Международный эндокринологический журнал Том 18, №1, 2022
Вернуться к номеру
Взаємозв’язок показників інтервалу QT з кардіальною автономною нейропатією у хворих на цукровий діабет
Авторы: Sanjay Kumar, Satyanath Reddy Kodidala, Srinivasa Jayachandra
Zydus Medical College and Hospital, Dahod, Gujarat, India
Рубрики: Эндокринология
Разделы: Клинические исследования
Версия для печати
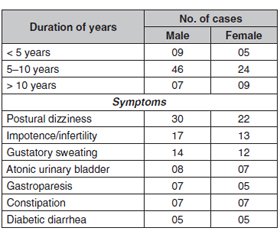
Актуальність. Кардіальна автономна нейропатія належить до тяжких, але недостатньо діагностованих станів у хворих на цукровий діабет. Поширеність кардіальної автономної нейропатії перебуває в межах від 2,5 (на основі профілактичного обстеження когорти хворих у дослідженні Diabetes Control and Complications Trial) до 90 % пацієнтів із цукровим діабетом. Клінічні прояви кардіальної автономної нейропатії є різноманітними аж до розвитку інфаркту міокарда. Діагноз виставляють за допомогою декількох тестів для оцінки як симпатичної, так і парасимпатичної функції. Мета: дане дослідження було проведене для оцінки взаємозв’язку між серцевою автономною нейропатією та показником інтервалу QT. Матеріали та методи. Перехресне дослідження проведене за участю 100 пацієнтів, які відвідували лікарню третинного рівня в Індії. Оцінювали глибокий дихальний тест, коефіцієнт Вальсальви, реакцію частоти серцевих скорочень при стоянні 30 : 15, підвищення артеріального тиску та постуральну гіпотензію. Проведена оцінка різних методів для діагностики кардіальної автономної нейропатії. Були визначені інтервали QT і QTc та отримана асоціація з кардіальною автономною нейропатією. Результати. Серед 100 пацієнтів із цукровим діабетом 2-го типу було 60 % чоловіків і 40 % жінок. 25 пацієнтів не мали кардіальної автономної нейропатії та подовженого інтервалу QTc. Водночас у 75 пацієнтів подовжений інтервал QTc був пов’язаний з ранньою та тяжкою кардіальною автономною нейропатією. Подовжений інтервал QTc був вірогідно пов’язаний з наявністю кардіальної автономної нейропатії в пацієнтів із цукровим діабетом порівняно з хворими без кардіальної автономної нейропатії й особами контрольної групи (р < 0,0001). Оцінка показників кардіальної автономної нейропатії показала, що 75 % пацієнтів мали бал > 2, а 25 % — < 2. Із 75 пацієнтів 44 мали вираженість показників 2–4 бали, а 31 — понад 4 бали. Вірогідний зв’язок між QTc та наявністю кардіальної автономної нейропатії спостерігали при порівнянні з хворими без кардіальної автономної нейропатії та особами контрольної групи. Висновки. Діабетична кардіальна автономна нейропатія пов’язана з подовженням інтервалів QTc. Тому у хворих на цукровий діабет необхідно регулярно проводити обстеження вегетативної нервової системи для запобігання подальшим ускладненням.
Background. Cardiovascular autonomic neuropathy (CAN) is a severely debilitating yet underdiagnosed condition in patients with diabetes mellitus. The prevalence can range from 2.5 % (based on the primary prevention cohort in the Diabetes Control and Complications Trial) to as high as 90 % of diabetic patients. Clinical manifestations range from orthostasis to myocardial infarction. The diagnosis is made using multiple autonomic function tests to assess both sympathetic and parasympathetic function. This study was conducted to assess the relationship between Cardiac autonomic neuropathy and QT interval. Material and methods. This was a cross-sectional study conducted in 100 patients attending a tertiary care hospital in India. Deep breathing test, Valsalva ratio, immediate heart rate response to standing 30 : 15, BP rise with sustained hand grip and postural hypotension were evaluated. Scoring was done for cardiac autonomic neuropathy. QT interval and QTc interval were determined and association with CAN was obtained. Results. Out of 100 type 2 diabetic patients, 60 % were males and 40 % were females. 25 patients having no cardiac autonomic neuropathy and had no prolonged QTc interval. While, 75 patients had QTc prolonged were associated with early and severe CAN cardiac autonomic neuropathy. The prolonged QTc was significantly associated with CAN in diabetic patients when compared without CAN and controls (P < 0.0001). The grading score for CAD showed that 75 % cases were having score > 2 were 25 % of cases had score < 2. Out of 75 patients 44 were between score 2–4 and 31 were above score 4. A significant association between QTc and Diabetic CAN patients observed when compared non CAN and controls. Conclusions. Diabetic cardiac autonomic neuropathy is associated with increase in prolongation of QTc intervals. Hence, there is need for regular checkup of autonomic nervous system in diabetic patient to prevent further complications.
цукровий діабет 2-го типу; вегетативна нейропатія серця; ЕКГ; інтервал QTc
type 2 diabetes mellitus; cardiac autonomic neuropathy; ECG; QTc interval
Introduction
Material and methods
Results
/19.jpg)
Discussion
Valsalva ratio
Deep Breath test
30 : 15 ratio
Postural hypotension
SGHT
Conclusions
- Khandoker A.H., Jelinek H.F., Palaniswami M. Identifying diabetic patients with cardiac autonomic neuropathy by heart rate complexity analysis. Biomed. Eng. Online. 2009. 8. 3. doi: 10.1186/1475-925X-8-3.
- Flügelman M.Y., Kanter Y., Abinader E.G., Lewis B.S., Barzilai D. Electrocardiographic patterns in diabetics without clinical ischemic heart disease. Isr. J. Med. Sci. 1983. 19(3). 252-5. PMID: 6853122.
- Kahn J.K., Sisson J.C., Vinik A.I. QT interval prolongation and sudden cardiac death in diabetic autonomic neuropathy. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1987. 64(4). 751-4. doi: 10.1210/jcem-64-4-751.
- Takebayashi K., Aso Y., Sugita R., Takemura Y., Inukai T. Clinical usefulness of corrected QT intervals in diabetic autonomic neuropathy in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Metab. 2002. 28(2). 127-32. PMID: 11976564.
- Bellavere F., Ferri M., Guarini L., Bax G., Piccoli A., Cardone C., Fedele D. Prolonged QT period in diabetic autonomic neuropathy: a possible role in sudden cardiac death? Br. Heart J. 1988. 59(3). 379-83. doi: 10.1136/hrt.59.3.379.
- Pillai J.N., Madhavan S. Cardiac Autonomic Neuropathy and QTc Interval in Type 2 Diabetes. Heart India. 2015. 3. 8-11. DOI: 10.4103/2321-449X.153279.
- Astrup A.S., Tarnow L., Rossing P., Hansen B.V., Hilsted J., Parving H.H. Cardiac autonomic neuropathy predicts cardiovascular morbidity and mortlity in type 1 diabetic patients with diabetic nephrolpathy. Diabetes Care. 2006. 29. 334-9. https://doi.org/10.2337/diacare.29.02.06.dc05-1242
- Ewing D.J., Campbell I.W., Clarke B.F. The natural history of diabetic autonomic neuropathy. Q. J. Med. 1980. 49(193). 95-108. PMID: 7433630.
- Bellavere F., Bosello G., Fedele D., Cardone C., Ferri M. Diagnosis and management of diabetic autonomic neuropathy. Br. Med. J. (Clin. Res. Ed.). 1983. 287(6384). 61. doi: 10.1136/bmj.287.6384.61-a.
- Lakhotia M., Shah P.K., Vyas R., Jain S.S., Yadav A., Parihar M.K. Clinical dysautonomia in diabetes mellitus — a study with seven autonomic reflex function tests. J. Assoc. Physicians India. 1997. 45(4). 271-4. PMID: 12521082.
- Bathwal S.P. QTc prolongation is diabetes mellitus — an indicator of Cardiac autonomic neuropathy. Journal of the Association of Physicians of India. 1997. 45(1). 15-17.
- Ewing D.J., Campbell I.W., Clarke B.F. Assessment of cardiovascular effects in diabetic autonomic neuropathy and prognostic implications. Ann. Intern. Med. 1980. 92(2 Pt 2). 308-11. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-92-2-308.
- Sucharita S., Bantwal G., Idiculla J., Ayyar V., Vaz M. Autonomic nervous system function in type 2 diabetes using conventional clinical autonomic tests, heart rate and blood pressure variability measures. Indian J. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011. 15(3). 198-203. doi: 10.4103/2230-8210.83406.
- Hong J., Liu W.Y., Hu X., Jiang F.F., Xu Z.R., Li F., Shen F.X., Zhu H. Association between heart rate-corrected QT interval and severe peripheral arterial disease in patients with type 2 diabetes and foot ulcers. Endocr. Connect. 2021. 10(8). 845-851. doi: 10.1530/EC-21-0140.
- Jayaprakash K., Vijayakumar K., Sujathan P., Adinegara L.A. Cardiac autonomic neuropathy in diabetes mellitus: prevalence, risk factors and utility of corrected QT interval in the ECG for its diagnosis. Postgrad. Med. J. 2008. 84(990). 205-10. doi: 10.1136/pgmj.2007.064048.
- Dimitropoulos G., Tahrani A.A., Stevens M.J. Cardiac autonomic neuropathy in patients with diabetes mellitus. World J. Diabetes. 2014. 5(1). 17-39. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v5.i1.17.
- Ogurtsova K., da Rocha Fernandes J.D., Huang Y., Linnenkamp U., Guariguata L., Cho N.H., Cavan D., Shaw J.E., Makaroff L.E. IDF Diabetes Atlas: Global estimates for the prevalence of diabetes for 2015 and 2040. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2017. 128. 40-50. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2017.03.024.

/20.jpg)