Журнал "Гастроэнтерология" Том 56, №3, 2022
Вернуться к номеру
Клініко-лабораторне та інструментальне дослідження ефективності та безпечності гепатотропного комплексу Ліводінол
Авторы: Степанов Ю.М. (1), Косинська С.В. (2), Горбунцова В.І. (1), Кленіна І.А. (1), Петішко О.П. (1)
(1) — ДУ «Інститут гастроентерології НАМН України», м. Дніпро, Україна
(2) — Дніпровський державний медичний університет, м. Дніпро, Україна
Рубрики: Гастроэнтерология
Разделы: Клинические исследования
Версия для печати
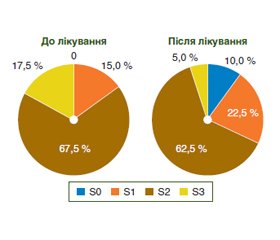
Мета дослідження: оцінка ефективності лікування комплексом Ліводінол у хворих на стеатоз та стеатогепатит на підґрунті комплексного вивчення стану функціональних та структурних порушень печінки до та після лікування цим засобом. Матеріали та методи. Дослідження проводилось у 40 хворих на НАЖХП, з них 20 хворих – на стеатогепатоз та 20 – на стеатогепатит, середній вік – (49,7±14,2) років, з них жінок 15 (37,5%) та чоловіків 25 (62,5%). Усім хворим проводилась оцінка функціонального стану печінки, вмісту продукту перекисного окислення ліпідів, ступеня фіброзу та стеатозу печінки методом фібросканування за допомогою апарата FibroScan® 502 touch (Echosens, Paris, France) та зсувнохвильової 2еластографії (2D-SWE) на апараті TOSHIBA XARIO (Japan). Результати. На фоні лікуванняЛіводінол больовий синдром купіровано у більшості хворих, 85% (p<0,001). Подібна картинаспостерігалась щодо диспепсичних явищ. Відмічається значне зменшення цитолізу на фонілікування, АЛТ нормалізувалось у 92,5% хворих, АСТ - у 95%, що вказує на вираженийвідновлювальний ефект Ліводінолу. Комплекс Ліводінол чинить нормалізуючий вплив на вміст МДА, який було підвищено у 37,5% до (34,6±1,5) мкмоль/л, знизився після лікування в цих хворих знизився показник до (31,9±2,6) мкмоль/л (р<0,001), залишившись підвищеним 12,5%. Він пов'язаний позитивним вираженим зв’язком з ГГТП, r=0,757, p<0,001. Оцінка структурнихзмін показала, що за даними фібросканування печінки до лікування у переважної більшості (55,0%) пацієнтів фіброз був відсутнім; перший ступінь фіброзу (F1) реєструвався у 40,0% пацієнтів, другий (F2) – у 2,5%, третій (F3) – у 2,5% та четвертий (F4) у жодному випадку не реєструвався. До лікування картина стеатоза була наступна: S1 – 15%, S2 – 67,5%, S3 – 17,5%, а після лікування: S0 – 10%, S1 – 22,5%, S2 – 62,5%, S3 – 5,0%. УЗД визначено зменшенняпоказника коефіцієнта затухання ультразвуку після лікування на 6,5% та покращення еластичності печінки на 6,3%. Переносимість та безпечність склала - 97,5%. Висновки. Комплекс Ліводінол є ефективним для лікування хворих на НАЖХП, що підтверджуєтьсяданими клінічних, лабораторних та інструментальних обстежень. Комплекс Ліовдінол показав безпечність та добру переносимість у хворих на стеатоз та стеатогепатит при застосуванні згідно інструкції на протязі 2 міс.
Materials and methods. The study was conducted in 40 patients with NAFLD, of whom 20 were patients with steatohepatosis and 20 with steatohepatitis, the average age was (49.7±14.2) years, of whom 15 were women (37.5%) and 25 were men (62.5%). All patients were evaluated for the functional state of liver, level of the product of lipid peroxidation, the degree of fibrosis and steatosis of the liver by fibroscanning with the FibroScan® 502 touch device (Echosens, Paris, France) and shear wave elastography (2D-SWE) on the TOSHIBA XARIO device (Japan). The results. Duringtreatment with Livodinol, the pain syndrome was stopped in the most patients, 85% (p<0.001). A similar picture was observed with regard to dyspeptic phenomena. A significant decrease in cytolysis was noted during treatment, ALT normalized in 92.5% of patients, AST – in 95%, which indicates a pronounced restorative effect of Livodinol. The complex Livodinol has a normalizing effect on level of MDA, which was increased in 37.5% to (34.6±1.5) μmol/l, decreased after treatment in these 3 patients, the indicator decreased to (31.9±2.6) μmol/l (р<0.001), remained elevated in 12.5%. It is associated with a positive expressed relationship with GGTP, r=0.757, p<0.001. The assessment of structural changes showed that, according to liver fibroscan data, before treatment, fibrosis was absent in the vast majority of patients (55.0%); the first degree of fibrosis (F1) was registered in 40.0% of patients, the second (F2) – in 2.5%, the third (F3) - in 2.5%, and the fourth (F4) was not registered in any case. Before treatment, the pattern of steatosis was as follows: S1 – 15%, S2 – 67.5%, S3 – 17.5%, and after treatment: S0 – 10%, S1 – 22.5%, S2 – 62.5%, S3 - 5.0%. Ultrasound revealed a decrease in attenuation coefficient (SAR) after treatment in 6.5% and an increase in liver elasticity in 6.3%. Tolerability and safety was 97.5%. Conclusions. The complex Livodinol is an effective drug for the treatment of patients with NAFLD, which is confirmed by the data of clinical, laboratory and instrumental examinations. The complex Livodinol showed safety and good tolerance in patients with steatosis and steatohepatitis when used according to the instructions for 2 months.
неалкогольна жирова хвороба печінки; функціональні та структурні порушення печінки; гепатотропний комплекс Ліводінол; ефективність лікування
non-alcoholic fatty liver disease; functional and structural liver disorders; hepatotropic complex Livodinol; treatment effectiveness
Вступ
Матеріали та методи
Результати
Характеристика клінічних проявіву хворих на неалкогольний стеатоз та стеатогепатит у динаміці лікування
/37.jpg)
Динаміка біохімічних показників після лікування
/38.jpg)
/38_2.jpg)
Оцінка стану структури печінки за даними фібросканування (транзієнтна еластометрія FibroScan)
Результати дослідження змін печінки за даними зсувнохвильової еластографії (2D-SWE) та стеатометрії печінки
/40.jpg)
Оцінка безпеки та побічних ефектів
Висновки
- Kardashian A., Serper M., Terrault N., Nephew L.D. Health Disparities in Chronic Liver Disease. Hepatology (Baltimore, Md.). 2022. 32743. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.32743
- Takuissu G.R., Kenmoe S., Amougou Atsama M., Atenguena Okobalemba E., Mbaga D.S., Ebogo-Belobo J.Т. et al. Global epidemiology of occult hepatitis B virus infections in blood donors, a systematic review and meta-analysis. PloS One. 2022. 17(8). e0272920. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0272920
- Perumpail B.J., Khan M.A., Yoo E.R., Cholankeril G., Kim D., Ahmed A. Clinical epidemiology and disease burden of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. World Journal of Gastroenterology. 2017. 23(47). 8263-8276. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i47.8263
- Huang T.D., Behary J., Zekry A. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: a review of epidemiology, risk factors, diagnosis and management. Internal Medicine Journal. 2020. 50(9). 1038-1047. https://doi.org/10.1111/imj.14709
- Conde I., Vinaixa C., Berenguer M. Hepatitis C-related cirrhosis. Current status. Cirrosis por hepatitis C. Estado actual. Medicina Clinica. 2017. 148(2). 78-85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.medcli.2016.09.019
- Clemente-Sánchez A., Oliveira-Mello A., Bataller R. Moderate Alcoholic Hepatitis. Clinics in Liver Disease. 2021. 25(3). 537-555. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cld.2021.03.001
- Craciun A., Cortez-Pinto H. Alarming increase of NASH as cause of liver cancer. Cell reports. Medicine. 2022. 3(8). 100723. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.xcrm.2022.100723
- Zubieta-Rodríguez R., Gómez-Correa J., Rodríguez-Amaya R., Ariza-Mejia K.А., Toloza-Cuta N.A. Hospital mortality in cirrhotic patients at a tertiary care center. Mortalidad hospitalaria en pacientes cirróticos en un hospital de tercer nivel. Revista de Gastroenterologia de Mexico. 2017. 82(3). 203-209. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rgmx.2016.10.002
- Xing G., Huang Y., Liu X. Association between Dietary Pattern, Nutritional Status, Metabolic Factors, and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Contrast Media & Molecular Imaging. 2022. 4157403. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/4157403
- Tang M., Wei X.Н., Cao H., Zhen Q., Liu F., Wang Y.F. et al. Association between Chinese visceral adiposity index and metabolic-associated fatty liver disease in Chinese adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Frontiers in endocrinology. 2022. 13. 935980. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2022.935980
- Ferro Y., Pujia R., Mazza E., Lascala L., Lodari O., Maurotti S. et al. A new nutraceutical (Livogen Plus®) improves liver steatosis in adults with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Journal of Translational Medicine. 2022. 20(1). 377. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12967-022-03579-1
- Virukalpattigopalratnam M.Р., Singh T., Ravishankar A.C. Гептрал (адеметіонін) у пацієнтів з внутрішньопечінковим холестазом при хронічному захворюванні печінки внаслідок неалкогольної хвороби печінки: результати багатоцентрового обсерваційного дослідження в Індії. Журнал Індійської медичної асоціації. 2013. 111(12). 856-859.
- Li L., Wang J., Geng S., Liu F., Ping L., Gu X. et al. Efficacy of adenosylmethionine combined with Si Mo Tang in treatment of neonatal jaundice. American Journal оf Translational Research. 2022. 14(6). 3926-3935.
- Fadieienko G.D., Skrypnyk I.М., Oisodlo G.V., Gridnev O.Е., Nikiforova Ya.V. Effectiveness and safety of the drug ademetionine in the correction of liver function in patients with steatohepatitis. Results of an open-label, multicenter, comparative postmarketing study. Modern Gastroenterology. 2019. 1. 13-20. https://doi.org/10.30978/MG-2019-1-13 (in Ukrainian)
- Shen Y., Huang H., Wang Y., Yang R., Ke X. Antioxidant effects of Se-glutathione peroxidase in alcoholic liver disease. Journal of Trace Elements in Medicine and Biology: organ of the Society for Minerals and Trace Elements (GMS). 2022. 74. 127048. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtemb.2022.127048
- Sanabria-Cabrera J., Tabbai S., Niu H., Alvarez-Alvarez I., Licata A., Björnsson E. et al. N-Acetylcysteine for the Management of Non-Acetaminophen Drug-Induced Liver Injury in Adults: A Systematic Review. Frontiers in pharmacology. 2022. 13. 876868. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2022.876868
- Wen X., Leisinger F., Leopold V., Seebeck F.P. Synthetic reagents for enzyme-catalyzed methylation. Angewandte Chemie (International ed. in English). 2022. 08746. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.202208746
- Kumar P., Liu C., Suliburk J., Hsu J.W., Muthupillai R., Jahoor F. et al. Supplementing Glycine and N-Acetylcysteine (GlyNAC) in Older Adults Improves Glutathione Deficiency, Oxidative Stress, Mitochondrial Dysfunction, Inflammation, Physical Function, and Aging Hallmarks: A Randomized Clinical Trial. The Journals оf Gerontology. Series A. Biological Sciences and Medical Sciences, glac135. 2022. https://doi.org/10.1093/gerona/glac135
- du Preez H.N., Aldous C., Kruger H.G., Johnson L. N-Acetylcysteine and Other Sulfur-Donors as a Preventative and Adjunct Therapy for COVID-19. Advances in Pharmacological аnd Pharmaceutical Sciences. 2022. 4555490. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/4555490
- Leilei L., Wenke Q., Yuyuan L., Sihang L., Xue S., Weiqiang C. et al. Oleanolic acid-loaded nanoparticles attenuate activation of hepatic stellate cells via suppressing TGF-β1 and oxidative stress in PM2.5-exposed hepatocytes. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacolo–gy. 2022. 437. 115891. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2022.115891

/36.jpg)
/37_2.jpg)
/39.jpg)
/39_2.jpg)