Журнал "Гастроэнтерология" Том 55, №2, 2021
Вернуться к номеру
Особливості цитокінового балансу при прогресуванні структурних змін слизової оболонки шлунка у хворих на атрофічний гастрит
Авторы: Мосійчук Л.М., Татарчук О.М., Сімонова О.В., Петішко О.П.
ДУ «Інститут гастроентерології НАМН України», м. Дніпро, Україна
Рубрики: Гастроэнтерология
Разделы: Клинические исследования
Версия для печати
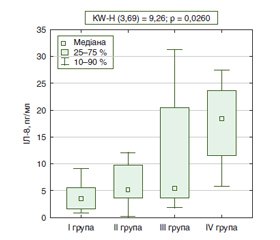
Актуальність. До сьогодні питання взаємодії цитокінового балансу та прогресування структурних змін слизової оболонки шлунка (СОШ) залишаються остаточно не визначеними. Водночас визначення ролі цитокінового балансу як складової шлункового канцерогенезу дозволить обґрунтувати нові підходи до тактики ведення пацієнтів з атрофічним гастритом. Мета: оцінити рівень про- та протизапальних цитокінів, васкулоендотеліального фактора росту на етапах прогресування структурних змін СОШ у хворих на атрофічний гастрит. Матеріали та методи. У дослідження включено 79 хворих на атрофічний гастрит, яким проведено ендоскопічне дослідження в режимі NBI. Хворі були розподілені на групи з урахуванням виявлених структурних змін у СОШ: І група — 8 пацієнтів з атрофією СОШ без кишкової метаплазії (КМ); ІІ група — 16 хворих з атрофією СОШ із КМ, обмеженою антральним відділом шлунка; ІІІ група — 45 осіб з дифузною КМ на фоні атрофії СОШ; IV група — 10 пацієнтів з дисплазією СОШ. Усім хворим оцінювали рівень інтерлейкінів (ІЛ-8, ІЛ-10, ІЛ-18), фактора некрозу пухлини альфа (TNF-α), васкулоендотеліального фактора росту (VEGF). Результати. У хворих IV групи концентрація ІЛ-8 в сироватці крові становила 18,6 (11,3; 23,9) пг/мл і була вірогідно вище порівняно з пацієнтами І групи (в 5,0 раза; р < 0,05), ІІ групи (в 3,6 раза; р < 0,05) та ІІІ групи (в 3,4 раза; р < 0,05). За результатами Kruskal-Wallis test, вірогідність різниці рівня ІЛ-8 між групами становила 0,0260. Рівень VEGF у сироватці крові хворих із дисплазією СОШ був вірогідно підвищений проти рівня у хворих з атрофією СОШ без КМ (в 1,8 раза; р < 0,05) та хворих з атрофією СОШ із КМ (1,7 раза; р < 0,05). Зміни цитокінового балансу в бік прозапальних цитокінів були найбільш виражені у хворих ІІІ та IV груп; за результатами Kruskal-Wallis test, вірогідність різниці коефіцієнта співвідношення ІЛ-8/ІЛ-10 між групами становила 0,0207. Висновки. При прогресуванні структурних змін СОШ у хворих на атрофічний гастрит підвищення рівня прозапальних цитокінів (ІЛ-8, ІЛ-18, TNF-α) у сироватці крові не індукує секрецію протизапальних цитокінів (ІЛ-10). За результатами ROC-аналізу, діагностичними критеріями формування групи ризику виявлення диспластичних змін СОШ є рівень VEGF понад 341,4 мОд/мл (чутливість — 90,0 %, специфічність — 77,2 %) та рівень ІЛ-8 понад 14,4 пг/мл (чутливість — 80,0 %, специфічність — 78,3 %).
Background. Until now, the issue of the correlation between the cytokine balance and the progression of structural changes in the gastric mucosa remain completely uncertain. At the same time, the determination of the role of cytokine balance as a component of gastric carcinogenesis will make it possible to substantiate new approaches to managing patients with atrophic gastritis. The purpose was to assess the level of pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines, vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) at the stages of progression of structural changes in the gastric mucosa of patients with atrophic gastritis. Materials and methods. The study included 79 individuals with atrophic gastritis who underwent narrow band imaging endoscopic examination. The patients were divided into groups taking into account the revealed structural changes in the gastric mucosa: group I — 7 people with gastric mucosal atrophy without intestinal metaplasia (IM); group II — 16 individuals with gastric mucosal atrophy with IM limited by the antrum; group III — 45 people with diffuse IM against the background of gastric mucosal atrophy; group IV — 10 individuals with gastric mucosal dysplasia. In all patients, we assessed the level of interleukins (IL-8, IL-10, IL-18), tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α), VEGF. Results. In patients of group IV, the concentration of IL-8 in the blood serum was 18.6 (11.3; 23.9) pg/ml that was significantly higher than in group I (by 5.0 times, p < 0.05), group II (by 3.6 times, p < 0.05) and group III (by 3.4 times, p < 0.05). According to the results of the Kruskal-Wallis test, the probability of a difference in the IL-8 level between the groups was 0.0260. The level of VEGF in the blood serum of patients with gastric mucosal dysplasia was significantly increased compared to that in people with gastric mucosal atrophy without IM (by 1.8 times, p < 0.05) and those with gastric mucosal atrophy with IM (by 1.7 times, p < 0.05). Changes in the cytokine balance towards proinflammatory cytokines were most pronounced in patients of groups III and IV; according to the results of the Kruskal-Wallis test, the probability of a difference in the IL-8/IL-10 ratio between the groups was 0.0207. Conclusions. With the progression of structural changes in the gastric mucosa of patients with atrophic gastritis, an increase in the level of proinflammatory cytokines (IL-8, IL-18 and TNF-α) in the blood serum does not induce the secretion of anti-inflammatory cytokines (IL-10). According to the results of the ROC analysis, the diagnostic criteria for the formation of the risk group for detecting dysplastic changes in the gastric mucosa are VEGF level of more than 341.4 mU/ml (sensitivity — 90.0 %, specificity — 77.2 %) and the level of IL-8 above 14.4 pg/ml (sensitivity — 80.0 %, specificity — 78.3 %).
атрофічний гастрит; цитокіновий баланс; кишкова метаплазія; дисплазія; діагностичні критерії
atrophic gastritis; cytokine balance; intestinal metaplasia; dysplasia; diagnostic criteria
Вступ
Матеріали та методи
Результати
Обговорення
Висновки
- Li Y., Xia R., Zhang B., Li C. Chronic atrophic gastritis: a review. J. Environ. Pathol. Toxicol. Oncol. 2018. Vol. 37. № 3. P. 241-259.
- Botezatu A., Bodrug N. Chronic atrophic gastritis: an update on diagnosis. Med. Pharm. Rep. 2021. Vol. 94(1). P. 7-14.
- Koulis A., Buckle A., Boussioutas A. Premalignant lesions and gastric cancer: Current understanding. World J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2019. № 11. P. 665-678.
- Sugano K. et al. Kyoto global consensus report on Helicobacter pylori gastritis. Gut. 2015. Vol. 64(9). P. 1353-1367.
- Lahner E. et al. Chronic atrophic gastritis: natural history, diagnosis and therapeutic management. A position paper by the Italian Society of Hospital Gastroenterologists and Digestive Endoscopists (AIGO), the Italian Society of Digestive Endoscopy (SIED), the Italian Society of Gastroenterology (SIGE), and the Italian Society of Internal Medicine (SIMI). Dig. Liver Dis. 2019. № 51. P. 1621-1632.
- Pimentel-Nunes P. et al. Management of epithelial precancerous conditions and lesions in the stomach (MAPS II): European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE), European Helicobacter and Microbiota Study Group (EHMSG), European Society of Pathology (ESP), and Sociedade Portuguesa de Endoscopia Digestiva (SPED) guideline update 2019. Endoscopy. 2019. Vol. 51(4). P. 365-388.
- Bang C.S., Lee J.J., Baik G.H. Diagnostic performance of serum pepsinogen assay for the prediction of atrophic gastritis and gastric neoplasms: Protocol for a systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019. № 98. P. e14240.
- Kutluana U., Kilciler A.G., Mizrak S., Dilli U. Can neopterin be a useful immune biomarker for differentiating gastric intestinal metaplasia and gastric atrophy from non-atrophic non-metaplastic chronic gastritis? Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019. Vol. 42(5). P. 289-295.
- Wiwanitkit V. Genetic polymorphisms in TLR1, TLR2, TLR4, and TLR10 of Helicobacter pylori-associated gastritis in Thai population. Eur. J. Cancer. Prev. 2019. Vol. 28(2). P. 142-143.
- Navegantes K.C. et al. Immune modulation of some autoimmune diseases: the critical role of macrophages and neutrophils in the innate and adaptive immunity. J. Transl. Med. 2017. Vol. 15(1). P. 36.
- Dutta N., Lillehoj P.B., Estrela P., Dutta G. Electrochemical biosensors for cytokine profiling: recent advancements and possibilities in the near future. Biosensors (Basel). 2021. Vol. 11(3). P. 94.
- Джндоян З.Т., Баблумян А.Ю., Гиносян К.В., Шекоян С.В. Корреляционные связи между показателями интерлейкина-10 и интерлейкина-6 у больных периодической болезнью. Терапевтический архив. 2018. Т. 90. № 3. C. 38-41.
- Ashizawa T. et al. Clinical significance of interleukin-6 (IL-6) in the spread of gastric cancer: Role of IL-6 as a prognostic factor. Gastric. Cancer. 2005. № 8. P. 124-131.
- Siregar G.A., Halim S., Sitepu V.R. Serum TNF-α, IL-8, VEGF levels in Helicobacter pylori infection and their association with degree of gastritis. Acta Med. Indones. 2015. Vol. 47(2). P. 120-126.
- Esmailbeig M., Ghaderi A. Interleukin-18: a regulator of cancer and autoimmune diseases. Eur. Cytokine Netw. 2017. Vol. 28(4). P. 127-140.
- Yasuda K., Nakanishi K., Tsutsui H. Interleukin-18 in health and disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019. Vol. 20(3). P. 649.
- Liu D., He Q., Liu C. Correlations among Helicobacter pylori infection and the expression of cyclooxygenase-2 and vascular endothelial growth factor in gastric mucosa with intestinal metaplasia or dysplasia. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2010. Vol. 25(4). P. 795-799.
- Aksoy E.K. et al. Clinical significance of serum vascular endothelial growth factor, pigment epithelium-derived factor, tumor necrosis factor alpha, and progranulin levels in patients with gastric cancer and gastric precancerous lesions. J. Gastrointest Cancer. 2019. Vol. 50(3). P. 537-542.
- Rajendran P. et al. The vascular endothelium and human diseases. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2013. Vol. 9(10). P. 1057-1069.
- Пасієшвілі Т.М. Оцінка особливостей змін та діагностичної інформативності цитокінового профілю в осіб молодого віку з гастроезофагеальною рефлюксною хворобою, яка перебігає на тлі автоімунного запалення. Сучасна гастроентерологія. 2019. № 2(106). С. 16-21.

/16.jpg)
/17.jpg)
/18.jpg)
/18_2.jpg)