Международный эндокринологический журнал Том 18, №5, 2022
Вернуться к номеру
Функціональний стан щитоподібної залози в дітей, хворих на виразку дванадцятипалої кишки
Авторы: Сокольник С.В., Нечитайло Д.Ю., Лозюк І.Я., Остапчук В.Г.
Буковинський державний медичний університет, м. Чернівці, Україна
Рубрики: Эндокринология
Разделы: Клинические исследования
Версия для печати
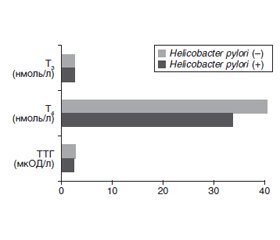
Актуальність. Більшість фахівців одностайні щодо того, що в дітей значно частіше трапляється виразка дванадцятипалої кишки. Останніми роками став проявлятися дослідницький інтерес відношень тиреоїдної системи з процесами виразки у дванадцятипалій кишці. Мета. Дослідити функціональний стан щитоподібної залози в дітей, хворих на виразку дванадцятипалої кишки. Матеріали та методи. Групу спостереження становили 56 дітей віком від 7 до 18 років із верифікованою виразкою дванадцятипалої кишки та 15 здорових дітей. Усім педіатричним пацієнтам проводили фіброезофагогастродуоденоскопію з прицільною щитковою біопсією та дослідженням на наявність бактерії Helicobacter pylori, внутрішньошлункову рН-метрію, ультразвукове дослідження органів черевної порожнини та щитоподібної залози, досліджували концентрацію тиреоїдних гормонів (ТТГ, Т3, Т4). Оцінка вірогідності здійснювалася за допомогою критерію Стьюдента (t). Різниця вважалася вірогідною при р < 0,05. Результати. Середній вік виникнення виразки дванадцятипалої кишки в дітей становив 13,1 ± 3,1 року. У всіх вікових категоріях виразка дванадцятипалої кишки частіше траплялася у хлопчиків — 58,9 %. Під час поглибленого ультразвукового дослідження структура щитоподібної залози в 52 (92,8 %) дітей була однорідною, у 4 (7,1 %) дітей — неоднорідною, але без вузлових утворень. Концентрації ТТГ та Т3 в крові дітей із виразкою дванадцятипалої кишки також не відрізнялися від середніх показників у дітей групи порівняння. При цьому відзначалося зниження концентрації Т4, що можна розглядати як варіант синдрому еутиреоїдної слабкості — синдрому зниженого Т4. Середній рівень Т4 у крові (32,67 ± 3,84 нмоль/л) був значно нижчим (p = 0,001) у дітей, інфікованих Helicobacter pylori, ніж у дітей без інфікування (39,45 ± 4,23 нмоль/л) та здорових (89,12 ± 5,91 нмоль/л). Висновки. Діти, хворі на виразку дванадцятипалої кишки, мають порушення тиреоїдного статусу за рахунок зниження концентрації тироксину. Функціональне зрушення в тиреоїдному статусі в цих пацієнтів може розглядатися як прогностично несприятлива ознака ймовірного погіршення перебігу виразки.
Background. Most experts agree that duodenal ulcers are much more common in children. In recent years, the research interest in the relationship between the thyroid system and duodenal ulcer processes has become evident. The purpose of the study is to investigate the thyroid functional state in children with duodenal ulcer. Materials and methods. The observation group consisted of 56 children aged 7 to 18 years with a verified duodenal ulcer and 15 healthy children. All pediatric patients underwent fibroesophagogastroduodenoscopy with a targeted thyroid biopsy and examination for the presence of the Helicobacter pylori bacterium, intragastric pH-metry, ultrasound examination of the abdominal cavity and thyroid gland; the concentration of thyroid hormones (thyroid-stimulating hormone, T3, T4) was also studied. Reliability was assessed using Student’s t-test. The difference was considered significant at p < 0.05. Results. The average age of children with duodenal ulcer was 13.1 ± 3.1 years. In all age categories, duodenal ulcer occurred more often in boys — 58.9 %. During an in-depth ultrasound examination, the structure of the thyroid gland in 52 (92.8 %) children was homogeneous, in 4 (7.1 %) individuals it was heterogeneous, but without nodular formations. Serum concentrations of thyroid-stimulating hormone and T3 in children with duodenal ulcer also did not differ from the average levels in children of the comparison group. At the same time, a decrease in the concentration of T4 was noted, which can be considered as a variant of euthyroid sick syndrome — the syndrome of reduced T4. The average serum level of T4 (32.67 ± 3.84 nmol/l) was significantly lower (p = 0.001) in children infected with Helicobacter pylori than in those without infection (39.45 ± 4.23 nmol/l) and healthy individuals (89.12 ± 5.91 nmol/l). Conclusions. Children with a duodenal ulcer have a violation of the thyroid status due to a decrease in the thyroxine concentration. A functional shift in the thyroid status in these patients can be considered as a prognostically unfavorable sign of possible deterioration of the ulcer course.
тиреоїдні гормони; діти; виразка дванадцятипалої кишки; Helicobacter pylori
thyroid hormones; children; duodenal ulcer; Helicobacter pylori
Вступ
Матеріали та методи
Результати
/56_2.jpg)
Обговорення
Висновки
- Carli D.М., Pires R.С., Rohde S.L., Kavalco C.М., Fagundes R.B. Peptic ulcer frequency differences related to h. Pylori or aines. Arq. Gastroenterol. 2015. 52(1). 46-9. doi: 10.1590/S0004-28032015000100010. PMID: 26017082.
- Han Y., Jung H.К., Chang J.Y. et al. Identification of distinctive clinical significance in hospitalized patients with endoscopic duodenal mucosal lesions. Korean J. Intern. Med. 2017. 32(5). 827-835. doi: 10.3904/kjim.2015.149.
- Bates J.А., Dinnan K., Sharp V. Biliary hyperkinesia, a new diagnosis or misunderstood pathophysiology of dyskinesia: A case report. Int. J. Surg. Case Rep. 2019. 55. 80-83. doi: 10.1016/j.ijscr.2019.01.0.9.
- Sokolnyk S., Sorokman T., Sokolnyk S., Zymagorova N. Posteradication Period of Helicobacter-Associated Peptic Ulcer in Children. Child’s health. 2014. 52(1). 16-19 (in Ukrainian). https://doi.org/10.22141/2224-0551.1.52.2014.75601
- Lee K.D., Kayano T., Nishiura H. Dramatic shift in the epidemiology of peptic ulcer in Japan: the impact of Helicobacter pylori eradication therapy. Epidemiol. Infect. 2021. 150. e4. doi: 10.1017/S095026882100265X.
- Lee J.S.G., Brown I.E., Semrad A.M., Zeki A.A. Getting around the gut: a unique management challenge of thyroid storm precipitated by amphetamine-associated duodenal ischaemia leading to compromised enteric absorption. BMJ Case Rep. 2021. 14(8). e238889. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2020-238889.
- Urmanova Y., Azimova S., Rikhsieva N. Prevalence and structure of thyroid diseases in children and adolescents according to the data of appealability. International Journal of Endocrinology (Ukraine). 2018. 14(2). 163-167. doi: 10.22141/2224-0721.14.2.2018.130562. (in Russian).
- Pankiv V.I. Correction of the functional state of the liver in patients with autoimmune diseases of the thyroid gland. International Journal of Endocrinology (Ukraine). 2018. 14(5). 499-502. doi: 10.22141/2224-0721.14.5.2018.142687. (in Ukrainian).
- Namulema J., Nansunga M., Kato C.D., Kalange M., Olaleye S.B. Thyroid hormones increase stomach goblet cell numbers and mucin expression during indomethacin induced ulcer healing in Wistar rats. Thyroid Res. 2018. 11. 6. doi: 10.1186/s13044-018-0050-0.
- Fitzgerald S.Р., Falhammar H. Redefinition of Successful Treatment of Patients With Hypothyroidism. Is TSH the Best Biomarker of Euthyroidism? Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne). 2022. 13. 920854. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.920854.
- Silva I.N., Marçal L.V., Queiroz D.М.M. Helicobacter pylori Infection Is Associated With Thyroid Dysfunction in Children With Congenital Hypothyroidism. Front. Pediatr. 2022. 10. 875232. doi: 10.3389/fped.2022.875232.
- Wittekind D.А., Kratzsch J., Mergl R. et al. Free triiodothyronine (T3) is negatively associated with fasting ghrelin serum levels in a population sample of euthyroid subjects. J. Endocrinol. Invest. 2021. 44(12). 2655-2664. doi: 10.1007/s40618-021-01578-5.
- Han L., Shu X., Wang J. Helicobacter pylori-Mediated Oxidative Stress and Gastric Diseases: A Review. Front. Microbiol. 2022. 13. 811258. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.811258.
- Figura N., Di Cairano G., Moretti E. et al. Helicobacter pylori Infection and Autoimmune Thyroid Diseases: The Role of Virulent Strains. Antibiotics (Basel). 2019. 9(1). 12. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics9010012.
- Larizza D., Calcaterra V., Martinetti M. et al. Helicobacter pylori infection and autoimmune thyroid disease in young patients: the disadvantage of carrying the human leukocyte antigen-DRB1*0301 allele. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2006. 91. 176-9. 10.1210/jc.2005-1272.

/55.jpg)
/56.jpg)