Журнал "Гастроэнтерология" Том 56, №1, 2022
Вернуться к номеру
Морфофункціональні паралелі шлунка у хворих на хронічний атрофічний гастрит
Авторы: Мосійчук Л.М., Гайдар Ю.А., Кленіна І.А., Петішко О.П.
ДУ «Інститут гастроентерології НАМН України», м. Дніпро, Україна
Рубрики: Гастроэнтерология
Разделы: Клинические исследования
Версия для печати
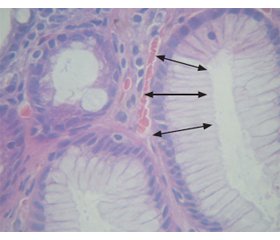
Незважаючи на певні успіхи у вирішенні проблеми раку шлунка, помітне зниження захворюваності в усіх розвинутих країнах, пошук змін, що передують виникненню канцерогенезу, залишається актуальним і далеким від остаточного завершення. Мета дослідження: оцінити вміст агресивних та протективних факторів шлункового соку і ротової рідини у порівнянні з морфологічними змінами у хворих на хронічний атрофічний гастрит. Матеріали та методи. У дослідження включені 56 хворих: у І групу увійшли 12 пацієнтів лише з атрофічними змінами слизової оболонки шлунка різного ступеня вираженості, у ІІ групу — 24 хворі, у яких на фоні атрофічних змін діагностовано кишкову метаплазію лише в антральному відділі шлунка, у ІІІ групу — 20 пацієнтів з кишковою метаплазією в тілі і антральному відділі шлунка. Контрольну групу становили 16 практично здорових осіб. Оцінку ступеня атрофії та запалення в слизовій оболонці шлунка проводили з наступною детермінацією інтегральних показників — стадії та ступеня атрофії за системою OLGA та метаплазії — за системою OLGIM. За даними морфометричного дослідження зрізів за допомогою світлового мікроскопу XSP-139TP («Ulab», Україна) розраховували показники: ядерно-цитоплазматичне співвідношення, коефіцієнт еліптичності ядер. У шлунковому соку та ротовій рідині визначали вміст глікопротеїнів, сіалових кислот, фукози, гексозамінів. Результати. Морфометричне дослідження показало виражене вірогідне зменшення ядерно-цитоплазматичного співвідношення до (0,12 ± 0,04) % у хворих ІІІ групи. Коефіцієнт еліптичності ядер нативних клітин зменшувався із розвитком кишкової метаплазії: у І групі він дорівнював (0,76 ± 0,04) %, для ІІ групи становив (0,65 ± 0,11) %, а для ІІІ — (0,41 ± 0,12) %. У хворих з кишковою метаплазією в 82 % випадків зі збільшенням в 3 рази вмісту сіалових кислот у шлунковому соку діагностували підвищення рівня гексозамінів на 35 %, тоді як у пацієнтів з лише атрофічними змінами шлунка відзначали зменшення рівня гексозамінів у 2 рази порівняно з контрольними показниками (р < 0,05). Поширення кишкової метаплазії у шлунку асоціюється з підвищенням кількості глікопротеїнів та гексозамінів у ротовій рідині пацієнтів, у той час як сіалові кислоти у цій біологічній рідині підвищуються в усіх досліджуваних групах. Встановлені прямі взаємозв’язки між наявністю кишкової метаплазії в тілі шлунка та вмістом глікопротеїнів як в шлунковому соку (r = 0,446, p = 0,008), так і в ротовій рідині (r = 0,378, p = 0,021). Також визначені взаємозв’язки вмісту сіалових кислот у шлунковому соку зі ступенем та стадією гастриту за OLGA (r = 0,431, р < 0,01; r = 0,482, р < 0,01), рівня гексозамінів у ротовій рідині — з коефіцієнтом еліптичності ядер (r = 0,447, р = 0,037). Висновки. Комплексне вивчення морфофункціональних змін шлунка та співвідношення агресивних і протективних факторів ротової рідини дозволить визначити групи ризику хворих з передраковими станами.
Background. Despite some progress in addressing gastric cancer, a marked reduction in morbidity in all developed countries, the search for changes that precede carcinogenesis remains relevant and far from complete. The purpose of the study: to assess the content of aggressive and protective factors of gastric juice and oral fluid in comparison with morphological changes in patients with chronic atrophic gastritis. Materials and methods. The study included 56 patients: group I included 12 patients with atrophic changes of the gastric mucosa of varying severity, group II — 24 patients with atrophic changes diagnosed with intestinal metaplasia only in the antrum of the stomach, in group III group — 20 patients with intestinal metaplasia in the body and antrum of the stomach. The control group consisted of 16 healthy individuals. Assessment of the degree of atrophy and inflammation in the gastric mucosa was performed with the subsequent determination of integral indicators — stage and degree of atrophy according to the OLGA system and metaplasia — according to the OLGIM system. According to the morphometric study of sections using a light microscope XSP-139TP (“Ulab“, Ukraine) calculated indicators: nuclear-cytoplasmic ratio, the ellipticity of the nuclei. The content of glycoproteins, sialic acids, fucose, hexosamines was determined in gastric juice and oral fluid. Results. Morphometric study showed a significant decrease in the nuclear-cytoplasmic ratio to (0.12 ± 0.04) % in patients of group III. The coefficient of ellipticity of the nuclei of native cells decreased with the development of intestinal metaplasia: in group I it was equal to (0.76 ± 0.04) %, for group II it was (0.65 ± 0.11) %, and for group III — 0.41 ± 0.12) %. In patients with intestinal metaplasia in 82 % of cases with a 3-fold increase in the content of sialic acids in gastric juice was diagnosed with an increase in hexosamines by 35 %, while patients with only atrophic changes in the stomach showed a decrease in hexosamines 2 times compared to controls (p < 0.05). The spread of intestinal metaplasia in the stomach is associated with an increase in the amount of glycoproteins and hexosamines in the oral fluid of patients, while sialic acids in this biological fluid are increased in all study groups. There are direct relationships between the presence of intestinal metaplasia in the body of the stomach and the content of glycoproteins in both gastric juice (r = 0.446, p = 0.008) and in oral fluid (r = 0.378, p = 0.021). The relationship between the content of sialic acids in gastric juice with the degree and stage of gastritis by OLGA (r = 0.431, p < 0.01; r = 0.482, p < 0.01), the level of hexosamines in oral fluid with the coefficient of ellipticity of the nuclei (r = 0.447, p = 0,037). Conclusions. A comprehensive study of morpho-functional changes in the stomach and the ratio of aggressive and projective factors of oral fluid will determine the risk groups of patients with precancerous conditions.
кишкова метаплазія; шлунковий сік; ротова рідина; гістологія слизової оболонки шлунка
intestinal metaplasia; gastric juice; oral fluid; histology of gastric mucosa
Вступ
Матеріали та методи
Результати та обговорення
Висновки
- Jencks D.S., Adam J.D., Borum M.L. Overview of current concepts in gastric intestinal metaplasia and gastric cancer. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018. Vol. 14(2). P. 92-101.
- Fang Y., Chen L., Chen D.F. Prevalence, histologic and clinical characteristics of heterotopic gastric mucosa in Chinese patients. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014. Vol. 20. № 46. P. 17588-1794.
- Fan X. et al. Gastric adenocarcinoma of the fundic gland type: a case report. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020. Vol. 99(21). P. e20361.
- Isajevs S. et al. High-risk individuals for gastric cancer would be missed for surveillance without subtyping of intestinal metaplasia. Virchows Arch. 2021.
- Ткач С.М. Современные подходы к классификации, диагностике и ведению больных с хроническим гастритом в свете международного Киотского консенсуса. Сучасна гастроентерологія. 2016. № 1 (87). С. 110-116.
- Никишаев В.И., Болотских Н.А., Тумак И.Н. Ведение пациентов с предраковыми состояниями и повреждениями в желудке. Клинические рекомендации Укр. журнал малоінвазивної та ендоскопічної хірургії. 2013. № 1 (17). С. 25-50.
- Степанов Ю.М., Сімонова О.В., Мосійчук Л.М. Сучасні ендоскопічні методи діагностики передракових станів шлунка: проблеми і перспективи. Гастроентерологія. 2017. № 1(51). С. 85-93.
- Song H., Ekheden I.G., Zheng Z. Incidence of gastric cancer among patients with gastric precancerous lesions: observational cohort study in a low risk Western population. BMJ. 2015. Vol. 351. P. h3867.
- Шушвал М.С., Волкова Л.В., Ныжник Л.М., Мусатов А.А. Предопухолевые и интраэпителиальные неопластические процессы при развитии карцином желудка. Современные проблемы науки и образования. 2019. № 4.
- Sarosiek J., McCallum R.W. Do salivary organic components play a protective role in health and disease of the esophageal mucosa? Digestion. 1995. Vol. 56. Suppl. 1. P. 32-37.
- Kim H.W. et al. Ascofuranone inhibits epidermal growth factor-induced cell migration by blocking epithelial-mesenchymal transition in lung cancer cells. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2020. Vol. 880. P. 173199.
- Rugge M., de Boni M., Pennelli G. Gastritis OLGA-staging and gastric cancer risk: a twelve-year clinico-pathological follow-up study. Aliment Pharmacol. Ther. 2010. № 31. P. 1104-1111.

/8.jpg)
/8_2.jpg)
/9.jpg)
/10.jpg)
/11.jpg)