Международный эндокринологический журнал Том 17, №5, 2021
Вернуться к номеру
Застосування міо-інозитолу в жінок репродуктивного віку з субклінічним гіпотиреозом та ожирінням на тлі дефіциту вітаміну D
Авторы: Пасєчко Н.В., Кульчінська В.М., Кадубець С.В.
Тернопільський національний медичний університет імені І.Я. Горбачевського Міністерства охорони здоров’я України, м. Тернопіль, Україна
Рубрики: Эндокринология
Разделы: Клинические исследования
Версия для печати
Актуальність. Захворювання щитоподібної залози на сьогодні посідають перше місце серед усієї ендокринної патології. Тісний функціональний взаємозв’язок тиреоїдної та репродуктивної систем зумовлює високу ймовірність розвитку поєднаних порушень при розладах однієї з цих ланок гомеостазу. Проблема порушень репродуктивного здоров’я зумовлює особливо серйозне занепокоєння у всьому світі та є актуальною щодо вивчення характеру впливу захворювань щитоподібної залози як на період фертильності, так і на саму вагітність, особливо за умов коморбідності. Метою дослідження було вивчити вплив міо-інозитолу на репродуктивну функцію жінок із субклінічним гіпотиреозом на тлі автоімунного тиреоїдиту та ожиріння. Матеріали та методи. Під спостереженням перебували 98 пацієнток віком 18–40 років із субклінічним гіпотиреозом, надмірною масою тіла або ожирінням на тлі автоімунного тиреоїдиту, які були рандомізовані на дві групи. Пацієнтки першої групи (n = 49) до основного лікування отримували міо-інозитол у дозі 2000 мг/добу та холекальциферол у дозі 2000 МО/добу. Пацієнтки другої групи (n = 49) до основного лікування отримували лише холекальциферол у дозі 2000 МО/добу. Результати. У 90,81 % жінок із субклінічним гіпотиреозом відзначався дефіцит вітаміну D, у 9,19 % — недостатність вітаміну D. Було виявлено негативний кореляційний зв’язок між рівнем 25(ОН)D та рівнем антитіл до тиреоїдної пероксидази (ТПО) (r = –0,189, р < 0,05). Виявлено негативний кореляційний зв’язок слабкої сили між рівнем 25(ОН)D та рівнем індексу НОМА (r = –0,168, р < 0,05). Призначення міо-інозитолу разом з вітаміном D призвело до вірогідного підвищення вмісту 25(OH)D у сироватці крові, а також до зниження титру антитіл до ТПО. Висновки. Встановлено позитивний вплив міо-інозитолу в поєднанні з вітаміном D на функціональний стан щитоподібної залози, на рівень антитіл до ТПО та рівень індексу НОМА в жінок репродуктивного віку з субклінічним гіпотиреозом та ожирінням.
Background. In recent years, thyroid diseases occupy the top places in the structure of the endocrine pathology. There exists a tight functional relationship between the thyroid and reproductive systems, which leads to a high probability of the development of combined disorders in one of these links of homeostasis. The problem of reproductive health disorders is of particular concern around the world and is relevant to the study of the impact of thyroid diseases on both fertility and pregnancy, especially in conditions of comorbidity. The purpose of the study was to investigate the effect of myo-inositol on the reproductive function of women with subclinical hypothyroidism on the background of autoimmune thyroiditis and obesity. Materials and methods. The study included 98 patients aged 18–40 years with subclinical hypothyroidism, overweight, or obesity on the background of autoimmune thyroiditis. They were randomly subdivided into two groups. Patients of the first group (n = 49) before the basic treatment received myo-inositol at a dose of 2000 mg/day and cholecalciferol at a dose of 2000 IU/day. Patients of the second group (n = 49) before the basic treatment received only cholecalciferol at a dose of 2000 IU/day. Results. Vitamin D deficiency was observed in 90.81 % of women with subclinical hypothyroidism, and vitamin D insufficiency in 9.19 %. A negative correlation was found between the level of 25(OH)D and the level of TPO-Ab (r = –0.189; p < 0.05). There was a weak negative correlation between the level of 25(OH)D and the level of the HOMA-IR (r = –0.168; p < 0.05). The administration of myo-inositol together with vitamin D led to a significant increase in the content of 25(OH)D, as well as to a decrease in the titer of TPO-Ab. Conclusions. The positive effect of myo-inositol drugs together with vitamin D on the functional state of the thyroid gland, on the level of TPO-Ab and HOMA-IR in women of reproductive age with subclinical hypothyroidism and obesity has been established.
субклінічний гіпотиреоз; міо-інозитол; вітамін D
subclinical hypothyroidism; myo-inositol; vitamin D
Вступ
Матеріали та методи
Результати
Обговорення
Висновки
- Taylor P.N., Albrecht D., Scholz A., Gutierrez-Buey G., Lazarus J.H., Dayan C.M., Okosieme O.E. Global epidemiology of hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2018. 14(5). 301-316. doi: 10.1038/nrendo.2018.18.
- Garmendia Madariaga A., Santos Palacios S., Guillén-Grima F., Galofré J.C. The incidence and prevalence of thyroid dysfunction in Europe: a meta-analysis. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014. 99(3). 923-31. doi: 10.1210/jc.2013-2409.
- Tkachenko V.I., Maksymets Ya.A., Vydyborets N.V., Kovalenko O.F. Analysis of the prevalence of thyroid pathology and morbidity in the middle of the population of Kyiv region and Ukraine for 2007–2017. International Journal of Endocrinology. 2018. 14(3). 279-284. doi: 10.22141/2224-0721.14.3.2018.136426. (in Ukrainian)
- Tronko M., Brenner A.V., Bogdanova T., Shpak V., Oliynyk V., Cahoon E.K., Drozdovitch V. et al. Thyroid neoplasia risk is increased nearly 30 years after the Chernobyl accident. Int. J. Cancer. 2017. 141(8). 1585-1588. doi: 10.1002/ijc.30857.
- Yalamanchi S., Cooper D.S. Thyroid disorders in pregnancy. Curr. Opin. Obstet. Gynecol. 2015. 27(6). 406-15. doi: 10.1097/GCO.0000000000000226.
- Biondi B., Cappola A.R., Cooper D.S. Subclinical Hypothyroidism: A Review. JAMA. 2019. 322(2). 153-160. doi: 10.1001/jama.2019.9052.
- Dong A.C., Stagnaro-Green A. Differences in Diagnostic Criteria Mask the True Prevalence of Thyroid Disease in Pregnancy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Thyroid. 2019. 29(2). 278-289. doi: 10.1089/thy.2018.0475.
- Ahmad S., Geraci S.A., Koch C.A. Thyroid disease in pregnancy (Women’s Health Series). South. Med. J. 2013. 106(9). 532-8. doi: 10.1097/SMJ.0b013e3182a66610.
- Benvenga S., Antonelli A. Inositol(s) in thyroid function, growth and autoimmunity. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2016. 17(4). 471-484. doi: 10.1007/s11154-016-9370-3.
- Chhetri D.R. Myo-Inositol and Its Derivatives: Their Emerging Role in the Treatment of Human Diseases. Front. Pharmacol. 2019. 10. 1172. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.01172.
- Croze M.L., Soulage C.O. Potential role and therapeutic interests of myo-inositol in metabolic diseases. Biochimie. 2013. 95(10). 1811-27. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2013.05.011.
- Ferrari S.M., Elia G., Ragusa F., Paparo S.R., Caruso C., Benvenga S., Fallahi P., Antonelli A. The protective effect of myoinositol on human thyrocytes. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2018. 19(4). 355-362. doi: 10.1007/s11154-018-9476-x.
- Reeh K., Summers P.A., Gould I.R. et al. Design, synthesis and evaluation of a tripodal receptor for phosphatidylinositol phosphates. Sci. Rep. 2020. 10. 18450. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-75484-w
- Song F., Zhang J., Zhao Y., Chen W., Li L., Xi Z. Synthesis and antitumor activity of inositol phosphotriester analogues. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2012. 10. 3642. doi: 10.1039/c2ob00031h.
- Aiba T., Sato M., Umegaki D., Iwasaki T., Kambe N., Fukase K., Fijimoto Y. Regioselective phosphorylation of myo-inositol with BINOL-derived phosphoramidites and its application for protozoan lysophosphatidylinositol. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2016. 14. 6672. doi: 10.1039/C6OB01062H.
- Frej A.D., Clark J., Le Roy C.I., Lilla S., Thomason P.A., Otto G.P., Churchill G. et al. The Inositol-3-Phosphate Synthase Biosynthetic Enzyme Has Distinct Catalytic and Metabolic Roles. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2016. 36(10). 1464-79. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00039-16.
- Nordio M., Pajalich R. Combined treatment with Myo-inositol and selenium ensures euthyroidism in subclinical hypothyroidism patients with autoimmune thyroiditis. J. Thyroid Res. 2013. 2013. 424163. doi: 10.1155/2013/424163.
- Morgante G., Musacchio M.C., Orvieto R., Massaro M.G., De Leo V. Alterations in Thyroid Function Among the Different Polycystic Ovary Syndrome Phenotypes. Gynecol. Endocrinol. 2013. 29(11). 967-9. doi: 10.3109/09513590.2013.829445.
- Nordio M., Basciani S. Treatment with Myo-Inositol and Selenium Ensures Euthyroidism in Patients with Autoimmune Thyroiditis. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2017. 2017. 2549491. doi: 10.1155/2017/2549491.
- Porcaro G., Angelozzi P. Myo-Inositol and Selenium Prevent Subclinical Hypothyroidism During Pregnancy: An Observational Study. Obstetric. 2018. 1(2). e164.
- Fallahi P., Ferrari S.M., Elia G., Ragusa F., Paparo S.R., Caruso C., Guglielmi G., Antonelli A. Myo-inositol in autoimmune thyroiditis, and hypothyroidism. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2018. 19(4). 349-354. doi: 10.1007/s11154-018-9477-9.
- Deja S., Dawiskiba T., Balcerzak W., Orczyk-Pawiłowicz M., Głód M., Pawełka D., Młynarz P. Follicular adenomas exhibit a unique metabolic profile. ¹H NMR studies of thyroid lesions. PLoS One. 2013. 8(12). e84637. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0084637.
- Nordio M., Basciani S. Evaluation of Thyroid Nodule Characteristics in Subclinical Hypothyroid Patients Under a Myo-Inositol Plus Selenium Treatment. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2018. 22(7). 2153-9. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_201804_14749.
- Benvenga S., Nordio M., Laganà A.S., Unfer V. The Role of Inositol in Thyroid Physiology and in Subclinical Hypothyroidism Management. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021. 12. 662582. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.662582.
- Pankiv I.V., Pashkovska N., Koval G., Piddubna A., Marchuk Yu., Abramova N., Tsaryk I. Efficacy of a combined administration of myo-inositol and vitamin D in patients with autoimmune thyroiditis. Endocrine Abstracts. 23rd European Congress of Endocrinology. 2021. Vol. 73. PEP10.4. doi: 10.1530/endoabs.73.PEP10.4.

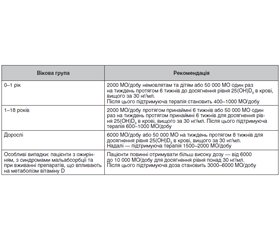
/79.jpg)