Вступ
Хронічний біль у нижній частині спині є серйозною проблемою охорони здоров’я у світі [1]. Від 85 до 90 % пацієнтів з хронічним болем у нижній частині спини класифікуються як неспецифічні, що вказує на неможливість визначення конкретної першопричини болю [2]. Результати візуалізації поперекового відділу хребта погано корелюють з тяжкістю болю й порушенням функцій, що часто призводить до нецільових методів лікування з незадовільними результатами в цій когорті пацієнтів [3]. Ця когорта досить неоднорідна й включає кілька підгруп, що представляють різні та/або співіснуючі базові механізми [4].
Феномени периферичної та центральної сенситизації відіграють важливу роль у переході гострого болю в хронічний, а також у підтримці хронічного болю [5]. Підвищена збудливість центральної нервової системи є одним з найважливіших феноменів, які спостерігаються в людей з хронічним болем у спині й іншими хронічними больовими станами [6, 7]. Одним із низхідних інгібуючих механізмів, який модулює сприйняття болю у тварин, є дифузний гальмівний контроль больової аферентації (diffuse noxious inhibitory controls), а в людей — умовна модуляція болю (conditioned pain modulation) [8, 9]. Активація системи умовної модуляції болю зменшує нейрональну активність на рівні задніх рогів спинного мозку, що призводить до зменшення больових відчуттів та пригнічення гіпералгезії [10].
Часто феномени центральної сенситизації клінічно проявляються наявністю зон алодинії та гіпералгезії, невропатичними дескрипторами болю та тривалим больовим синдромом високої інтенсивності [11, 12]. Для патогенетичної терапії хронічного болю в нижній частині спини рекомендовані препарати з груп антидепресантів і антиконвульсантів, але на практиці частіше використовують препарати з групи нестероїдних протизапальних засобів (НПЗЗ) [13]. Традиційно вважається, що НПЗЗ впливають лише на периферичні механізми болю й запалення, усуваючи таким чином прояви периферичної сенситизації. У 2016 році вперше було показано, що один з представників групи НПЗЗ — високоселективний інгібітор ЦОГ-2 еторикоксиб ефективно усуває як периферичну, так і центральну сенситизацію при остеоартриті колінного суглоба. При цьому вплив на периферичну й центральну сенситизацію оцінювали, зокрема, за допомогою кількісного сенсорного тестування (рівні больових порогів), тесту умовної модуляції болю, опитувальника painDETECT та ін. Зокрема, було показано, що 4-тижневе застосування еторикоксибу в дозі 60 мг/д у пацієнтів з остеоартритом колінного суглоба вірогідно зменшувало як локальну (периферичну), так і розширену (центральну) сенситизацію, а також ефект часової сумації болю, що також є ознакою зменшення центральної сенситизації. Це супроводжувалося поліпшенням клінічних показників, причому клінічне поліпшення було сильніше у пацієнтів з більш вираженими ознаками центральної сенситизації, що не є типовим для традиційних НПЗЗ [14].
В іншому дослідженні оцінювали вплив 14-добового застосування еторикоксибу 60 мг/д на рівень болю при остеоартриті колінного суглоба, зокрема вплив на холодову та розширену механічну гіпералгезію. У цьому дослідженні для оцінки впливу на центральну сенситизацію (яка зумовлює, зокрема, й невропатичні прояви болю) використовували кількісне сенсорне тестування (оцінка рівнів больових порогів), опитувальник painDETECT та опитувальник з якісної оцінки болю (PQAS). Було показано, що еторикоксиб вірогідно зменшував інтенсивність та якісний рівень суглобового болю та зменшував, на додаток до локальної, розширену гіпералгезію [15].
З огляду на те, що при хронічному болі в нижній частині спини центральна сенситизація є одним з базових механізмів, а також на велику частоту застосування НПЗЗ, є потреба у вивченні впливу препаратів цієї групи на центральну сенситизацію при хронічному болі в нижній частині спини.
Мета дослідження: оцінити аналгетичну активність еторикоксибу та лорноксикаму та їх вплив на центральну сенситизацію при хронічному болі в нижній частині спини.
Матеріали та методи
У дослідження увійшло 60 пацієнтів з хронічним болем у нижній частині спини. Пацієнти були випадковим чином розподілені на 2 групи: 1-ша група (30 осіб) — особи, які приймали еторикоксиб у дозі 90 мг перорально один раз на добу протягом 21 доби; 2-га група (30 осіб) — хворі, які приймали лорноксикам у дозі 8 мг перорально двічі на добу протягом 21 доби.
Кожен пацієнт був поінформований про мету прийому препарату, можливі побічні ефекти терапії та підписав інформовану згоду. Усі пацієнти були обстежені й лікувались амбулаторно. Обстеження починалося з клініко-неврологічного огляду, за результатами якого проводився відбір пацієнтів згідно з критеріями включення і виключення.
Критерії включення:
— вік пацієнтів від 18 до 65 років;
— наявність хронічного болю у нижній частині спини неспецифічної етіології;
— тривалість захворювання ≥ 3 міс.;
— інтенсивність болю за візуальною аналоговою шкалою (ВАШ) ≥ 4 бали;
— наявність проявів центральної сенситизації (бал за опитувальником центральної сенситизації ≥ 40, або наявність зони алодинії, або позитивний тест умовної модуляції болю).
Критерії виключення:
— ішемічна хвороба серця;
— порушення ритму і провідності, небезпечні для життя;
— стійка, з високими цифрами, артеріальна гіпертонія;
— перенесений менше ніж 1 рік тому інфаркт міокарда;
— серцева недостатність 2–3-го ступеня;
— ниркова недостатність;
— виразкова хвороба шлунка в анамнезі;
— цукровий діабет (декомпенсація або нестабільний перебіг);
— злоякісні новоутворення і хвороби крові;
— вагітність і годування груддю.
Кожен пацієнт проходив обстеження за єдиною схемою. Неврологічне обстеження включало детальне сенсорне тестування з метою виявлення зон алодинії. У випадку виявлення зон алодинії проводилося вимірювання їх площі в квадратних сантиметрах. Інтенсивність болю визначалася в балах за ВАШ.
Для визначення наявності невропатичного компонента болю застосовували опитувальник painDETECT, який було розроблено спеціально для визначення невропатичного компонента при хронічному болі в нижній частині спини. Опитувальник складається з семи запитань, що стосуються якісних характеристик невропатичних симптомів болю, які оцінюються за п’ятибальною шкалою. Також опитувальник включає визначення характерного патерну болю й наявності іррадіації болю, яка сама по собі є дуже явною невропатичною ознакою. Максимальна кількість балів, можлива за опитувальником, — 38. Результат від 0 до 12 балів свідчить про малу (< 15 %) імовірність невропатичного компонента, значення від 13 до 18 балів є невизначеним, однак не виключає наявності невропатичного компонента болю. Результат від 19 до 38 балів є позитивним і свідчить про високу (> 90 %) імовірність наявності невропатичного компонента болю.
Для визначення наявності ознак центральної сенситизації використовувався опитувальник з центральної сенситизації, який складається з двох частин. Частина А включає 25 запитань, пов’язаних з клінічними проявами центральної сенситизації. На кожне запитання можна дати 1 з 5 варіантів відповідей за шкалою Лікерта: ніколи (0 балів), рідко (1 бал), іноді (2 бали), часто (3 бали) або завжди (4 бали). Центральна сенситизація вважається вираженою при результаті 40 балів і більше [16]. Частина В опитувальника не враховується при підрахунку балів, проте в ній пацієнт може вказати, чи встановлювалися йому раніше діагнози (фіброміалгія, синдром хронічної втоми, дисфункція скронево-нижньощелепного суглоба, синдром подразненої кишки, мігрень чи головний біль напруження, множинна хімічна чутливість чи синдром неспокійних ніг), які так чи інакше пов’язані з явищами центральної сенситизації.
Для кількісного визначення порогу болю проводили кількісне сенсорне тестування, яке складалось з вимірювання порогу болю та проведення тесту умовної модуляції.
Вимірювання порогу болю (алгометрія) проводили за допомогою цифрового алгометра в двох анатомічних ділянках: 1 — ніготь великого пальця домінантної руки пацієнта; 2 — середня лінія нижньої частини спини в проміжку між п’ятим поперековим (L5) і першим крижовим хребцем (S1). Алгометр має круглу насадку з наконечником площею 1 см2, який розміщується перпендикулярно в кожній ділянці тіла. Тиск наноситься з кроком 0,5 кг у секунду. Пацієнти інструктуються так, що вони вказують момент, коли відчуття тиску стає болючим. У момент, коли пацієнт говорить про те, що став відчувати біль, дослідник негайно прибирає алгометр і фіксує ступінь тиску (кг/см2), який викликав відчуття болю. Перед фактичним проведенням тестування проводиться ознайомлення пацієнта з процедурою тесту на домінантній руці. Протягом виконання тесту проводиться 3 вимірювання порогу болю на кожній ділянці тіла з 30-секундним інтервалом відпочинку. Усереднений результат 3 вимірювань записується й використовується в подальшому для аналізу даних.
Тест умовної модуляції болю (ТУМБ) використовували для оцінки функціонального стану низхідних гальмівних шляхів. Даний тест оцінює, чи змінюється больова чутливість основної ділянки тіла, що становить інтерес, при нанесенні спеціального больового стимулу на віддаленій ділянці тіла. У здорових осіб відповідь на спеціальний больовий подразник викликає нормальну нейрофізіологічну відповідь — вивільнення ендогенних опіоїдів і активацію низхідної аналгетичної системи, що призводить до зниження больової чутливості (підвищення больового порогу). У цьому дослідженні спеціальний больовий стимул створювався за допомогою сильної механічної компресії плеча недомінантної руки манжетою тонометра шириною 12 см, що викликало тимчасовий ішемічний біль. Манжета накачувалася до 260 мм рт.ст., після чого пацієнту було потрібно піднімати гантель вагою 1 кг для жінок і 2 кг — для чоловіків шляхом згинання — розгинання недомінантної руки в зап’ястку до тих пір, поки учасник або не виконає 45 підйомів або не повідомить про інтенсивність болю в руці ≥ 7 балів за ВАШ. Як тільки учасник виконав вправу з підняттям важких предметів, повторно оцінювали поріг болю на нігті великого пальця домінантної руки і в ділянці нижньої частини спини (по середній лінії між хребцями L5 і S1). Вимірювання порогу болю проводили повторно 3 рази з інтервалом 30 секунд, після чого значення порога болю усереднювалося. Відмінності між значеннями порогу болю до й після тесту умовної модуляції болю використовувались для аналізу даних. Тест умовної модуляції болю є перевіреним методом для визначення наявності центральної сенситизації у пацієнтів з хронічним болем у нижній частині спини [17].
Обстеження пацієнтів проводилося в першу добу, через 7, 14 та через 21 добу від початку лікування. Деталі дизайну дослідження наведені в табл. 1.
/88.jpg)
Статистичну обробку матеріалу проводили за допомогою комп’ютерної програми SPSS 17. Нормальність розподілу даних кількісного типу визначали за допомогою критерію Шапіро — Вілка. Кількісні дані описували середнім значенням і стандартним відхиленням, для їх визначення використовувалася програма описової статистики. Якісні змінні описувалися частотою та відсотком представленості. Вірогідність відмінностей між вибірками з нормальним розподілом визначали за допомогою критерію Стьюдента для незалежних вибірок, для вибірок з ненормальним розподілом використовувався непараметричний критерій Манна — Уїтні для незалежних вибірок. Для порівняння даних пов’язаних вибірок з нормальним розподілом використовували критерій Стьюдента для пов’язаних вибірок, для вибірок з ненормальним розподілом використовували критерій Вілкоксона. Рівень статистичної вірогідності при всіх розрахунках був встановлений як р < 0,05.
Результати
Середній вік пацієнтів у групі еторикоксибу становив 48,60 ± 6,90 року, кількість чоловіків — 11 (36,7 %), кількість жінок — 19 (63,3 %). Середня інтенсивність болю за ВАШ становила 7,47 ± 1,82 бала, що відповідало вираженому рівню болю. У 18 (60 %) пацієнтів були наявні ділянки алодинії — зони, ніжний дотик до яких викликав відчуття болю. Площа цих ділянок коливалась від 4 до 20 см2, середня площа становила 15,11 ± 8,65 см2. Середній бал за опитувальником painDETECT у групі становив 12,40 ± 4,54 бала. Середній бал за опитувальником центральної сенситизації становив 54,13 ± 6,74 бала, що відповідало вираженому рівню центральної сенситизації.
Середній вік пацієнтів у групі лорноксикаму становив 52,23 ± 7,27 року, кількість чоловіків — 8 (26,67 %), кількість жінок — 22 (73,33 %). Середня інтенсивність болю за ВАШ становила 6,80 ± 2,48, що відповідало вираженому рівню болю. У цій групі також були наявні зони алодинії, які відмічали 18 (60 %) пацієнтів. Площа ділянок алодинії коливалась від 10 до 30 см2, середня площа становила 15,50 ± 9,86 см2. Середній бал за опитувальником painDETECT у групі становив 13,90 ± 5,75 бала. Середній бал за опитувальником центральної сенситизації становив 54,80 ± 10,44 бала, що також відповідало вираженому рівню центральної сенситизації.
При проведенні в першу добу кількісного сенсорного тестування (алгометрії) у групі еторикоксибу були отримані такі дані: до ТУМБ поріг болю в ділянці нігтя (ПБН) великого пальця домінантної верхньої кінцівки становив 1,52 ± 0,46 кг/см2; поріг болю по середній лінії нижньої частини спини (ПБС) в проміжку між п’ятим поперековим і першим крижовим хребцем — 1,83 ± 0,98 кг/см2. Після ТУМБ ПБН зменшився і становив 1,14 ± 0,53 кг/см2, ПБС також зменшився і становив 1,21 ± 0,40 кг/см2.
У групі лорноксикаму в першу добу до ТУМБ ПБН становив 1,30 ± 0,25 кг/см2, ПБС — 1,31 ± 0,50 кг/см2. Після ТУМБ ПБН зменшився до 1,08 ± 0,19 кг/см2, ПБС — до 1,20 ± 0,49 кг/см2.
Таким чином, в обох групах у першу добу відмічались початково знижені пороги болю, які ще більше знижувались після ТУМБ.
Загалом групи лікування еторикоксибом і лорноксикамом були порівнянними і значно не відрізнялись за своїми характеристиками (р < 0,05). Початкова характеристика груп пацієнтів наведена в табл. 2, дані кількісного сенсорного тестування — у табл. 3.
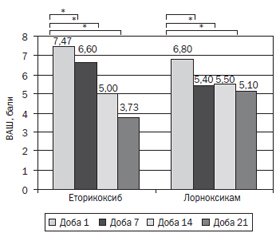
На 7-му добу від початку лікування у групі еторикоксибу відмічалось вірогідне (р < 0,05) порівняно з початковим значенням зниження інтенсивності болю за ВАШ з 7,47 ± 1,82 до 6,60 ± 1,31 бала, яке було більш виражене на 14-ту добу — 5,00 ± 2,00 бала та на 21-шу добу — 3,73 ± 1,81 бала.
У групі лорноксикаму також відмічалось вірогідне (р < 0,05) порівняно з початковим значенням зниження інтенсивності болю за ВАШ на 7-му добу від початку лікування з 6,80 ± 2,48 до 5,40 ± 1,91 бала, на 14-ту добу — до 5,50 ± 1,02 бала, на 21-шу добу — до 5,10 ± 1,04 бала. Динаміка показників інтенсивності болю за ВАШ в обох групах наведена на рис. 1.
Через 7 діб від початку лікування в групі еторикоксибу відмічалось зниження кількості пацієнтів з алодинією від 18 (60,0 %) до 16 (53,3 %), через 14 діб — вірогідне (р < 0,05) порівняно з початковим значенням зниження до 6 (20,0 %), через 21 добу — вірогідне зниження до 4 (13,3 %) пацієнтів. Через 7 діб від початку лікування в групі лорноксикаму відмічалось вірогідне (р < 0,05) зниження кількості пацієнтів з алодинією від 18 (60,0 %) до 15 (50,0 %). Через 14 діб їх кількість вірогідно знизилась до 12 (40,0 %), проте через 21 добу — підвищилась до 15 (50,0 %) пацієнтів. Динаміка кількості пацієнтів з алодинією в обох групах наведена на рис. 2.
Через 7 діб від початку лікування в групі еторикоксибу відмічалось вірогідне (р < 0,05) порівняно з початковим значенням зниження площі зони алодинії з 15,11 ± 8,65 см2 до 11,38 ± 6,20 см2, через 14 діб — до 9,00 ± 6,00 см2, через 21 добу — до 6,00 ± 2,04 см2. У групі лорноксикаму через 7 діб відмічалось вірогідне (р < 0,05) порівняно з початковим значенням зниження площі зони алодинії з 17,50 ± 9,86 см2 до 12,00 ± 6,63 см2, через 14 діб — до 11,75 ± 6,64 см2, через 21 добу — до 9,40 ± 4,78 см2. Динаміка площі зони алодинії в обох групах наведена на рис. 3.
Через 7 діб від початку лікування у групі еторикоксибу відмічалось вірогідне (р < 0,05) порівняно з початковим значенням зниження бала за опитувальником painDETECT з 12,40 ± 4,54 до 9,07 ± 6,06, через 14 діб — до 7,87 ± 6,90, через 21 добу — до 6,67 ± 6,50. У групі лорноксикаму через 7 діб відмічалось вірогідне (р < 0,05) порівняно з початковим значенням зниження бала за опитувальником painDETECT з 13,90 ± 5,75 до 11,00 ± 2,76. Через 14 діб бал за опитувальником painDETECT підвищився до 12,40 ± 2,24, а через 21 добу — до 12,50 ± 5,08, що не мало вірогідної різниці з початковим значенням. Динаміка бала за опитувальником painDETECT в обох групах наведена на рис. 4.
/100.jpg)
У групі еторикоксибу відмічались вірогідні (р < 0,05) порівняно з початковим значенням зміни в сторону зменшення кількості балів за опитувальником з центральної сенситизації з 54,13 ± 6,74 бала до 44,00 ± 12,14 бала через 7 діб від початку лікування. Через 14 діб відмічалось невелике підвищення до 44,20 ± 19,85 бала, а через 21 добу — зниження до 33,67 ± 12,38 бала. У групі лорноксикаму через 7 діб також відмічалось вірогідне (р < 0,05) порівняно з початковим значенням зниження бала за опитувальником з центральної сенситизації з 54,80 ± 10,44 бала до 48,00 ± 10,60 бала, через 14 діб — до 47,80 ± 9,34 бала, а через 21 добу — до 46,00 ± 14,55 бала. Динаміка бала за опитувальником з центральної сенситизації в обох групах наведена на рис. 5.
На фоні лікування в обох групах відмічались зміни у ПБН та ПБС до та після ТУМБ. Так, через 7 діб від початку лікування в групі еторикоксибу ПБН до ТУМБ становив 1,34 ± 0,54 кг/см2, ПБС — 1,99 ± 1,02 кг/см2; після ТУМБ ПБН становив 1,36 ± 0,52 кг/см2, ПБС — 1,87 ± 0,91 кг/см2. У групі еторикоксибу після ТУМБ показники ПБН на 14-ту та 21-шу добу від початку лікування і ПБС на 21-шу добу були вірогідно більші від аналогічних показників до ТУМБ. Так, через 14 діб від початку лікування ПБН до ТУМБ становив 1,69 ± 1,11 кг/см2, ПБС — 2,20 ± 1,08 кг/см2; після ТУМБ ПБН становив 2,28 ± 1,21 кг/см2, ПБС — 2,52 ± 0,98 кг/см2. Через 21 добу від початку лікування до ТУМБ ПБН становив 2,02 ± 1,33 кг/см2, ПБС — 2,22 ± 1,06 кг/см2; після ТУМБ ПБН становив 2,64 ± 1,47 кг/см2, ПБС — 2,94 ± 1,25 кг/см2. Динаміка показників ПБН до та після ТУМБ у групі еторикоксибу наведена на рис. 6, динаміка показників ПБС до та після ТУМБ у групі еторикоксибу наведена на рис. 7.
/111.jpg)
У групі лорноксикаму через 7 діб від початку лікування ПБН до ТУМБ становив 1,65 ± 0,38 кг/см2, ПБС — 1,72 ± 0,732 кг/см2; після ТУМБ ПБН становив 1,44 ± 0,39 кг/см2, ПБС — 1,64 ± 0,63 кг/см2. Через 14 діб від початку лікування ПБН до ТУМБ становив 1,67 ± 0,40 кг/см2, ПБС — 1,79 ± 0,63 кг/см2; після ТУМБ ПБН становив 1,56 ± 0,39 кг/см2, ПБС — 1,62 ± 0,45 кг/см2. Через 21 добу від початку лікування до ТУМБ ПБН становив 1,75 ± 0,51 кг/см2, ПБС — 1,96 ± 0,74 кг/см2; після ТУМБ ПБН становив 1,61 ± 0,41 кг/см2, ПБС — 1,78 ± 0,63 кг/см2. Вірогідних змін у показниках порогу болю в групі на фоні лікування лорноксикамом не відмічалось. Динаміка показників ПБН до та після ТУМБ у групі лорноксикаму наведена на рис. 8, динаміка показників ПБС до та після ТУМБ у групі лорноксикаму наведена на рис. 9.
/112.jpg)
Під час лікування деякі пацієнти відмічали побічні дії препаратів. Так, у групі еторикоксибу 6 пацієнтів відмічали гіркоту в роті, 2 пацієнти — дискомфорт у ділянці епігастрія. У групі лорноксикаму 3 пацієнти відмічали печію, 2 пацієнти — дискомфорт у ділянці епігастрія. Усі побічні дії препаратів були виражені незначно і не впливали на курс лікування.
Обговорення
У цьому дослідженні група пацієнтів з хронічним болем у нижній частині спини характеризувалася високою інтенсивністю больового синдрому, високою представленістю зон алодинії, високими балами за опитувальником painDETECT та опитувальником з центральної сенситизації. Тривала персистенція хронічного болю та неефективність попереднього лікування, імовірно, зумовлює виснаження ендогенних опіоїдних систем, розвиток центральної сенситизації та появу невропатичних ознак.
Виявлені під час кількісного сенсорного тестування в першу добу знижені пороги болю, а також ще більше їх зниження (на відміну від підвищення у здорових осіб) у відповідь на тест умовної модуляції болю підтверджують факт наявності центральної сенситизації та виснаження ендогенних опіоїдних систем контролю болю.
Обидва препарати продемонстрували вірогідне зниження болю за ВАШ, але вираженість динаміки була різна: еторикоксиб продемонстрував більш виражене зниження на 21-шу добу лікування порівняно з початковим рівнем — з 7,47 до 3,73 бала (–50 %), тоді як лорноксикам — з 6,80 до 5,10 бала (–25 %).
Динаміка показників алодинії, центральної сенситизації та невропатичних проявів за painDETECT між групами лікування теж була різною. У групі еторикоксибу на 21-шу добу лікування кількість пацієнтів з алодинією зменшилася порівняно з першим днем з 18 до 4 пацієнтів (–77,8 %), а в групі лорноксикаму — з 18 до 15 пацієнтів (–16,7 %). Схожою була й динаміка площі зони алодинії: у групі еторикоксибу на 21-шу добу площа алодинії зменшилася порівняно з першим днем з 15,11 до 6 см2 (–60,3 %), а в групі лорноксикаму — з 17,5 до 9,4 см2 (–46,3 %).
Динаміка ознак за опитувальником центральної сенситизації також відрізнялась. У групі еторикоксибу ці зміни були більш виражені — зниження з 54,13 бала у 1-шу добу до 33,67 бала (–37,8 %) на 21-шу добу, що відповідало легкому ступеню вираженості центральної сенситизації, тоді як у групі лорноксикаму показник знизився лише до помірного рівня — з 54,80 до 46,00 бала (–16 %).
Невропатичні прояви за опитувальником painDETECT у групі еторикоксибу статистично вірогідно знижувались протягом усього періоду лікування, досягнувши майже двократного зменшення на 21-шу добу (з 12,40 у 1-шу добу до 6,67 у 21-шу добу), тоді як у групі лорноксикаму вірогідне покращення спостерігалось лише на 7-му добу лікування, а в подальшому, на 14-ту та 21-шу добу, результати повернулись майже до попереднього рівня, вірогідна різниця з початковим значенням була відсутня.
Визначення порогів болю під час проведення алгометрії як одного з методів кількісного сенсорного тестування показало їх базове зниження в усіх пацієнтів. Проведення тесту умовної модуляції болю й повторне визначення порогів болю продемонструвало ще більше їх зниження після тесту. Це може свідчити про виснаження ендогенних опіоїдних систем, які в нормі пригнічують біль, унаслідок тривало персистуючого болю.
На 14-ту добу терапії еторикоксибом поріг болю в ділянці нігтя після тесту умовної модуляції болю був вірогідно вищим, ніж до тесту, що на 21-шу добу відзначалося вже в ділянці нігтя та спини. У групі лорноксикаму такі зміни не спостерігались.
Отримані результати можуть свідчити про наявність певних центральних механізмів дії еторикоксибу [18], який чинить принаймні частину своєї дії безпосередньо в центральній нервовій системі і здатен усувати прояви центральної сенситизації, а також невропатичні прояви.
Висновки
Пацієнти з хронічним болем у нижній частині спини характеризуються високою інтенсивністю больового синдрому та наявністю проявів центральної сенситизації (наявність зон алодинії, високі бали за опитувальником painDETECT та опитувальником з центральної сенситизації, низькі пороги болю до та після тесту умовної модуляції болю).
Еторикоксиб і лорноксикам показали різний вплив на зниження інтенсивності болю та проявів центральної сенситизації. Еторикоксиб продемонстрував більш виражене зниження болю за ВАШ, зменшення алодинії та бала за опитувальником центральної сенситизації порівняно з початковим рівнем через 21 добу лікування. Додатково на фоні застосування еторикоксибу спостерігалось зменшення невропатичних проявів за опитувальником painDETECT, а також збільшення порогів болю до та після тесту умовної модуляції болю, що може свідчити про деяке відновлення ендогенних опіоїдних систем, тобто збільшення активності антиноцицептивної системи, зазвичай зниженої при хронічних больових станах.
Необхідне проведення додаткових досліджень з метою вивчення механізмів визначених змін, а також уточнення доз, режимів і оптимальної тривалості терапії.
Обмеження дослідження. До обмежень дослідження можна віднести відсутність контрольної групи з числа здорових випробовуваних. У цій групі може проводитись дослідження показників кількісного сенсорного тестування з метою контролю їх динаміки. Розширений дизайн дослідження з включенням контрольної групи може бути запропонований для майбутніх досліджень.
Конфлікт інтересів. Автор заявляє про відсутність конфлікту інтересів та власної фінансової зацікавленості при підготовці даної статті.
Отримано/Received 26.01.2022
Рецензовано/Revised 08.02.2022
Прийнято до друку/Accepted 14.02.2022
/112.jpg)

/88.jpg)
/99.jpg)
/100.jpg)
/111.jpg)