Международный эндокринологический журнал Том 17, №6, 2021
Вернуться к номеру
Характеристика хворих на цукровий діабет 2-го типу з гіпоглікемією на третинному рівні стаціонарної допомоги
Авторы: Satilmis Bilgin, Gulali Aktas, Ozge Kurtkulagi, Burcin M. Atak, Gizem Kahveci, Muhammed E. Demirkol, Tuba T. Duman
Abant Izzet Baysal University Hospital, Department of Internal Medicine, Bolu, Turkey
Рубрики: Эндокринология
Разделы: Клинические исследования
Версия для печати
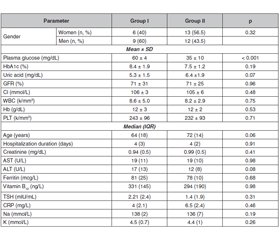
Актуальність. Гіпоглікемія — важливе ускладнення при лікуванні цукрового діабету 2-го типу, що створює труднощі для досягнення контролю захворювання. Крім того, явища гіпоглікемії зумовлюють майже 10 % випадків госпіталізацій у відділення невідкладної допомоги, вони також збільшують захворюваність та смертність шляхом виникнення кардіологічних, неврологічних порушень тощо. Гіпоглікемія залишається найпоширенішим побічним ефектом лікування інсуліном, однак пероральні протидіабетичні засоби також можуть викликати гіпоглікемічні ускладнення. Мета дослідження: у даному ретроспективному дослідженні авторами наведена динаміка клінічних та лабораторних показників хворих на цукровий діабет 2-го типу, у яких спостерігалася гіпоглікемія легкого або середнього ступеня тяжкості. Матеріали та методи. Проведено ретроспективний аналіз пацієнтів із цукровим діабетом 2-го типу з явищами гіпоглікемії, які перебували на стаціонарному лікуванні упродовж періоду із січня 2019 року по січень 2020 року. Обстежені пацієнти були розподілені на дві групи. До першої групи увійшли пацієнти з легкою гіпоглікемією, до другої — пацієнти з помірною чи тяжкою гіпоглікемією. Наведено порівняльну характеристику осіб першої та другої груп. Результати. У першій групі було 15 хворих на ЦД 2-го типу, у другій — 23. Показники глікованого гемоглобіну (HbA1c) та інші лабораторні маркери істотно не відрізнялися в досліджуваних групах. Аналогічно тривалість ЦД та антидіабетичне лікування істотно не відрізнялися в досліджуваних групах. Частка осіб старшої вікової групи була вірогідно вищою в другій групі порівняно з першою групою (р = 0,04). Висновки. Пацієнти з помірною чи тяжкою гіпоглікемією належать до старшої вікової групи, а рівень HbA1c не корелює зі ступенем гіпоглікемії. Оскільки ані тривалість цукрового діабету, ані антидіабетичне лікування не були пов’язані з тяжкістю гіпоглікемії, кожен випадок слід оцінювати індивідуально, щоб запобігти подальшим епізодам, які можуть збільшити захворюваність та смертність у діабетичній популяції.
Background. Hypoglycemia is an important complication of the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus, which constitutes a barrier in stringent diabetic control. Beside it constitutes nearly 10 % of emergency department admissions that caused by adverse drug events, it may also increase morbidities and mortality by inducing, cardiac arrhythmias, neurological impairment and ischemic events. Hypoglycemia is the most common side effect of insulin treatment, however, oral antidiabetic agents may also induce hypoglycemic complications. In present retrospective study, we purposed to observe general characteristics and laboratory data of the type 2 diabetic patients whom presented with mild or moderate/severe hypoglycemia. Materials and methods. Patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus whom presented to our institution with hypoglycemia between January 2019 and January 2020 were retrospectively analyzed. General characteristics and laboratory data of the subjects recorded. Patients grouped into two groups, group I consisted of subjects with mild hypoglycemia and group II consisted of patients with moderate/severe hypoglycemia. Data of the subjects in groups I and II were compared. Results. There were 15 subjects in group I and 23 in group II. HbA1c and other laboratory markers were not significantly different in study groups. Similarly diabetes duration and anti-diabetic treatment were not significantly different in study groups. The rate of geriatric patients was significantly higher in group II compared to group I (p = 0.04). Conclusions. Subjects with moderate/severe hypoglycemia tend to be more frequently in geriatric age and HbA1c not correlates with the degree of the hypoglycemia. Since neither duration of diabetes, nor anti-diabetic treatment were associated with the severity of the hypoglycemia, each case should be evaluated individually to prevent further episodes which could increase morbidity and mortality in diabetic population.
гіпоглікемія; цукровий діабет 2-го типу; глікований гемоглобін
hypoglycemia; type 2 diabetes mellitus; glycated hemoglobin
Introduction
Materials and methods
Results
Discussion
Conclusions
- Freeland B. Hypoglycemia in Diabetes Mellitus. Home Healthc Now. 2017 Sep. 35(8). 414-419. doi: 10.1097/NHH.0000000000000584.
- Geller A.I., Shehab N., Lovegrove M.C., Kegler S.R., Weidenbach K.N., Ryan G.J., Budnitz D.S. National estimates of insulin-related hypoglycemia and errors leading to emergency department visits and hospitalizations. JAMA Intern. Med. 2014. 174(5). 678-686. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2014.136.
- Tourkmani A.M., Alharbi T.J., Rsheed A.M.B., AlRasheed A.N., AlBattal S.M., Abdelhay O., Hassali M.A. et al. Hypoglycemia in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus patients: A review article. Diabetes Metab Syndr. 2018 Sep. 12(5). 791-794. doi: 10.1016/j.dsx.2018.04.004.
- Lee S.J. So much insulin, so much hypoglycemia. JAMA Intern. Med. 2014. 174. 686-688. DOI: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2013.13307.
- Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes — 2021. Diabetes Care. 2021. 44(Suppl. 1). 1-2. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc21-Sint.
- Hsu P.F., Sung S.H., Cheng H.M., Yeh J.S., Liu W.L., Chan W.L., Chen C.H. et al. Association of clinical symptomatic hypoglycemia with cardiovascular events and total mortality in type 2 diabetes: a nationwide population-based study. Diabetes Care. 2013 Apr. 36(4). 894-900. doi: 10.2337/dc12-0916.
- Unger J. Educating patients about hypoglycemia prevention and self-management. Clinical Diabetes. 2013. 31. 179-188. https://doi.org/10.2337/diaclin.31.4.179.
- Cryer P.E. Hypoglycemia-Associated Autonomic Failure in Diabetes: Maladaptive, Adaptive, or Both? Diabetes. 2015. 64. 2322-2323. DOI: 10.2337/db15-0331.
- Weinstock R.S., Xing D., Maahs D.M., Michels A., Ric-kels M.R., Peters A.L., Bergenstal R.M. et al. T1D Exchange Clinic Network. Severe hypoglycemia and diabetic ketoacidosis in adults with type 1 diabetes: results from the T1D Exchange clinic registry. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013 Aug. 98(8). 3411-3419. doi: 10.1210/jc.2013-1589.
- Cryer P.E. Severe hypoglycemia predicts mortality in diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2012. 35. 1814-1816. DOI: 10.2337/dc12-0749.
- Orchard T.J., Nathan D.M., Zinman B., Cleary P., Brillon D., Backlund J.Y., Lachin J.M.; Writing Group for the DCCT/EDIC Research Group. Association between 7 years of intensive treatment of type 1 diabetes and long-term mortality. JAMA. 2015, Jan 6. 313(1). 45-53. doi: 10.1001/jama.2014.16107.
- Cryer P.E. Glycemic goals in diabetes: trade-off between glycemic control and iatrogenic hypoglycemia. Diabetes. 2014. 63. 2188-2195. DOI: 10.2337/db14-0059.
- Cryer P.E. Mechanisms of hypoglycemia-associated autonomic failure in diabetes. The New England Journal of Medicine. 2013. 369. 362-372. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMra1215228.
- Nathan D.M. Diabetes: Advances in Diagnosis and Treatment. JAMA. 2015. 314. 1052-1062. DOI: 10.1001/jama.2015.9536.
- Inzucchi S.E., Bergenstal R.M., Buse J.B., Diamant M., Ferrannini E., Nauck M., Peters A.L. et al. Management of hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes, 2015: a patient-centered approach: update to a position statement of the American Diabetes Association and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2015 Jan. 38(1). 140-149. doi: 10.2337/dc14-2441. PMID: 25538310.
- Lipska K.J., Krumholz H., Soones T., Lee S.J. Polypharmacy in the Aging Patient: A Review of Glycemic Control in Older Adults With Type 2 Diabetes. JAMA. 2016, Mar 8. 315(10). 1034-1045. doi: 10.1001/jama.2016.0299.
- Yu S., Fu A.Z., Engel S.S., Shankar R.R., Radican L. Association between hypoglycemia risk and hemoglobin A1C in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 2016 Aug. 32(8). 1409-1416. doi: 10.1080/03007995.2016.1176017.
- Sircar M., Bhatia A., Munshi M. Review of Hypoglycemia in the Older Adult: Clinical Implications and Management. Canadian Journal of Diabetes. 2016. 40. 66-72. DOI: 10.1016/j.jcjd.2015.10.004.
- Frier B.M. Hypoglycaemia in diabetes mellitus: epidemiology and clinical implications. Nature Reviews Endocrinology. 2014. 10. 711-722. DOI: 10.1038/nrendo.2014.170.
- Meneilly G.S., Elahi D. Metabolic alterations in middle-aged and elderly lean patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2005. 28. 1498-1499. DOI: 10.2337/diacare.28.6.1498.
- Ligthelm R.J., Kaiser M., Vora J., Yale J.F. Insulin use in elderly adults: risk of hypoglycemia and strategies for care. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2012 Aug. 60(8). 1564-1570. doi: 10.1111/j.1532-5415.2012.04055.x.

/29.jpg)