M., Thunga G., Mallayasamy S. Factors that correlate with poor glycemic control in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients with complications. Osong Public Health and Research Perspectives. 2018. 9(4). 167-174. DOI: 10.24171/j.phrp.2018.9.4.05.
- Özer E., Şengül A.М., Gedik S., Salman S., Salman F., Sargin M. et al. Diabetes education: A chance to improve well-being of Turkish people with type 2 diabetes. Patient Education and Counseling [Internet]. 2003. 51(1). 39-44. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0738-3991(02)00246-X
- LaManna J., Litchman M.L., Dickinson J.K., Todd A., Julius M.М., Whitehouse C.R., Hyer S., Kavookjian J. Diabetes Education Impact on Hypoglycemia Outcomes: A Systematic Review of Evidence and Gaps in the Literature. Diabetes Educ. 2019. 45(4). 349-369. doi: 10.1177/0145721719855931.
- Lee S.K., Shin D.Н., Kim Y.Н., Lee K.S. Effect of diabetes education through pattern management on self-care and self-efficacy in patients with type 2 diabetes. Int. J. Environ Res Public Health. 2019. 16(18). 3323. doi: 10.3390/ijerph16183323.

/18.jpg)
/19.jpg)
/20.jpg)
/21.jpg)
/22.jpg)