Журнал "Гастроэнтерология" Том 55, №2, 2021
Вернуться к номеру
Раціональний підхід до профілактики тромбоемболічних ускладнень при хірургічному лікуванні ускладнених форм холелітіазу у хворих iз цирозом печінки
Авторы: S.D. Khimich(1), F.T. Muraviov(2)
(1) — National Pirogov Memorial Medical University, Vinnytsia, Ukraine
(2) — Zhytomyr Regional Clinical Hospital, Zhytomyr, Ukraine
Рубрики: Гастроэнтерология
Разделы: Клинические исследования
Версия для печати
Актуальність. З літератури відомо, що значна частка ускладнень циррозу печінки пов’язана з негативним впливом цієї патології на систему згортання крові. За даними багатьох вчених, у більшості випадків при цирозі печінки існує ризик розвитку як тромботичних, так і геморагічних ускладнень. Мета дослідження: виявити раціональний підхід до профілактики тромбоемболічних ускладнень при хірургічному лікуванні ускладнених форм холелітіазу у хворих iз цирозом печінки. Матеріали та методи. Проведено ретроспективний аналіз історій хвороб 62 пацієнтів, які лікувалися з приводу ускладнених форм жовчнокам’яної хвороби та верифікованого цирозу печінки. Розподіл пацієнтів за нозологією був таким: гострий калькульозний холецистит — 48 осіб, синдром Міріззі — 7 та холедохолітіаз — 7. Результати. На основі порівняльної оцінки двох груп ризик інтраопераційної кровотечі в пацієнтів із передопераційною профілактикою був вищий (3 випадки — 8,1 %) при крововтраті понад 400 мл. Гематоми післяопераційних ран спостерігалися в 5 випадках у першій групі та в одному — у другій. У групі передопераційної профілактики розвинулися тромбоз ворітної вени (n = 1), тромбоз дрібних гілок легеневої артерії (n = 1) і тромбоз глибоких вен гомілки (n = 1). У групі післяопераційної профілактики таких ускладнень не спостерігалося. Висновки. Рішення щодо профілактики тромбоемболічних ускладнень у цієї категорії пацієнтів має бути зваженим і включати оцінку ризиків розвитку як геморагічних розладів, так і ускладнень, пов’язаних із тромбозом.
Background. It is known from scientific sources that a significant proportion of complications of liver cirrhosis is associated with negative impact of this pathology on the coagulation system. According to many scientists, liver cirrhosis in most cases poses a risk of developing both thrombotic and hemorrhagic complications. Objective: to identify a rational approach to the prevention of thromboembolic complications in the surgical treatment of complicated forms of cholelithiasis in patients with cirrhosis. Materials and methods. We retrospectively analyzed the hospital records of 62 patients who were treated for complicated forms of cholelithiasis with verified liver cirrhosis for the period from 2005 to 2018. The distribution of patients by nosology was as follows: acute calculous cholecystitis — 48 patients, Mirizzi syndrome — 7, choledocholithiasis — 7. Results. Based on a comparative analysis of two groups, the risk of intraoperative bleeding in patients with preoperative prophylaxis was higher (3 cases — 8.1 %), with a blood loss of more than 400 ml. Hematomas of postoperative wounds were observed in 5 cases in group 1 and in one case in group 2. In the group of preoperative prophylaxis, portal vein thrombosis (n = 1), thrombosis of small branches of the pulmonary artery (n = 1), and deep vein thrombosis of the leg (n = 1) developed. No such complications were observed in the group with postoperative prophylaxis. Conclusions. The decision on the prevention of thromboembolic complications in this category of patients should be balanced and include an assessment of the risks of developing both hemorrhagic disorders and complications associated with thrombosis.
жовчнокам’яна хвороба; цироз печінки; коагулопатії
gallstone disease; liver cirrhosis; coagulopathy
Introduction
Materials and methods
/54.jpg)
Results and discussion
Conclusions
- Lledó J.B., Ibañez J.C., Mayor L.G. et al. Laparoscopic cholecystectomy and liver cirrhosis. Surg. Laparosc. Endosc. Percutan. Tech. 2011. 21. 391-5.
- Pinheiro R., Waisberg D., Lai Q., Andraus W., Nacif L., Rocha-Santos V., D’Albuquerque L. Laparoscopic cholecystectomy and cirrhosis: patient selection and technical considerations. Annals of Laparoscopic and Endoscopic Surgery. 2017. 2(3). doi: 10.21037/3784.
- Strömberg J., Hammarqvist F., Sadr-Azodi O., Sandblom G. Cholecystectomy in patients with liver cirrhosis. Gastroenterol. Res. Pract. 2015. 2015. 783823. doi: 10.1155/2015/783823.
- Abbas N., Makker J., Abbas H., Balar B. Perioperative care of patients with liver cirrhosis: a review. Health Services Insights. 2017 Jan. doi: 10.1177/1178632917691270.
- Buresi M., Hull R., Coffin C.S. Venous thromboembolism in cirrhosis: a review of the literature. Can. J. Gastroenterol. 2012. 26(12). 905-908. doi: 10.1155/2012/175849.
- García-Fuster M.J., Abdilla N., Fabiá M.J., Fernández C., Oliver V., Forner M.J. Enfermedad tromboembólica venosa y cirrosis hepática [Venous thromboembolism and liver cirrhosis]. Rev. Esp. Enferm. Dig. 2008 May. 100(5). 259-62. (in Spanish). doi: 10.4321/s1130-01082008000500002. PMID: 18662076.
- Khoury T., Ayman A.R., Cohen J., Daher S., Shmuel C., Mizrahi M. The complex role of anticoagulation in cirrhosis: an updated review of where we are and where we are going. Digestion. 2016. 93. 149-159. doi: 10.1159/000442877.
- O’Leary J.G., Greenberg C.S., Patton H.M., Caldwell S.H. AGA clinical practice update: coagulation in cirrhosis. Gastroenterology. 2019 Jul. 157(1). 34-43.e1. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2019.03.070. Epub 2019 Apr 12. PMID: 30986390.
- Senzolo M., Sartori M.T., Lisman T. Should we give thromboprophylaxis to patients with liver cirrhosis and coagulopathy? HPB (Oxford). 2009. 11(6). 459-464. doi: 10.1111/j.1477-2574.2009.00079.x.

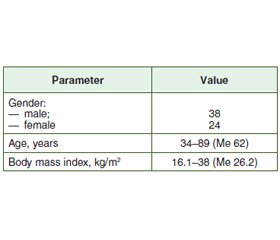
/55.jpg)