Вступ
Зі зростанням хірургічної активності на користь органозберігаючих операцій збільшується і кількість ускладнень, характерних для ендопротезування. Серед них переважають інфекційні ускладнення (3–13 %) і різні види нестабільності ендопротеза і його вузлів, які становлять від 2 до 10 % [1–3]. Загальна частота інфекційних ускладнень ендопротезування великих суглобів в онкологічних хворих становить 10 %, ранніх — 57,6 % та пізніх — 13,6 %. При локалізації пухлини в дистальному відділі стегнової кістки після ендопротезування колінного суглоба інфекційні ускладнення виникають у середньому у 8 % хворих, асептична нестабільність — у 10 % і рецидиви — у 10 %, загальний п’ятирічний термін служби ендопротеза становить близько 54 % [4, 5]. При ураженні проксимального відділу великогомілкової кістки після ендопротезування колінного суглоба інфекційні ускладнення виникають у 10–16 % хворих, асептична нестабільність — у 18 % і рецидиви — у 13 %, загальний п’ятирічний термін служби ендопротеза становить близько 38 % [6].
Деякі автори [7] вказують на ускладнення (близько 45 %) при спостереженні хворих до 10 років після ендопротезування колінного суглоба при пухлинах кісток. Низка дослідників [8–10] повідомляє про ускладнення після органозберігаючих операцій у вигляді ендопротезування: нестабільність ніжки ендопротеза — від 5 до 60 % випадків, нагноєння — 3–20 %, порушення цілісності імплантату — 3–15 %. За даними R. Capanna та P. Ruggieri [11], ревізійне ендопротезування виконувалося у 13,68–31,2 % випадків після ендопротезування. Причинами були: інфекційні ускладнення — від 7,3 до 17 %, асептична нестабільність — від 1 до 12 %, перелом конструкції ендопротеза — від 1,5 до 10,6 %, знос поліетиленових компонентів — від 3,1 до 35,6 %. За даними R. Windhager зі співавт. [12], загалом при ендопротезуванні в 77 пацієнтів із пухлинним ураженням інфекційні ускладнення становили 32 %, у 17 % із цих хворих виконані ампутації. Нестабільність ендопротеза є другим частим ускладненням ендопротезування кісток та суглобів. Майже в половині випадків (44–47 %) причиною ревізійної операції є механічна нестабільність імплантату [13]. Автори [14] повідомляють, що причиною ускладнень є: великий обсяг резекції кістки, висічення м’язів, фасціально-сухожильних утворень та значна травматичність. 10-річне виживання ендопротезів дистального суглобового кінця стегнової кістки зменшується з 94 до 49 %, якщо сегмент, що резецюється, більше 40 % довжини стегнової кістки.
Після ендопротезування колінного суглоба із заміщенням пострезекційних дефектів дистального суглобового кінця стегнової кістки та проксимального суглобового кінця великогомілкової кістки ймовірність ревізійного втручання становить 70 % через 10 років після первинної операції [15].
Після реендопротезування відмічається набагато більший відсоток ускладнень, ніж при первинній процедурі, необхідність повторного втручання після ревізійного реендопротезування виникає в строки до 5 років у 20–56 % випадків [16].
Таким чином, ендопротезування колінного суглоба після видалення пухлин кісток є складним питанням, вирішення якого вимагає удосконалення як імплантів, так і методик їх встановлення. У даній статті ми наводимо строки виникнення ускладнень після ендопротезування колінного суглоба з приводу пухлин кісток і проводимо їх аналіз із метою зменшення кількості післяопераційних ускладнень та рецидивів пухлини та удосконалення технології ендопротезування.
Мета дослідження: на основі аналізу результатів лікування хворих на місцевоагресивні та злоякісні пухлини кісток виявити фактори, що призводять до післяопераційних ускладнень при ендопротезуванні колінного суглоба, та визначити методики корекції цих ускладнень.
Матеріали та методи
Проводилося клінічне спостереження за 72 хворими на місцевоагресивні та злоякісні пухлини кісток, яким виконано ендопротезування колінного суглоба. Для морфологічної ідентифікації пухлин при проведенні даного дослідження ми користувались гістологічними класифікаціями первинних пухлин та пухлиноподібних уражень кісток і м’яких тканин, запропонованими Всесвітньою організацією охорони здоров’я (ВООЗ) (6-те видання, 2002) та клінічними класифікаціями пухлин кісток та м’яких тканин за системою TNM, ВООЗ (6-те видання, 2002).
Для вивчення ефективності розроблених методів комбінованого та комплексного лікування досліджувались однотипні групи хворих за основними прогностичними показниками (вік, стать хворих, гістологічна будова новоутворення, стадія пухлинного процесу). У табл. 1 наведений розподіл пацієнтів за віком та статтю.
53 (73,61 %) пацієнти були віком до 39 років. Середній вік хворих становив 26,9 ± 1,25 року.
За локалізацією пухлини в кістках, які формують колінний суглоб, розподіл пацієнтів був таким (табл. 2).
Частіше пухлина розташовувалась у дистальному відділі стегнової кістки — 45 (62,5 %) пацієнтів, у проксимальному відділі великогомілкової кістки — 27 (37,5 %) пацієнтів.
Розподіл хворих за гістологічними формами пухлин та статтю наведений у табл. 3.
Найчастіше операції ендопротезування виконувалися у хворих з остеогенною саркомою — 26 (36,11 %) та у хворих із гігантоклітинною пухлиною кістки — 26 (36,11 %), рідше — у хворих із хондросаркомою різного ступеня зрілості — 7 (9,72 %). Решта гістологічних варіантів пухлин зустрічалася рідше з різною частотою.
Розподіл хворих на пухлини кісток за гістологічними формами і стадією пухлинного процесу наведений у табл. 4.
Найчастіше прооперовані хворі були з ІІБ стадією пухлинного процесу — 30 пацієнтів, ІІА стадія пухлинного процесу була встановлена у 11 паці-єнтів.
Пацієнти, яким виконано ендопротезування колінного суглоба, були розподілені на дві групи: основну групу (n = 31) становили пацієнти, яким було виконано ендопротезування колінного суглоба з використанням модульних онкологічних ендопротезів Stryker (США) і Valdemar Link (Німеччина), контрольну групу (n = 41) становили пацієнти, яким було виконано ендопротезування колінного суглоба з використанням індивідуальних онкологічних ендопротезів «Інмед» (Україна) та Beznoska (Чехія). За час роботи ми імплантували 72 ендопротези колінного суглоба, із них індивідуальних онкологічних ендопротезів «Інмед» (Україна) — 40 та Beznoska (Чехія) — 1, модульних онкологічних ендопротезів «Вальдемар Лінк» (Німеччина) — 22 та «Страйкер» (США) — 9.
Розподіл хворих на пухлини кісток за нозологічною формою та за локалізацією пухлини в дослідній групі наведений у табл. 5.
Розподіл хворих на пухлини кісток за гістологічною формою та за локалізацією пухлини в контрольній групі наведений у табл. 6.
Передопераційне обстеження хворих включало клінічне та рентгенологічне (рентгенографія, комп’ютерна томографія, магнітно-резонансна томографія) обстеження, обов’язково проводилась трепан- або відкрита біопсія ураженого сегмента кістки з метою верифікації процесу, а також визначення протяжності ураження кістки з метою визначення довжини резекції сегмента кістки та розрахунок розмірів ендопротеза за даними рентгенографії, комп’ютерної томографії чи магнітно-резонансної томографії ураженої кістки.
/28.jpg)
При ендопротезуванні колінного суглоба були дотримані основні принципи онкохірургії — футлярність та абластичність: резекція кістки виконувалася на достатньому (5–6 см) віддаленні від пухлини, видаляли en bloc зону біопсії, що передувала ендопротезуванню, і всі вогнища потенційної дисемінації; виконувалась адекватна м’язова пластика, ендопротез вкривали м’якими тканинами або полімерною тубою фірми Mutars Implantcast (Німеччина), яка служить як чохол для укриття металевої частини ендопротеза, що сприяє зниженню ризику інфікування і дозволяє фіксувати прилеглі до неї м’язи, що прискорює відновлення функції кінцівки.
На рис. 1–4 наведений хід операції з приводу ендопротезування колінного суглоба при ураженні пухлиною дистального відділу стегнової кістки.
У 17 (23,61 %) хворих до операції відзначався патологічний перелом кістки на тлі пухлинного ураження, що в чималому ступені ускладнювало перед-операційне обстеження та створювало додаткові технічні складності під час операції і при подальшій реабілітації.
10 (13,89 %) пацієнтам до операції ендопротезування колінного суглоба за місцем проживання були виконані різноманітні хірургічні втручання (кістково-пластичні операції з використанням авто- та алотрансплантатів, керамічного матеріалу на основі гідроксіапатиту та трикальційфосфату, матеріалу на основі біоактивного скла — біокомпозиту, різні види металоостеосинтезу), що теж мало значення в розвитку післяопераційних ускладнень.
37 (51,39 %) хворим у передопераційному та післяопераційному періоді були проведені курси внутрішньоартеріальної або внутрішньовенної поліхіміотерапії, а 7 (9,72 %) пацієнтам у передопераційному періоді проведений курс променевої терапії до сумарної вогнищевої дози 40 Грей, що також відігравало роль у розвитку післяопераційних ускладнень.
Результати та обговорення
У результаті ендопротезування колінного суглоба післяопераційні ускладнення виявлено в 33 (45,8 %) пацієнтів. Строки виникнення ускладнень після операцій ендопротезування колінного суглоба у хворих на пухлини кісток наведені в табл. 7.
/29_2.jpg)
Інфекційні ускладнення спостерігалися у 2 (6,5 %) хворих дослідної групи у строки: в 1 випадку — до місяця (ранній післяопераційний період), а в іншому — через 24 місяці. Інфекційні ускладнення в 11 (26,8 %) хворих контрольної групи відмічалися в різні строки після ендопротезування: у 6 (14,6 %) хворих вони розвинулися в ранньому післяопераційному періоді до 1 місяця, у 2 випадках спостерігалися через 3 місяці після ендопротезування, в 1 — через 9 місяців, в 1 — через 11 місяців і в 1 — через 17 місяців. З отриманих нами даних, на наш погляд, важливим є те, що з 13 інфекційних ускладнень в обох групах хворих 7 розвинулися в ранньому післяопераційному періоді, що говорить про асептику та антисептику під час хірургічного втручання. Таким чином, всі гнійно-запальні процеси можна розділити на ранні, які розвинулися протягом першого місяця після операції, у нашому дослідженні їх було 7, і пізні, які розвинулися в більш віддалені терміни, їх було 6. Середній строк, за який відбувався розвиток інфекційних ускладнень, становив 5,8 ± 1,4 місяця. Інфекційні ускладнення, як правило, обумовлені асептикою та антисептикою під час хірургічного втручання, у всіх випадках застосовано поетапне реендопротезування суглоба.
Асептичне розхитування ніжки ендопротеза — ускладнення, що спостерігалося в 7 (22,6 %) хворих дослідної групи. У 1 пацієнта воно розвинулося через 11 місяців, у 1 хворого — через 13 місяців, у 2 хворих — через 24 місяці, у 2 — через 27 та 36 місяців. У 5 (12,2 %) хворих контрольної групи асептичне розхитування ніжки ендопротеза розвинулося через 5, 9, 13, 22, 30 місяців. Асептичне розхитування ніжки ендопротеза пояснюється технічними похибками при ендопротезуванні, біомеханічним навантаженням на кістку та кістковий цемент, що призводить до мікротріщин у кістковому цементі, зціплення кісткового цементу з кісткою зменшується, і як наслідок — відбувається розхитування ніжки ендопротеза. У всіх випадках застосоване реендопротезування суглоба.
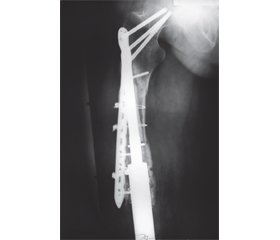
Перелом кістки в місці імплантації ніжки ендопротеза спостерігався у 5 (12,2 %) хворих конт-рольної групи в строки 13, 19, 22, 27, 33 місяці, з яких перелом великогомілкової кістки відбувся у 3 пацієнтів та перелом стегнової кістки — у 2 пацієнтів. У хворих дослідної групи переломів кісток у місці імплантації ніжки ендопротеза не спостерігалося. Переломи кістки в місці імплантації ніжки ендопротеза можна пояснити неадекватним навантаженням на кістку та остеопорозом кістки, що розвинувся за наявності кісткового цементу. У всіх випадках застосовано металоостеосинтез перелому накістковими пластинами та проволочними серкляжами.
Руйнування конструкції ендопротеза спостерігалося у 2 (4,9 %) хворих контрольної групи в строки 17 та 24 місяці та в 1 (3,2 %) хворого дослідної групи в 13 місяців. Як видно, ці ускладнення відмічалися у хворих протягом другого року після операції. Руйнування конструкцій ендопротезів пояснюються технічними помилками при їх виготовленні та дефектами конструкції ендопротеза. У даних випадках застосовано реендопротезування з частковою або повною заміною конструкції ендопротеза.
На рис. 5 наведений фотовідбиток рентгенограми хворого М. — перелом кістки в місці імплантації ніжки ендопротеза «Інмед».
Рецидиви пухлини спостерігалися у 7 хворих: у 4 (12,9 %) пацієнтів дослідної групи та 3 (7,3 %) — контрольної групи.
При рецидивах пухлини після ендопротезування було виконано у 5 випадках видалення рецидиву пухлини та у 2 випадках ампутацію кінцівки.
Висновки
1. Проведений аналіз ендопротезування колінного суглоба у хворих на пухлини кісток показав, що з ускладнень переважали інфекційні процеси, які становили 18,0 %, та асептичне розхитування ніжки ендопротеза — 16,7 %.
2. При інфекційних ускладненнях переважали ранні ускладнення, при асептичному розхитуванні ніжки ендопротеза, переломі кістки в місці імплантації ніжки ендопротеза, руйнуванні конструкції ендопротеза — пізні.
3. Основною методикою виправлення ускладнень при інфекційних процесах є правильна антибіотикопрофілактика, а також вчасна її корекція та ведення післяопераційної рани. При асептичній нестабільності компонентів ендопротеза та руйнуванні конструкції ендопротеза методикою виправлення є реендопротезування, при переломах кістки в місці імплантації ніжки ендопротеза методикою виправлення є металоостеосинтез перелому накістковими пластинами та проволочними серкляжами.
4. Із метою зниження рецидивів пухлини максимальні зусилля мають бути зосереджені на ранньому виявленні пухлинного ураження, широкому хірургічному видаленні пухлини за правилами абластичності та футлярності, подальшому адекватному лікуванні та вчасному моніторингу за пацієнтом.
Конфлікт інтересів. Автори заявляють про відсутність конфлікту інтересів та власної фінансової зацікавленості при підготовці даної статті.
Отримано/Received 20.07.2022
Рецензовано/Revised 07.08.2022
Прийнято до друку/Accepted 21.08.2022
Список литературы
1. Morii T., Yabe H., Morioka H., Beppu Y., Chuman H., Kawai A., Takeda K., Kikuta K., Hosaka S., Yazawa Y., Takeuchi K., Anazawa U., Mochizuki K., Satomi K. Postoperative deep infection in tumor endoprosthesis reconstruction around the knee. J. Orthop. Sci. 2010 May. 15(3). 331-9. doi: 10.1007/s00776-010-1467-z. Epub 2010 Jun 18. PMID: 20559801.
2. Martin A.J., Seagers K.A., Van Citters D.W. Assessment of Corrosion, Fretting, and Material Loss of Retrieved Modular Total Knee Arthroplasties. J. Arthroplasty. 2017 Jul. 32(7). 2279-2284. doi: 10.1016/j.arth.2017.02.047. Epub 2017 Feb 28. PMID: 28343824.
3. Mazaleyrat M., Le Nail L.R., Auberger G., Biau D., Rosset P., Waast D., Gouin F., Bonnevialle P., Ehlinger M., Pasquier G., Vaz G.; French Society of Orthopedic Surgery, Traumatology (SОFCOT). Survival and complications in hinged knee reconstruction prostheses after distal femoral or proximal tibial tumor resection: A retrospective study of 161 cases. Orthop. Traumatol. Surg. Res. 2020 May. 106(3). 403-407. doi: 10.1016/j.otsr.2019.11.027. Epub 2020 Apr 8. PMID: 32276844.
4. Bickels J., Wittig J.C., Kollender Y., Henshaw R.M., Kellar-Graney K.L., Meller I., Malawer M.M. Distal femur resection with endoprosthetic reconstruction: a long-term followup study. Clin. Orthop. 2002. 400. 225-35.
5. Li D., Ma H., Zhang W., Sun C., Lu X., Gao Y., Zhou D. [Analysis of implant-related complications after hinge knee replacement for tumors around the knee]. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2015 Aug. 29(8). 936-40. Chinese. PMID: 26677612.
6. Li Y., Xu H., Shan H., Sun Y., Huang Z., Niu X. [Non-cemented modular prosthetic reconstruction for bone defect after tumor resection in lower extremities]. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2019 Sep 15. 33(9). 1108-1115. Chinese. doi: 10.7507/1002-1892.201904057. PMID: 31512451; PMCID: PMC8355860.
7. Niimi R., Matsumine A., Hamaguchi T., Nakamura T., Uchida A., Sudo A. Prosthetic limb salvage surgery for bone and soft tissue tumors around the knee. Oncol. Rep. 2012 Dec. 28(6). 1984-90. doi: 10.3892/or.2012.2021. Epub 2012 Sep 11. PMID: 22965383.
8. Gerrand C.H., Bell R.S., Griffin A.M., Wunder J.S. Instability after major tumor resection: prevention and treatment. Orthop. Clin. North Am. 2001 Oct. 32(4). 697-710, ix-x. doi: 10.1016/s0030-5898(05)70238-8. PMID: 11689381.
9. Bus M.P., van de Sande M.A., Fiocco M., Schaap G.R., Bramer J.A., Dijkstra P.D. What Are the Long-term Results of MUTARS® Modular Endoprostheses for Reconstruction of Tumor Resection of the Distal Femur and Proximal Tibia? Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2017 Mar. 475(3). 708-718. doi: 10.1007/s11999-015-4644-8. Erratum in: Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2017 Mar. 475(3). 922. PMID: 26649558; PMCID: PMC5289150.
10. Jones K.B., Buckwalter J.A. Severe periprosthetic cortical atrophy in the skeletally immature: a report of three cases. Iowa Orthop. J. 2005. 25. 75-81.
11. Mercuri M., Capanna R., Manfrini M., Bacci G., Picci P., Ruggieri P., Ferruzzi A., Ferraro A., Donati D., Biagini R. et al. The management of malignant bone tumors in children and adolescents. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1991 Mar. 264. 156-68. PMID: 1997230.
12. Windhager R., Leithner A., Hochegger M. Wechsel von Tumorendoprothesen des Kniegelenks. Review und eigene Ergebnisse [Revision of tumour endoprostheses around the knee joint. Review and own results]. Orthopade. 2006 Feb. 35(2). 176-83. German. doi: 10.1007/s00132-005-0913-7. PMID: 16369846.
13. Wang L., Wu X., Wang S., Shi Y. [Ilizarov technique for treatment of infection after limb salvage operation of primary bone tumor]. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2016 Dec 8. 30(12). 1452-1456. Chinese. doi: 10.7507/1002-1892.20160301. PMID: 29786332.
14. Ogura K., Fujiwara T., Morris C.D., Boland P.J., Hea-ley J.H. Long-term competing risks for overall and cause-specific failure of rotating-hinge distal femoral arthroplasty for tumour reconstruction. Bone Joint J. 2021 Aug. 103-B(8). 1405-1413. doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.103B8.BJJ-2020-2323.R1. PMID: 34334040.
15. Kito M., Okamoto M., Aoki K., Tanaka A., Koma-tsu Y., Suzuki S., Takazawa A., Yoshimura Y., Takahashi J. Distal femoral impaction bone grafting in revision for tumor endoprosthesis. Knee. 2021 Mar. 29. 42-48. doi: 10.1016/j.knee.2021.01.016. Epub 2021 Feb 4. PMID: 33548830.
16. Eckardt J.J., Kabo J.M., Kelley C.M., Ward W.G. Sr, Asavamongkolkul A., Wirganowicz P.Z., Yang R.S., Eilber F.R. Expandable endoprosthesis reconstruction in skeletally immature patients with tumors. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2000 Apr. 373. 51-61. doi: 10.1097/00003086-200004000-00008. PMID: 10810462.
/29.jpg)

/25.jpg)
/26.jpg)
/27.jpg)
/28.jpg)
/28_2.jpg)
/30.jpg)
/29_2.jpg)