Международный эндокринологический журнал Том 17, №4, 2021
Вернуться к номеру
Фармакокінетичні характеристики й морфометричні ефекти інгібіторів натрійзалежних котранспортерів глюкози 2 в чоловіків і жінок, хворих на цукровий діабет 2-го типу (огляд літератури й власні результати)
Авторы: Прибила О.В.
ДУ «Інститут ендокринології та обміну речовин ім. В.П. Комісаренка НАМН України», м. Київ, Україна
Рубрики: Эндокринология
Разделы: Клинические исследования
Версия для печати
Актуальність. Згідно з останніми міжнародними клінічними рекомендаціями, препарати групи гліфлозинів — інгібіторів натрійзалежних котранспортерів глюкози 2-го типу (іНЗКТГ-2) показані як пероральні цукрознижувальні засоби 2–3-ї лінії терапії цукрового діабету (ЦД) 2-го типу. Завдяки незалежній від інсуліну стимуляції глюкозурії гліфлозини демонструють такі позаглікемічні ефекти, як зменшення маси тіла, поліпшення регіонального розподілу жирової тканини, ліпідного спектра плазми крові, зниження рівня урикемії, що в цілому сприяє зменшенню ризику серцево-судинних ускладнень. Метою даної роботи була оцінка ефективності дапагліфлозину в терапії чоловіків і жінок, хворих на ЦД 2-го типу, з метаболічно нездоровим фенотипом. Матеріали та методи. До дослідження включено 17 хворих на ЦД 2-го типу (11 чоловіків і 6 жінок) віком 58,0 ± 1,7 року (95% довірчий інтервал 53–62), яким проводилась оцінка показників композиції тіла методом біоелектричного імпедансу за допомогою аналізатора Tanita BC-545N (Японія). Пацієнти отримували терапію дапагліфлозином, антигіпертензивними й антигіперліпідемічними засобами (статинами). Результати. Тримісячне застосування дапагліфлозину в дозі 10 мг 1 раз на добу викликало в пацієнтів зниження індексу маси тіла, окружності талії, поліпшення показників композиції тіла, зокрема зниження відсотка загального жиру (вірогідність змін показників визначали з використанням парного t-тесту). Не виявлено вірогідних змін показників м’язової та кісткової маси, оцінки будови тіла, а також ліпідного комплексу та рівня урикемії. Особливістю групи жінок, на відміну від чоловіків, було зменшення рівня вісцерального жиру, що супроводжувалось покращенням водного забезпечення організму, зниженням розрахункового метаболічного віку. Висновки. Терапія хворих на ЦД 2-го типу препаратами групи іНЗКТГ-2 вже впродовж трьох місяців забезпечила зменшення ступеня ожиріння та поліпшення деяких показників композиції тіла. Підтвердження цієї тенденції може бути отримано при подальшому спостереженні.
Background. According to the latest international clinical guidelines, gliflozins — sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors — are indicated as oral antidiabetic drugs of second-third-line therapy in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Due to insulin-independent stimulation of glucosuria, gliflozins have extraglycemic effects such as weight loss, improved adipose tissue distribution, better plasma lipid profile, and decreased uricemia that in generally reduce the risk of cardiovascular complications. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effectiveness of dapagliflozin in the treatment of men and women with type 2 diabetes mellitus with a metabolically unhealthy phenotype. Materials and methods. The study included 17 individuals with diabetes mellitus type 2 (11 men and 6 women), aged 58.0 ± 1.7 years (95% confidence interval 53–62), whose body composition was evaluated by bioelectric impedance using a Tanita analyzer BC-545N (Japan). Patients received therapy with dapagliflozin, antihypertensive and antihyperlipidemic drugs (statins). Results. A three-month use of dapagliflozin in a dose of 10 mg once daily caused a decrease in body mass index, waist circumference, improvement of body composition, in particular a reduction in total body fat (the significance of changes was determined using a paired t-test). No significant changes in muscle and bone mass, body composition, lipid profile, and uricemia level were observed. The group of women, in contrast to men, had a decreased level of visceral fat, which was accompanied by an improvement in the body’s water supply, and a reduction in the estimated metabolic age. Conclusions. Treatment of type 2 diabetes patients with sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors for 3 months has reduced the degree of obesity and improved some indices of body composition. Confirmation of this trend can be obtained in further observations.
цукровий діабет 2-го типу; дапагліфлозин; композиція тіла; вісцеральний жир; урикемія; ліпідний спектр
type 2 diabetes mellitus; dapagliflozin; body composition; visceral fat; uricemia; lipid profile
Огляд літератури
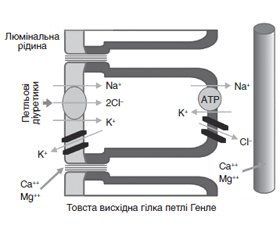
Інгібітори НЗКТГ-2 — препарати групи гліфлозинів
/40.jpg)
Клінічні дослідження ефектів іНЗКТГ-2 на композицію тіла у хворих на ЦД 2-го типу
Власне дослідження
Матеріали та методи
Результати
Обговорення
Висновки
- Alvarez Guisasola F., Mavros P., Nocea G., Alemao E., Ale–xander C.M., Yin D. Glycaemic control among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus in seven European countries: findings from the Real-Life Effectiveness and Care Patterns of Diabetes Management (RECAP-DM) study. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2008 Jun. 10 Suppl. 1. 8-15. doi: 10.1111/j.1463-1326.2008.00881.x. PMID: 18435669.
- Hoerger T.J., Segel J.E., Gregg E.W., Saaddine J.B. Is glycemic control improving in U.S. adults? Diabetes Care. 2008 Jan. 31(1). 81-6. doi: 10.2337/dc07-1572. Epub 2007 Oct 12. PMID: 17934153.
- American Diabetes Association Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes-2020. Diab. Care. 2020. 43(1). S14-S31.
- Grundy S.M., Stone N.J., Bailey A.L., Beam C., Birtcher K.K., Blumenthal R.S. et al. 2018 AHA/ACC/AACVPR/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/ADA/AGS/APhA/ASPC/NLA/PCNA Guideline on the Management of Blood Cholesterol: Executive Summary: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2019 Jun 25. 73(24). 3168-3209. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2018.11.002. Epub 2018 Nov 10. Erratum in: J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2019 Jun 25. 73(24). 3234-3237. PMID: 30423391.
- DeFronzo R.A., Eldor R., Abdul-Ghani M. Pathophysiologic Approach to Therapy in Patients With Newly Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2013. 36(2). S127-S138.
- Meng W., Ellsworth B.A., Nirschl A.A., McCann P.J., Patel M., Girotra R.N. et al. Discovery of dapagliflozin: a potent, selective renal sodium-dependent glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. J. Med. Chem. 2008 Mar 13. 51(5). 1145-9. doi: 10.1021/jm701272q. Epub 2008 Feb 9. PMID: 18260618.
- Ferrannini E., Ramos S.J., Salsali A., Tang W., List J.F. Dapagliflozin monotherapy in type 2 diabetic patients with inadequate glycemic control by diet and exercise: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Diabetes Care. 2010 Oct. 33(10). 2217-24. doi: 10.2337/dc10-0612. Epub 2010 Jun 21. PMID: 20566676; PMCID: PMC2945163.
- Bailey C.J., Gross J.L., Pieters A., Bastien A., List J.F. Effect of dapagliflozin in patients with type 2 diabetes who have inadequate glycaemic control with metformin: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet. 2010 Jun 26. 375(9733). 2223-33. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(10)60407-2. PMID: 20609968.
- Strojek K., Yoon K.H., Hruba V., Elze M., Langkilde A.M., Parikh S. Effect of dapagliflozin in patients with type 2 diabetes who have inadequate glycaemic control with glimepiride: a randomised, 24-week, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2011. 13. 928-38.
- Bolinder J., Ljunggren Ö., Kullberg J., Johansson L., Wilding J., Langkilde A.M., Sugg J., Parikh S. Effects of dapagliflozin on body weight, total fat mass, and regional adipose tissue distribution in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus with inadequate glycemic control on metformin. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012 Mar. 97(3). 1020-31. doi: 10.1210/jc.2011-2260. Epub 2012 Jan 11. PMID: 22238392.
- Schork A., Saynisch J., Vosseler A., Jaghutriz B.A., Heyne N., Peter A. et al. Effect of SGLT2 inhibitors on body composition, fluid status and renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system in type 2 diabetes: a prospective study using bioimpedance spectroscopy. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2019 Apr 5. 18(1). 46. doi: 10.1186/s12933-019-0852-y. PMID: 30953516; PMCID: PMC6451223.
- Giugliano D., Longo M., Scappaticcio L. et al. Sodium-glucose transporter-2 inhibitors for prevention and treatment of cardiorenal complications of type 2 diabetes [Internet]. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2021. 20(17). Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33430860.
- Tsushima Y., Lansang M.C., Makin V. The role of SGLT-2 inhibitors in managing type 2 diabetes. Cleve Clin. J. Med. 2020 Dec 31. 88(1). 47-58. doi: 10.3949/ccjm.88a.20088. PMID: 33384315.
- Koval S.M., Yushko K.O., Snihurska I.O., Starchenko T.G., Pankiv V.I., Lytvynova O.M., Mysnychenko O.V. Relations of angiotensin-(1-7) with hemodynamic and cardiac structural and functional parameters in patients with hypertension and type 2 diabetes. Arterial Hypertension (Poland). 2019. 23(3). 183-189. DOI: 10.5603/AH.a2019.0012.
- Chiang K.M., Tsay Y.C., Vincent Ng T.C., Yang H.C., Huang Y.T., Chen C.H., Pan W.H. Is Hyperuricemia, an Early-Onset Metabolic Disorder, Causally Associated with Cardiovascular Disease Events in Han Chinese? J. Clin. Med. 2019 Aug 12. 8(8). 1202. doi: 10.3390/jcm8081202. PMID: 31408958; PMCID: PMC6723695.
- Kalra S. Sodium Glucose Co-Transporter-2 (SGLT2) Inhibitors: A Review of Their Basic and Clinical Pharmacology. Diabetes Ther. 2014 Dec. 5(2). 355-66. doi: 10.1007/s13300-014-0089-4. Epub 2014 Nov 26. Erratum in: Diabetes Ther. 2015 Mar. 6(1). 95. PMID: 25424969; PMCID: PMC4269649.
- Zinman B., Wanner C., Lachin J.M., Fitchett D., Bluhmki E., Hantel S. et al.; EMPA-REG OUTCOME Investigators. Empagliflozin, Cardiovascular Outcomes, and Mortality in Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015 Nov 26. 373(22). 2117-28. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1504720. Epub 2015 Sep 17. PMID: 26378978.
- Fitchett D. A safety update on sodium glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitors. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2019 Apr. 21 Suppl. 2. 34-42. doi: 10.1111/dom.13611. PMID: 31081590.
- McGill J.B., Subramanian S. Safety of Sodium-Glucose Co-Transporter 2 Inhibitors. Am. J. Cardiol. 2019 Dec 15. 124 Suppl. 1. S45-S52. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2019.10.029. PMID: 31741440.
- Scheen A.J. Pharmacodynamics, efficacy and safety of sodium-glucose co-transporter type 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Drugs. 2015 Jan. 75(1). 33-59. doi: 10.1007/s40265-014-0337-y. PMID: 25488697.
- Jabbour S., Seufert J., Scheen A., Bailey C.J., Karup C., Langkilde A.M. Dapagliflozin in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A pooled analysis of safety data from phase IIb/III clinical trials. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2018 Mar. 20(3). 620-628. doi: 10.1111/dom.13124. Epub 2017 Oct 26. PMID: 28950419; PMCID: PMC5836959.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention [Internet]. Diabetes public health resource. 2015. Available from: http://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/statistics/prevalence_national.htm.
- Ferrannini E., Ramos S.J., Salsali A., Tang W., List J.F. Dapagliflozin monotherapy in type 2 diabetic patients with inadequate glycemic control by diet and exercise: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Diabetes Care. 2010 Oct. 33(10). 2217-24. doi: 10.2337/dc10-0612. Epub 2010 Jun 21. PMID: 20566676; PMCID: PMC2945163.
- Polidori D., Sanghvi A., Seeley R.J., Hall K.D. How Strongly Does Appetite Counter Weight Loss? Quantification of the Feedback Control of Human Energy Intake. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2016 Nov. 24(11). 2289-2295. doi: 10.1002/oby.21653. PMID: 27804272; PMCID: PMC5108589.
- Cai X., Yang W., Gao X., Chen Y., Zhou L., Zhang S., Han X., Ji L. The Association Between the Dosage of SGLT2 Inhibitor and Weight Reduction in Type 2 Diabetes Patients: A Meta-Analysis. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2018 Jan. 26(1). 70-80. doi: 10.1002/oby.22066. Epub 2017 Nov 22. PMID: 29165885.
- Schork A., Saynisch J., Vosseler A., Jaghutriz B.A., Heyne N., Peter A., Häring H.U., Stefan N., Fritsche A., Artunc F. Effect of SGLT2 inhibitors on body composition, fluid status and renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system in type 2 diabetes: a prospective study using bioimpedance spectroscopy. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2019 Apr 5. 18(1). 46. doi: 10.1186/s12933-019-0852-y. PMID: 30953516; PMCID: PMC6451223.
- Tobita H., Sato S., Miyake T., Ishihara S., Kinoshita Y. Effects of Dapagliflozin on Body Composition and Liver Tests in Patients with Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis Associated with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Prospective, Open-label, Uncontrolled Study. Curr. Ther. Res. Clin. Exp. 2017 Jul 8. 87. 13-19. doi: 10.1016/j.curtheres.2017.07.002. PMID: 28912902; PMCID: PMC5587885.
- Kahn S.E., Cooper M.E., Del Prato S. Pathophysiology and treatment of type 2 diabetes: perspectives on the past, present, and future. Lancet. 2014 Mar 22. 383(9922). 1068-83. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(13)62154-6. Epub 2013 Dec 3. PMID: 24315620; PMCID: PMC4226760.
- Fulcher G., Matthews D.R., Perkovic V., de Zeeuw D., Mahaffey K.W., Mathieu C. et al.; CANVAS trial collaborative group. Efficacy and safety of canagliflozin when used in conjunction with incretin-mimetic therapy in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2016 Jan. 18(1). 82-91. doi: 10.1111/dom.12589. Epub 2015 Dec 8. PMID: 26450639.
- Sinclair A., Bode B., Harris S., Vijapurkar U., Mayer C., Fung A., Shaw W., Usiskin K., Desai M., Meininger G. Efficacy and safety of canagliflozin compared with placebo in older patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a pooled analysis of clinical studies. BMC Endocr. Disord. 2014 Apr 18. 14. 37. doi: 10.1186/1472-6823-14-37. PMID: 24742013; PMCID: PMC4021426.
- Griffin M., Rao V.S., Ivey-Miranda J., Fleming J., Mahoney D., Maulion C. et al. Empagliflozin in Heart Failure: Diuretic and Cardiorenal Effects. Circulation. 2020 Sep 15. 142(11). 1028-1039. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.120.045691. Epub 2020 May 15. PMID: 32410463; PMCID: PMC7521417.
- Novikov A., Fu Y., Huang W., Freeman B., Patel R., van Ginkel C. et al. SGLT2 inhibition and renal urate excretion: role of luminal glucose, GLUT9, and URAT1. Am. J. Physiol. Renal. Physiol. 2019 Jan 1. 316(1). F173-F185. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00462.2018. Epub 2018 Nov 14. PMID: 30427222; PMCID: PMC6383194.
- Yuan T., Liu S., Dong Y., Fu Y., Tang Y., Zhao W. Effects of dapagliflozin on serum and urinary uric acid levels in patients with type 2 diabetes: a prospective pilot trial. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2020 Oct 27. 12. 92. doi: 10.1186/s13098-020-00600-9. PMID: 33117454; PMCID: PMC7590796.
- Cicero A.F.G., Fogacci F., Kuwabara M., Borghi C. Therapeutic Strategies for the Treatment of Chronic Hyperuricemia: An Evidence-Based Update. Medicina (Kaunas). 2021 Jan 10. 57(1). 58. doi: 10.3390/medicina57010058. PMID: 33435164; PMCID: PMC7827966.

/36.jpg)
/37.jpg)
/39.jpg)
/41.jpg)
/42.jpg)