Международный эндокринологический журнал Том 17, №5, 2021
Вернуться к номеру
Вплив COVID-19 та цукрового діабету на рівень аполіпопротеїну А1 у плазмі крові пацієнтів
Авторы: V.V. Pushkarev, L.K. Sokolova, S.A. Cherviakova, Yu.B. Belchina, M.V. Bigun, O.I. Kovzun, V.M. Pushkarev, M.D. Tronko
State Institution “V.P. Komisarenko Institute of Endocrinology and Metabolism of the National Academy
of Medical Sciences of Ukraine”, Kyiv, Ukraine
Рубрики: Эндокринология
Разделы: Клинические исследования
Версия для печати
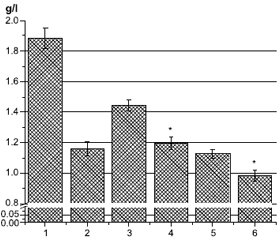
Актуальність. Підвищений рівень холестерину ліпопротеїнів високої щільності (ЛПВЩ) та аполіпопротеїну А1 (ApoA1) у плазмі асоціюється із зниженим ризиком розвитку серцево-судинних захворювань. Окрім потенційної кардіопротекторної функції, ЛПВЩ та ApoA1, основні аполіпопротеїни ЛПВЩ, також мають протидіабетичні властивості. Метою дослідження було визначити рівень ApoA1 у крові пацієнтів (n = 81) із цукровим діабетом (ЦД) та COVID-19. Матеріали та методи. Уміст ApoA1 визначали за допомогою наборів для імуноферментного аналізу (Elabscience, США). Вимірювання проводили при оптичній щільності 450 нм. Результати. Рівень ApoA1 у крові хворих на цукровий діабет і особливо на COVID-19 був значно нижчим, ніж у здорових людей. Дослідження залежності вмісту ApoA1 у плазмі від рівня Hb1Ac, статі та типу ЦД показало, що в крові хворих на ЦД 2-го типу кількість ApoA1 нижча, ніж в осіб із ЦД 1-го типу, і зі збільшенням рівня HbA1c уміст ApoA1 зменшується. Також була вірогідною гендерна різниця. Зі збільшенням індексу маси тіла рівень ApoA1 у плазмі крові зменшується нижче норми — 0,9 г/л, а при індексі маси тіла < 25 кг/м2 кількість ApoA1 значно перевищує середній рівень ліпопротеїну у хворих на ЦД. У пацієнтів із вперше діагностованим ЦД рівень ApoA1 значно вищий, а у пацієнтів із хворобою понад 10 років — нижчий від середнього та норми. Лікування бігуанідами в поєднанні з іншими препаратами (переважно інсуліном) або у вигляді монотерапії суттєво не впливає на вміст ApoA1 порівняно із середнім показником для всієї групи. У пацієнтів, які отримували похідні сульфонілсечовини, рівень ApoA1 значно нижчий від середнього для групи та від норми. Значний позитивний вплив на кількість ApoA1 у плазмі спостерігався в пацієнтів, які отримували комбінацію препаратів з інгібіторами натрійзалежного котранспортера глюкози 2-го типу, інсуліном та особливо інгібіторами дипептидилпептидази-4. Однак монотерапія інсуліном суттєво не впливала на вміст ApoA1. Обговорюються можливі механізми зниження ApoA1 за умов COVID-19 та ЦД. Висновки. Рівень ApoA1 може бути одним із перспективних маркерів тяжкого перебігу COVID-19.
Background. Increased level of high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol and apolipoprotein A1 (ApoA1) in plasma is associated with a reduced risk of developing cardiovascular diseases. In addition to its potential cardioprotective function, HDL and ApoA1, the main HDL apolipoprotein, also have antidiabetic properties. The aim of the study was to determine the level of ApoA1 in the blood of patients (n = 81) with diabetes mellitus and COVID-19. Materials and methods. ApoA1 was determined by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay kits (Elabscience, USA). The measurements were performed at an optical density of 450 nm. Results. ApoA1 level in the blood of patients with diabetes and especially with COVID-19 was significantly lower than in healthy people. The study of the dependence of plasma ApoA1 content on the level of Hb1Ac, the gender and the type of diabetes showed that in blood of patients with type 2 diabetes the amount of ApoA1 is lower than in those with type 1 diabetes, and with an increase in the level of Hb1Ac the amount of ApoA1 decreases. There was also significant gender difference. With an increase in the body mass index, the content of ApoA1 in blood plasma decreases below normal — 0.9 g/L, and at body mass index < 25 kg/m2, the amount of ApoA1 is significantly higher than the average lipoprotein level in diabetic patients. In individuals with newly diagnosed diabetes, the level of ApoA1 is significantly higher, and in patients with more than 10 years of illness, it is below average and below normal. Biguanide treatment, either in combination with other drugs (mainly insulin) or as monothe-rapy, does not significantly affect the level of ApoA1 compared to the entire group average. In patients treated with sulfonylurea, the level of ApoA1 is significantly lower than the average level for the group and the norm. A significant positive effect on the amount of ApoA1 in plasma was observed in people treated with a combination of drugs with sodium-glucose cotransporter type 2 inhibitors, insulin and especially dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors. However, insulin monotherapy did not significantly affect the ApoA1 content. Possible mechanisms of ApoA1 decrease in COVID-19 and diabetes are discussed. Conclusions. Thus, the level of ApoA1 may be one of the promising markers of severe COVID-19.
аполіпопротеїн А1; COVID-19; цукровий діабет; серцево-судинні захворювання; гіпоглікемічні засоби
apolipoprotein A1; COVID-19; diabetes mellitus; cardiovascular diseases; hypoglycemic agents
Introduction
Materials and methods
Results
/46.jpg)
Discussion
Conclusions
- Lund-Katz S., Phillips M.C. High density lipoprotein structure-function and role in reverse cholesterol transport. Subcell. Biochem. 2010. 51. 183-227. doi: 10.1007/978-90-481-8622-8_7.
- Inoue Y., Okamoto T., Honda T. et al. Disruption in the ba-lance between apolipoprotein A-I and mast cell chymase in chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Immun. Inflamm. Dis. 2020. 8(4). 659-671. doi: 10.1002/iid3.355.
- Kareinen I., Baumann M., Nguyen S.D. et al. Chymase released from hypoxia-activated cardiac mast cells cleaves human apoA-I at Tyr192 and compromises its cardioprotective activity. J. Lipid Res. 2018. 59(6). 945-957. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M077503.
- Mineo C., Shaul P.W. Regulation of signal transduction by HDL. J. Lipid Res. 2013. 54(9). 2315-24. doi: 10.1194/jlr.R039479.
- Rye K.A., Barter P.J., Cochran B.J. Apolipoprotein A-I interactions with insulin secretion and production. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 2016. 27(1). 8-13. doi: 10.1097/MOL.0000000000000253.
- Di Bartolo B.A., Cartland S.P., Genner S. et al. HDL improves cholesterol and glucose homeostasis and reduces atherosclerosis in diabetes-associated atherosclerosis. J. Diabetes Res. 2021. 2021. 6668506. doi: 10.1155/2021/6668506.
- Fritzen A.M., Domingo-Espín J., Lundsgaard A.M. et al. ApoA-1 improves glucose tolerance by increasing glucose uptake into heart and skeletal muscle independently of AMPKα2. Mol. Metab. 2020. 35. 100949. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2020.01.013.
- Mao Y., Xu Y., Lu L. The nonlinear association between apolipoprotein B to apolipoprotein A1 ratio and type 2 diabetes. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017. 96(1). e5834. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000005834.
- Dong H., Chen W., Wang X. et al. Apolipoprotein A1, B le-vels, and their ratio and the risk of a first stroke: a meta-analysis and case-control study. Metab. Brain Dis. 2015. 30(6). 1319-1330. doi: 10.1007/s11011-015-9732-7.
- Chyu K.Y., Shah P.K. HDL/ApoA-1 infusion and ApoA-1 gene therapy in atherosclerosis. Front. Pharmacol. 2015. 6. 187. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2015.00187.
- Wolkowicz P., White C.R., Anantharamaiah G.M. Apolipoprotein mimetic peptides: an emerging therapy against diabetic inflammation and dyslipidemia. Biomolecules. 2021. 11(5). 627. doi: 10.3390/biom11050627.
- Cochran B.J., Ong K.L., Manandhar B., Rye K.A. High density lipoproteins and diabetes. Cells. 2021. 10(4). 850. doi: 10.3390/cells10040850.
- Gao L., Zhang Y., Wang X., Dong H. Association of apolipoproteins A1 and B with type 2 diabetes and fasting blood glucose: a cross-sectional study. BMC Endocr. Disord. 2021. 21(1). 59. doi: 10.1186/s12902-021-00726-5.
- Retnakaran R., Ye C., Connelly P.W., Hanley A.J., Sermer M., Zinman B. Serum apoA1 (apolipoprotein A-1), insulin resistance, and the risk of gestational diabetes mellitus in human pregnancy — brief report. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2019. 39(10). 2192-2197. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.119.313195.
- Hilser J.R., Han Y., Biswas S. et al. Association of serum HDL-cholesterol and apolipoprotein A1 levels with risk of severe SARS-CoV-2 infection. J. Lipid Res. 2021. 62. 100061. doi: 10.1016/j.jlr.2021.100061.
- Zamanian Azodi M., Arjmand B., Zali A., Razzaghi M. Introducing APOA1 as a key protein in COVID-19 infection: a bioinformatics approach. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. Bed Bench. 2020 Fall. 13(4). 367-373.
- Yang Y., Zhu Z., Fan L. et al. Low serum level of apolipoprotein A1 is an indicator of severity in patients with coronavirus disease 2019. Preprint. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-31251/v1.
- Begue F., Tanaka S., Mouktadi Z. et al. Altered high-density lipoprotein composition and functions during severe COVID-19. Sci. Rep. 2021. 11(1). 2291. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-81638-1.
- Wei X., Zeng W., Su J. et al. Hypolipidemia is associated with the severity of COVID-19. J. Clin. Lipidol. 2020. 14(3). 297-304. doi: 10.1016/j.jacl.2020.04.008.
- Usami Y., Kobayashi Y., Kameda T. et al. Identification of sites in apolipoprotein A-I susceptible to chymase and carboxypeptidase A digestion. Biosci. Rep. 2012. 33(1). 49-56. doi: 10.1042/BSR20120094.
- Park J.H., Park S.M., Park K.H., Cho K.H., Lee S.T. Analysis of apolipoprotein A-I as a substrate for matrix metalloproteinase-14. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2011. 409(1). 58-63. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2011.04.105.
- Georgila K., Vyrla D., Drakos E. Apolipoprotein A-I (ApoA-I), immunity, inflammation and cancer. Cancers (Basel). 2019. 11(8). 1097. doi: 10.3390/cancers11081097.
- Koval S.M., Yushko K.O., Snihurska I.O., Starchenko T.G., Pankiv V.I., Lytvynova O.M., Mysnychenko O.V. Relations of angiotensin-(1-7) with hemodynamic and cardiac structural and functional parameters in patients with hypertension and type 2 diabetes. Arterial Hypertension (Poland). 2019. 23(3). 183-189. doi: 10.5603/AH.a2019.0012.
- Calanna S., Scicali R., Di Pino A. et al. Lipid and liver abnormalities in haemoglobin A1c-defined prediabetes and type 2 diabetes. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2014. 24(6). 670-676. doi: 10.1016/j.numecd.2014.01.013.
- Wu X., Yu Z., Su W. et al. Low levels of ApoA1 improve risk prediction of type 2 diabetes mellitus. J. Clin. Lipidol. 2017. 11(2). 362-368. doi: 10.1016/j.jacl.2017.01.009.
- Zheng J., Yin Q., Cao J., Zhang B. Obesity contributes more to increasing ApoB/ApoA1 ratio than hyperandrogenism in PCOS women aged 20–38 years in China. Exp. Ther. Med. 2017. 13(4). 1337-1342. doi: 10.3892/etm.2017.4094.
- Da Costa L.A., Arora P., García-Bailo B., Karmali M., El-Sohemy A., Badawi A. The association between obesity, cardiometabolic disease biomarkers, and innate immunity-related inflammation in Canadian adults. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2012. 5. 347-355. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S35115.
- Li F.R., Yang H.L., Zhou R. et al. Diabetes duration and glycaemic control as predictors of cardiovascular disease and mortality. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2021. 23(6). 1361-1370. doi: 10.1111/dom.14348.
- Sola D., Rossi L., Schianca G.P. et al. Sulfonylureas and their use in clinical practice. Arch. Med. Sci. 2015. 11(4). 840-848. doi: 10.5114/aoms.2015.53304.
- Garratt K.N., Brady P.A., Hassinger N.L., Grill D.E., Terzic A., Holmes D.R. Jr. Sulfonylurea drugs increase early mortality in patients with diabetes mellitus after direct angioplasty for acute myocardial infarction. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 1999. 33(1). 119-24. doi: 10.1016/s0735-1097(98)00557-9.
- Terao Y., Ayaori M., Ogura M. et al. Effect of sulfonylurea agents on reverse cholesterol transport in vitro and vivo. J. Atheroscler. Thromb. 2011. 18(6). 513-530. doi: 10.5551/jat.7641.
- Davies M.J., D’Alessio D.A., Fradkin J. et al. Management of hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes, 2018. A consensus report by the American Diabetes Association (ADA) and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD). Diabetes Care. 2018. 41(12). 2669-2701. doi: 10.2337/dci18-0033.
- Scheen A.J. The safety of gliptins: updated data in 2018. Expert Opin. Drug Saf. 2018. 17(4). 387-405. doi: 10.1080/14740338.2018.1444027.
- Patti A.M., Giglio R.V., Papanas N., Rizzo M., Rizvi A.A. Future perspectives of the pharmacological management of diabetic dyslipidemia. Expert Rev. Clin. Pharmacol. 2019. 12(2). 129-143. doi: 10.1080/17512433.2019.1567328.
- Golshahi J., Validi E., Akbari M. The association between fasting serum insulin, apo-lipoproteins level, and severity of coronary artery involvement in non-diabetic patients. Adv. Biomed. Res. 2014. 3. 192. doi: 10.4103/2277-9175.140624.
- Sokolova L.K., Belchina Yu.B., Pushkarev V.V., Chervia-kova S.A., Vatseba T.S., Kovzun O.I., Pushkarev V.M., Tronko M.D. The effect of metformin treatment on the level of GLP-1, NT-proBNP and endothelin-1 in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. International Journal of Endocrinology (Ukraine). 2020. 16(8). 26-31. doi: 10.22141/2224-0721.16.8.2020.222882.
- Sokolova L.K., Belchina Y.B., Pushkarev V.V., Chervia-kova S.A., Vatseba T.S., Kovzun O.I., Pushkarev V.M. The level of endothelin-1 in the blood of patients with diabetes, treated with hypoglycemic drugs. Endokrynologia. 2020. 25(3). 201-206. doi: 10.31793/1680-1466.2020.25-3.201.

/47.jpg)