Журнал «Здоровье ребенка» Том 16, №7, 2021
Вернуться к номеру
Стан системних про- та антиоксидантних процесів у дітей дошкільного віку, які часто хворіють на гострі респіраторні захворювання
Авторы: Овчаренко Л.С., Тимошина О.В., Вертегел А.О., Андрієнко Т.Г., Самохін І.В., Кряжев О.В., Чакмазова О.М.
Державний заклад «Запорізька медична академія післядипломної освіти МОЗ України», м. Запоріжжя, Україна
Рубрики: Педиатрия/Неонатология
Разделы: Клинические исследования
Версия для печати
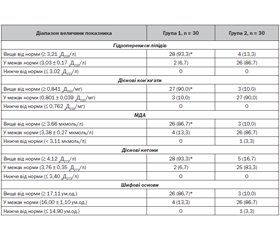
Актуальність. Дисбаланс ранніх механізмів вродженого захисту дитини від патогенів — перекисного окиснення та антиоксидантної системи — здатний призводити до зниження ефективності функціонування всієї ланки імунітету. Дослідження стану перекисного окиснення ліпідів (ПОЛ) та антиоксидантного захисту (АОЗ) у дітей із частими гострими респіраторними захворюваннями (ГРЗ) доповнить наукові дані щодо процесів формування протимікробного імунітету. Мета дослідження: підвищення інформативності своєчасного виявлення порушень про- та антиоксидантних процесів у дітей із частими ГРЗ шляхом дослідження первинних, вторинних, третинних та четвертинних сполук ПОЛ та АОЗ у крові. Матеріали та методи. Під спостереженням перебували 60 дітей віком від 2 до 5 років, із яких було сформовано 2 групи: 1) діти, які хворіють на гострі інфекційні захворювання респіраторного тракту більш ніж 6 разів на рік (n = 30); 2) діти, які хворіють на гострі інфекційні захворювання респіраторного тракту 6 та менше разів на рік (n = 30). Результати. Серед дітей, які хворіють на ГРЗ більше 6 разів на рік, збільшується частота реєстрації високих показників сироваткового вмісту гідроперекисів ліпідів (на 80,0 %, р < 0,05), дієнових кон’югат (на 80,0 %, р < 0,05), малонового діальдегіду (на 76,7 %, р < 0,05), дієнових кетонів (на 76,7 %, р < 0,05), шифових основ (на 76,7 %, р < 0,05), церулоплазміну (на 80,0 %, р < 0,05), супероксиддисмутази (на 80,0 %, р < 0,05), глутатіонпероксидази (на 86,7 %, р < 0,05), активності каталази (на 86,7 %, р < 0,05). Показники вмісту ретинолу, токоферолу, аскорбінової кислоти у дітей груп спостереження статистично значуще не відрізнялись. Висновки. У дітей віком 2–5 років, які хворіли на ГРЗ більше 6 разів на рік, має місце дисбаланс системи «ПОЛ — АОЗ». Він характеризувався одночасним збільшенням сироваткового вмісту первинних, вторинних і кінцевих метаболітів пероксидації ліпідів, ферментів антиперекисного й антикисневого захисту на фоні відсутності адаптивного підвищення вмісту сполук антирадикальної спрямованості.
Background. The imbalance of innate defense early mechanisms in children from pathogens — peroxidation and antioxidant system, can lead to a decrease in the efficiency of the entire immune system. The study of the lipid peroxidation (LPO) and antioxidant protection (AOP) status in children with recurrent acute respiratory diseases will complement the scientific data on the antimicrobial immunity formation processes. The study was aimed to increase the information value of timely detected pro- and antioxidant processes disorders in children with recurrent acute respiratory diseases by studying the primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary compounds of LPO and AOP in the serum. Materials and methods. Sixty children aged from 2 to 5 years were examined. Two groups were formed: group 1 — children with respiratory acute infectious more than six times per year (n = 30); group 2 — children with respiratory acute infectious six or fewer times per year (n = 30). Results. The children in group 1 more often presented with high serum levels of lipid hydroperoxides (by 80.0 %; p < 0.05), diene conjugates (by 80.0 %; p < 0.05), malonic dialdehyde (76.7 %; p < 0.05), diene ketones (76.7 %; p < 0.05), Schiff bases (76.7 %; p < 0.05). ceruloplasmin (80.0 %; p < 0.05), superoxide dismutase (80.0 %; p < 0.05), glutathione peroxidase (86.7 %; p < 0.05), catalase activity (86.7 %; p < 0.05). The values of retinol, tocopherol, ascorbic acid in children in the observation groups did not differ statistically significantly. Conclusions. The children aged from 2 to 5 years old with recurrent acute respiratory diseases have an imbalance of the LPO and AOP systems. It was characterized by a simultaneous increase in the serum content of the primary, secondary, and end-products of LPO, enzymes of anti-peroxide and anti-oxygen protection against the background of the lack of adaptive increase in the content of anti-radical compounds.
діти; пероксидація; антиоксидантний захист; інфекція
children; peroxidation; anti-oxidant protection; infection
Вступ
Матеріали та методи
Результати
Обговорення
Висновки
- Albrecht M., Arck P.C. Vertically transferred immunity in neonates: mothers, mechanisms and mediators. Frontiers in immunology. 2020. № 11. P. 555. doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2020.00555.
- Woitzik P., Linder S. Molecular Mechanisms of Borrelia burgdorferi Phagocytosis and Intracellular Processing by Human Macrophages. Biology. 2021. № 10(7). P. 567. doi.org/10.3390/biology10070567.
- Emam M., Tabatabaei S., Sargolzaei M., Mallard B. Response to Oxidative Burst-Induced Hypoxia Is Associated With Macrophage Inflammatory Profiles as Revealed by Cellular Genome-Wide Association. Front. Immunol. 2021. № 12. Article 688503. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.688503. PMID: 34220845. PMCID: PMC8253053.
- Cantin A.M., Ouellet C., Cloutier A., McDonald P.P. Airway Mucins Inhibit Oxidative and Non-Oxidative Bacterial Killing by Human Neutrophils. Front. Pharmacol. 2020. № 11. Article 554353. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.554353.
- Talukdar P.M., Abdul F., Maes M., Binu V.S., Venkatasubramanian G., Kutty B.M., Debnath M. Maternal Immune Activation Causes Schizophrenia-like Behaviors in the Offspring through Activation of Immune-Inflammatory, Oxidative and Apoptotic Pathways, and Lowered Antioxidant Defenses and Neuroprotection. Mol. Neurobiol. 2020. № 57. P. 4345-4361. doi.org/10.1007/s12035-020-02028-8.
- Xiao J., Khan M.Z., Ma Y., Alugongo G.M., Ma J., Chen T., Cao Z. The Antioxidant Properties of Selenium and Vitamin E; Their Role in Periparturient Dairy Cattle Health Regulation. Antioxidants. 2021. № 10(10). P. 1555. doi.org/10.3390/antiox10101555.
- Baldissera M.D., Souza C.F., Parmeggiani B., Leipnitz G., Verdi C.M., Santos R.V., Baldisserotto B. The disturbance of antioxidant/oxidant balance in fish experimentally infected by Aeromonas caviae: relationship with disease pathophysiology. Microbial pathogenesis. 2018. № 122. P. 53-57. doi.org/10.1016/j.micpath.2018.06.011.
- Cuppari C., Colavita L., Miraglia Del Giudice M., Chimenz R., Salpietro C. Recurrent respiratory infections between immunity and atopy. Pediatric Allergy and Immunology. 2020. № 31. P. 19-21. doi.org/10.1111/pai.13160.
- Laforge M., Elbim C., Frère C., Hémadi M., Massaad C., Nuss P., Benoliel J.-J., Becker C. Tissue damage from neutrophil-induced oxidative stress in COVID-19. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2020. № 20. P. 515-516. doi.org/10.1038/s41577-020-0407-1.
- Nadeem A., Ahmad S.F., Attia S.M., Al-Ayadhi L.Y., Al-Harbi N.O., Bakheet S.A. Dysregulated enzymatic antioxidant network in peripheral neutrophils and monocytes in children with autism. Progress in Neuro-Psychopharmacology and Biological Psychiatry. 2019. № 88. P. 352-359. doi.org/10.1016/j.pnpbp.2018.08.020.
- Soltani M., Zarei M.H., Salimi A., Pourahmad J. Mitochondrial protective and antioxidant agents protect toxicity induced by depleted uranium in isolated human lymphocytes. Journal of environmental radioactivity. 2019. № 203. Р. 112-116. doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvrad.2019.03.009.
- Naresh C.K., Rao S.M., Shetty P.R., Ranganath V., Patil A.S., Anu A.J. Salivary antioxidant enzymes and lipid peroxidation product malondialdehyde and sialic acid levels among smokers and non-smokers with chronic periodontitis — A clinico-biochemical study. J. Family Med. Prim. Care. 2019. № 8(9). P. 2960-2964. doi: 10.4103/jfmpc.jfmpc_438_19.
- Shearn C.T., Orlicky D.J., Petersen D.R. Dysregulation of antioxidant responses in patients diagnosed with concomitant primary sclerosing cholangitis/inflammatory bowel disease. Experimental and molecular pathology. 2018. № 104(1). P. 1-8. doi.org/10.1016/j.yexmp.2017.11.012.
- Ruhee R.T., Ma S., Suzuki K. Protective Effects of Sulforaphane on Exercise-Induced Organ Damage via Inducing Antioxidant Defense Responses. Antioxidants. 2020. № 9(2). Р. 136. doi.org/10.3390/antiox9020136.
- Bacchetti T., Simonetti O., Ricotti F., Offidani A., Ferretti G. Plasma oxidation status and antioxidant capacity in psoriatic children. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2020. № 312. P. 33-39. doi.org/10.1007/s00403-019-01976-z.
- Szczeklik K., Krzyściak W., Cibor D., Domagała-Rodacka R., Pytko-Polończyk J., Mach T., Owczarek D. Markers of lipid peroxidation and antioxidant status in the serum and saliva of patients with active Crohn disease. Polskie Archiwum Medycyny Wewnętrznej. 2018. № 128(6). P. 362-370. doi.org/10.20452/pamw.4273.

/14.jpg)
/15.jpg)