Вступ
Печінка є найважливішим органом для метаболізму ліків та хімічних речовин. Чотирихлористий вуглець (CCl4) — це добре відомий гепатотоксин, який може викликати ураження печінки за допомогою різних механізмів, включаючи окиснювальний стрес, запальну відповідь та апоптоз [1, 2]. Ця речовина широко використовується для експериментальної індукції стеатозу та фіброзу у печінці тварин [1–3].
Фіброз пов’язаний з надлишковим синтезом сполучної тканини внаслідок тривалої дії окремих ушкоджуючих факторів [4]. У цьому складному процесі, крім гепатоцитів і непаренхіматозних клітин печінки, задіяні ще й імунні клітини. Загибель гепатоцитів відбувається через апоптоз, некроз чи некроптоз, що індукує запальну та профіброгенну активність непаренхіматозних клітин та імуноклітинну інфільтрацію, сприяючи розростанню фіброзної тканини [5, 6]. Відомо, що тривалі ін’єкції CCl4 викликають фіброз, який подібний до фіброзу у біоптатах печінки людини [7]. Стеатоз — це рання стадія жирової хвороби печінки, що характеризується розвитком перекисного окиснення ліпідів, запалення, активацією зірчастих клітин печінки та фіброзу через накопичення в гепатоцитах неетерифікованих жирних кислот [8].
Печінка має високу здатність поглинати вільні жирні кислоти (ВЖК) із плазми та включати їх у триацилгліцериди, ефіри холестерину та мембранні ліпіди. Нерозчинні у воді триацилгліцериди упаковуються або в ліпідні краплі, які слугують тимчасовим клітинним запасом ліпідів, або в ліпопротеїни дуже низької щільності (ЛПДНЩ), що транспортують ліпіди до позапечінкових тканин. Центральною функцією ліпідних крапель є зберігання триацилгліцеридів та ефірів холестерину, якщо синтез та/або поглинання ВЖК і холестерину перевищує потребу клітини, і вивільнення цих ліпідів у протилежному випадку. Оскільки насичені ВЖК (НВЖК) і вільний холестерин є потенційно цитотоксичними сполуками, то їх перетворення в нетоксичні тригліцериди та ефіри холестерину і подальше відкладення у вигляді ліпідних крапель має вирішальне значення для підтримки цілісності клітини [9].
В гомеостатичних умовах підтримуються відносно низькі концентрації ліпідів у печінці. Але порушення регуляції цього процесу може призвести до їх накопичення у гепатоцитах [10, 11]. І при надмірному накопиченні ВЖК та їх метаболітів у печінці відбувається ліпотоксичне гепатоцелюлярне ураження та прогресування хвороби органа [12].
Zhang et al. на тваринних клітинних культурах in vitro показано, що насичені ВЖК (гексадеканова та октадеканова кислоти) викликають більш серйозний окиснювальний стрес та стрес ендоплазматичного ретикулуму порівняно з НВЖК (cis-9-гексадеценова, cis-9-октадеценова та cis-9,cis-12-октадієнова кислоти). Однак ненасичені ВЖК спричиняють значне накопичення ліпідів (тригліцеридів) у гепатоцитах, хоча цей ефект був пов’язаний із меншим викидом ЛПДНЩ у середовище для культивування клітин [8, 13].
Сьогодні вченими проводяться переважно дослідження in vitro на первинних гепатоцитах або на різних клітинних лініях гепатоцитів з метою вивчення впливу на них ВЖК. Тому існує потреба в дослідженнях in vivo спектра ВЖК при патологіях печінки будь-якого генезу, у тому числі і при токсичному ураженні.
Метадоксин активно використовується для лікування експериментальної гепатотоксичності, у тому числі спричиненої CCl4 [14]. Для нас становило інтерес порівняння ефективності використання гепатотропної речовини метадоксину та метабіотика у щурів при токсичному ураженні печінки. Відомо, що кишечник безпосередньо пов’язаний з печінкою через портальний тракт, тому зміни мікрофлори кишечника можуть впливати на стан печінки [15]. Трансформація кишкової мікрофлори за допомогою метабіотиків виглядає багатообіцяючою терапевтичною стратегією для лікування дисфункцій кишкового бар’єра.
Мета роботи: оцінити морфобіохімічні зміни у печінці щурів з тетрахлорметан-індукованим ураженням печінки після медикаментозної корекції виявлених порушень.
Матеріали та методи
Дослідження проведено на 36 статевозрілих щурах лінії Wistar обох статей (18 самців та 18 самок) вагою 180–200 грамів згідно із загальними етичними принципами експериментів на тваринах, затвердженими І Національним конгресом України з біоетики (2001 р.).
Моделювання токсичного ураження печінки здійснювали в 2 етапи шляхом введення розчину CCl4 (Sigma-Aldrich Corp., Germany) в оливковій олії: I етап — підшкірні ін’єкції 3 рази на тиждень (50% олійний розчин, 4 мл/кг) протягом 1 тижня; ІІ етап — підшкірні ін’єкції 2 рази на тиждень (10% олійний розчин, 4 мл/кг) ще протягом 6 тижнів. Введення розчину CCl4 припиняли після сьомого тижня експерименту. Протягом наступних 30 днів одній частині піддослідних тварин проводили медикаментозну корекцію, а іншу частину щурів утримували на стандартній дієті без корекції. Відповідно до цього були сформовані такі групи: контрольна група (n = 15), що складалася зі здорових тварин; I група — CCl4-індуковане ураження печінки без медикаментозної корекції — уведення CCl4 протягом 7 тижнів з подальшим утриманням тварин на стандартній дієті протягом наступних 30 днів (n = 6); ІІ група — CCl4-індуковане ураження печінки + метадоксин (Ліверія IC) — уведення CCl4 протягом 7 тижнів з подальшою корекцією метадоксином протягом наступних 30 днів (300 мг/кг/добу в їжу; n = 8); ІІІ група — CCl4-індуковане ураження печінки + метабіотик (Хілак форте) — уведення CCl4 протягом 7 тижнів з подальшою корекцією метабіотиком протягом наступних 30 днів (3 мл/кг/добу в їжу; n = 7). Після закінчення експерименту тварин під кетаміновим наркозом декапітували; для подальшого гістологічного і біохімічного аналізу вилучали печінку.
Для проведення морфологічного дослідження зразки печінки щурів заливали в парафінові блоки, робили зрізи товщиною 5 мкм і забарвлювали їх гематоксиліном та еозином за загальноприйнятим в гістологічній практиці методом. Для оцінки стеатозу та фіброзу використовували трикольорове якісне забарвлення зразків тканини печінки піддослідних тварин за методом Маллорі в модифікації Слінченка [16], які в подальшому вивчали за допомогою світлового мікроскопа XSP-139TP («Ulab», Україна) та фотографували фотоапаратом Canon A630 (Японія). Ступінь гістологічного ураження оцінювався таким чином: «–» — відсутне; «+» — легкий ступінь; «++» — середній ступінь; «+++» — тяжкий ступінь.
Для приготування гомогенату печінки її спочатку промивали 0,9% розчином хлориду натрію, потім зважували і подрібнювали. Усі маніпуляції проводили при 0–4 °С. Із печінки готували 10% гомогенат на 0,1 М фосфатному буфері (рН = 7,4) у гомогенізаторі Даунса. Потім гомогенат переносили у пробірки з робочим об’ємом 10 мл та центрифугували з використанням центрифуги ОПН-8 при 0–4 °С протягом 15 хв при 5000 g. Отриману надосадову рідину використовували для подальших біохімічних досліджень.
Хроматографічне дослідження МНЖК у гомогенаті печінки експериментальних щурів проводили на газовому хроматографі з полум’яно-іонізаційним детектором «Хроматек-Кристалл 5000» за методикою Степанова та співавт. [17]. KOH-метилювання МНЖК здійснювали за методикою Ichihara та співавт. [18].
Для мікробіологічного дослідження видового та кількісного складу мікрофлори товстої кишки проводили посів десятикратних розведень зразків калу (10–1–10–9) на стандартний набір селективних та диференційно-діагностичних поживних середовищ для виділення аеробних та анаеробних мікроорганізмів. Оцінку ефективності проведеної терапії проводили шляхом порівняння ступеня дисбіотичних порушень, виявлених до і після корекції, використовуючи градацію за ступенями, яка свідчить про амплітуду відхилень мікробіоценозу товстої кишки: відсутність відхилень — еубіоз; наявність відхилень — дисбактеріоз.
Статистичний аналіз отриманих даних здійснювали за допомогою прикладних програм Statistica 6.1. Нормальність розподілу кількісних показників оцінювали за допомогою критерію Шапіро — Уїлка. Для опису даних застосовували медіану (Me), нижній (25 %) і верхній (75 %) квартилі. Порівняння показників медіани здійснювали за U-критерієм Манна — Уїтні. Статистичну значущість оцінювали на рівні не нижче, ніж 95,0 % (р < 0,05).
Результати та обговорення
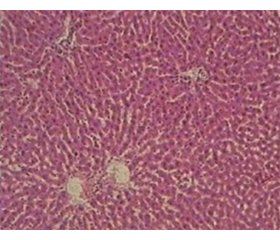
Дослідження гепатобіоптатів контрольних щурів показало збережену структуру печінки без ознак інфільтрації запальними клітинами у 100 % випадків. Ядра гепатоцитів мали округлу форму. Синусоїди були помірно розширені, з невеликою кількістю клітин крові (табл. 1, рис. 1).
Оцінка гепатобіоптатів у І групі щурів з CCl4-індукованим ураженням печінки без медикаментозної корекції показала, що зміни гістологічної структури печінки зумовлювалися в основному наявністю поширеного великокраплинного стеатозу у понад 30 % гепатоцитів (переважно в 3 зоні ацинуса), гідропічної дистрофії гепатоцитів та легкого ступеня інфільтрації лімфоцитами і плазматичними клітинами. Фіброзні зміни у 100 % випадків були представлені тонкими сполучнотканинними тяжами, розташованими в перицентральній зоні печінкової часточки.
У 66,7 % щурів у печінковій часточці спостерігалося порушення кровообігу з нерівномірним розширенням просвітів синусоїдів, з обструкцією їх еритроцитами, а також з дилатацією міжчасточкових і, рідше, центральних вен. У паренхімі печінки формувалися вогнища ліпідно-білкової дистрофії та некрозу гепатоцитів, переважно в перицентральній зоні часточок (табл. 1, рис. 2А).
Порівняння з результатами проведеного нами раніше дослідження, у якому описана подібна модель CCl4-індукованого ураження печінки [19], показало, що для часткового відновлення гепатоцитів достатньо 30 днів після припинення введення токсичного агента. За цей час жирова дистрофія стає менш вираженою і заміщується поширеною гідропічною дистрофією. Однак загибель клітин та запальноклітинна інфільтрація з вивільненням запальних цитокінів, ймовірно, призвели до більш вираженої активації зірчастих клітин та розвитку необоротних фіброзних змін [20].
У 100 % щурів ІІ та ІІІ групи після 30-денної корекції метадоксином та метабіотиком відповідно у зразках печінки гепатоцити у всіх полях зору мали більш чіткі контури та округлу форму ядра, а також спостерігалося зменшення ознак білково-жирової дистрофії порівняно з І групою тварин. Проте у гепатобіоптатах щурів ІІ групи виявлялися вогнища цирозу, а в ІІІ групі — множинні міжчасточкові фіброзні септи. Жирові краплини в обох групах тварин мали великі розміри; у деяких гепатоцитах у цитоплазмі знаходилася одна ліпідна вакуоль, що відтісняє ядро до периферії клітини. У 62,5 % тварин ІІ групи у зразках печінки визначалися «балонні» клітини (кінцева форма гідропічної дистрофії), схожі на наповнені рідиною балони з центрально розташованим ядром зі зміненою формою. Ці клітини виявлялися як поодинці, так і скупченнями, що є проявом вогнищевого колікваційного некрозу та, скоріше за все, свідчить про автофагію гепатоцитів як механізм їх виживання при токсичному ураженні печінки [21]. Однак, незважаючи на позитивні ефекти автофагії, які можуть мати вирішальне значення при ендотоксемії та стеатозі печінки, індукований апоптоз субпопуляції гепатоцитів був пов’язаний з активацією зірчастих клітин [22] — фіброзні тяжі виявлялися майже в усіх зразках печінки тварин ІІ та ІІІ групи. Визначалися вогнища лімфоцитарно-гістіоцитарної інфільтрації в обох групах щурів (табл. 1, рис. 2Б, В).
Результати біохімічного дослідження наведені на рис. 3, у табл. 2.
Визначено вірогідне підвищення сумарного вмісту МНЖК у гомогенаті печінки І групи щурів у 118 разів до 0,823 (0,230–1,410) мкг/мкл (р < 0,001), у ІІ групі — у 34 рази до 0,235 (0,170–0,500) мкг/мкл (р < 0,001) та в ІІІ групі — у 99 разів до 0,690 (0,530–1,080) мкг/мкл (р < 0,001) порівняно з контрольними значеннями (0,007 (0,007–0,013) мкг/мкл). Слід відзначити, що у ІІ групі тварин даний показник мав тенденцію до зниження в 3,5 (p = 0,430) та 2,9 раза (р = 0,064) порівняно з І та ІІІ групами відповідно (рис. 3).
/28_2.jpg)
У гомогенаті печінки тварин І групи визначено вірогідне зростання вмісту таких фракцій МНЖК: cis-10-пентадеценової, cis-10-гептадеценової, cis-9-октадеценової та cis-11-ейкозенової кислот у 5 (р < 0,001), 6,5 (р < 0,001), 62 (р < 0,001) та 48 разів (р < 0,001) відповідно порівняно зі слідовими кількостями у контролі. Також виявлені у високій концентрації cis-9-тетрадеценова та trans-9-октадеценова кислоти, які не визначалися у контрольній групі. Не ідентифікувалася в гомогенаті печінки тварин І групи та контролі cis-9-гексадеценова кислота.
Щодо ІІ групи щурів, то вміст cis-10-пентадеценової, cis-10-гептадеценової, cis-9-октадеценової та cis-11-ейкозенової кислот вірогідно збільшувався в гомогенаті печінки в 8 (р < 0,001), 22 (р < 0,001), 32 (р < 0,001) та 149 (р = 0,0011) разів відповідно порівняно з контрольною групою. На відміну від контролю в цій групі тварин була виявлена trans-9-октадеценова кислота в значній концентрації. У слідових кількостях визначався вміст cis-9-тетрадеценової та cis-9-гексадеценової кислот, тоді як у контрольній групі ці кислоти не виявлялися.
У гомогенаті печінки ІІІ групи щурів також вірогідно збільшувався вміст cis-10-пентадеценової, cis-10-гептадеценової, cis-9-октадеценової та cis-11-ейкозенової кислот у 17 (р < 0,001), 34 (р < 0,001), 138 (р < 0,001) та 91 (р < 0,001) раз відповідно порівняно з контролем. У цій же групі тварин виявлені в високій концентрації cis-9-тетрадеценова та trans-9-октадеценова кислоти та в незначній кількості — cis-9-гексадеценова кислота, тоді як у контролі ці кислоти не ідентифікувалися.
Слід відзначити, що вміст МНЖК підвищувався за рахунок досить високих значень у І групі щурів cis-9-тетрадеценової, trans- і cis-9-октадеценової та cis-11-ейкозенової кислот, у ІІ групі — cis-10-гептадеценової, trans- і cis-9-октадеценової та cis-11-ейкозенової кислот та у ІІІ групі — cis-9-тетрадеценової, cis-10-пентадеценової, cis-10-гептадеценової, trans- і cis-9-октадеценової та cis-11-ейкозенової кислот, тоді як ці фракції або не визначалися, або знаходилися у слідових кількостях у контролі.
Міжгруповий аналіз показав, що у гомогенаті печінки щурів І групи концентрація cis-10-пентадеценової та cis-10-гептадеценової кислот залишалася вірогідно нижчою в 1,6 (р = 0,017) та 3,4 раза (р = 0,002) відповідно порівняно з ІІ групою і в 3,4 (р = 0,016) та 5,2 (р = 0,005) раза відповідно порівняно з ІІІ групою. Також у І групі тварин вміст cis-9-октадеценової кислоти був вірогідно нижчим у 2,1 раза (р = 0,009) порівняно з ІІІ групою. Уміст cis-9-тетрадеценової, cis-9-гексадеценової, trans-9-октадеценової та cis-9-октадеценової кислот у ІІ групі щурів вірогідно знижувався у 19 (р = 0,003), 5 (р = 0,05), 16,3 (р = 0,011) та 4,3 раза (р = 0,015) відповідно порівняно з ІІІ групою.
На сьогодні низка вчених вивчають in vitro процеси пошкодження гепатоцитів, викликані вільними жирними кислотами. У дослідженні Zhang et al. було встановлено, що інкубація первинної культури гепатоцитів теляти протягом 12 год з 1,2 ммоль/л cis-9-гексадеценової (пальмітолеїнової) або cis-9-октадеценової (олеїнової) кислоти призводила до зростання концентрації триацилгліцеридів, експресії білка, що зв’язує регулюючий елемент стеролу-1 (SREBP-1c), синтази жирних кислот, ацетил-КоА карбоксилази 1, аполіпопротеїну В-100 та сортиліну-1 (SORT1). Таким чином, ненасичені жирні кислоти викликали значне накопичення ліпідів у гепатоцитах [8]. Zhang et al. in vitro дослідили, що інкубація з 1,2 мМ сумішшю неетерифікованих жирних кислот (cis-9-октадеценова, cis-9,cis-12-октадекадієнова, гексадеканова, октадеканова та cis-9-гексадеценова кислоти) протягом 12 год призводила до значного утворення ліпідних крапель і посилення синтезу тригліцеридів у клітинах печінки щурів BRL-3A [13]. У нашому експерименті в печінці щурів після тривалого впливу CCl4 визначалася висока концентрація саме cis-9-октадеценової кислоти та незначна — cis-9-гексадеценової кислоти, що могло сприяти розвитку стеатозу.
Таким чином, окрема жирна кислота може по-різному впливати на метаболізм печінки. Але в літературі досить мало інформації з аналізу in vivo вмісту ВЖК у печінці щурів після її токсичного ураження. Тому визначений у нашому дослідженні спектр МНЖК у печінці може слугувати додатковим діагностичним маркером для верифікації розвитку окиснювального стресу, стеатозу та фіброзу при різних гепатотоксичних пошкодженнях.
Нами було досліджено стан мікробіоценозу товстої кишки у щурів з CCl4-індукованим ураженням печінки. Виявлено дисбіоз кишечника у І групі тварин: зменшення колонієутворюючих одиниць Bifidobacterium spp., Lactobacillus spp., Escherichia coli та збільшення Candida spp., гемолітичної Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus та умовно-патогенних ентеробактерій Proteus spp., тоді як у ІІІ групі щурів спостерігалося відновлення кількісного складу Bifidobacterium spp., Lactobacillus spp., E. coli з нормальною ферментативною активністю, грибів роду Candida spp. і вже не виділялися Staphylococcus aureus та Proteus spp. Саме тому з метою виявлення можливого ефекту на вміст МНЖК у печінці щурів з токсичним ураженням нами був застосований метабіотик.
Корекція метадоксином дозволила отримати кращі результати вмісту МНЖК у печінці порівняно з метабіотиком. Тому для збільшення ефективності метабіотика його, можливо, краще застосовувати в комбінованій терапії з іншими препаратами (наприклад, з метадоксином) з подовженим періодом уведення, що планується зробити в подальших наших дослідженнях.
Висновки
1. У результаті експериментального дослідження на щурах виявлено, що при тетрахлорметан-індукованому ураженні печінки розвивається великокраплинний стеатоз з множинними фіброзними септами між печінковими частками. Корекція метадоксином та метабіотиком зменшила прояви білково-жирової дистрофії в гепатоцитах.
2. У всіх дослідних групах тварин уміст мононенасичених жирних кислот підвищується переважно за рахунок значних концентрацій cis-10-пентадеценової, cis-10-гептадеценової, trans- і cis-9-октадеценової та cis-11-ейкозенової кислот, що може сприяти розвитку стеатозу печінки. Уміст МНЖК більше знижувався під впливом метадоксину, ніж метабіотика.
Конфлікт інтересів. Автори заявляють про відсутність конфлікту інтересів при підготовці даної статті.
Інформація про фінансування. Робота виконується відповідно до плану наукових досліджень ДУ «Інститут гастроентерології НАМН України» в рамках науково-дослідної роботи «Вивчити клініко-біохімічні та структурні особливості формування стеатозу і фіброзу у пацієнтів з хронічними дифузними захворюваннями печінки», номер держреєстрації 0118U001834.
Внесок авторів у роботу над статтею. Діденко В.І. — концепція і дизайн дослідження; Карачинова В.А. — проведення біохімічних досліджень та їх аналіз, написання тексту та оформлення статті; Кленіна І.А. — аналіз літературних джерел, редагування статті; Гайдар Ю.А. — проведення морфологічних досліджень; Ошмянська Н.Ю. — аналіз морфологічних досліджень; Грабовська О.І. — проведення експерименту, статистична обробка матеріалу; Галінський О.О. — розробка методики та відтворення в експерименті хронічного тетрахлоретан-індукованого ураження печінки щурів та проведення корекції; Вішнаревська Н.С. — проведення мікробіологічних досліджень та їх аналіз.
Отримано/Received 21.03.2022
Рецензовано/Revised 03.04.2022
Прийнято до друку/Accepted 12.04.2022
/27_2.jpg)
/28_2.jpg)

/27.jpg)
/28.jpg)
/29.jpg)