Журнал «Здоровье ребенка» Том 17, №6, 2022
Вернуться к номеру
Сучасні моделі харчової поведінки у дітей
Авторы: Стоєва Т.В. (1), Джагіашвілі О.В. (1), Прохорова С.В. (1), Годлевська Т.Л. (1), Ларіонов О.П. (2), Стуканова С.Г. (3)
(1) — Одеський національний медичний університет МОЗ України, м. Одеса, Україна
(2) — ДЗ «Український медичний центр реабілітації матері та дитини» МОЗ України, м. Одеса, Україна
(3) — КНП «Дитячий консультативно-діагностичний центр ім. Б.Я. Резніка» ОМР, м. Одеса, Україна
Рубрики: Педиатрия/Неонатология
Разделы: Клинические исследования
Версия для печати
Актуальність. Проблемі харчування як ключовому фактору у впливі на стан здоров’я та розвиток дитини останніми роками приділяється все більше уваги. Порушення формування харчової поведінки можуть виявлятися вже у ранньому дитячому віці, починаючи із періоду новонародженості. Мета: вивчення сучасних моделей харчової поведінки у дітей з урахуванням вікового аспекту. Матеріали та методи. Методом анкетування обстежено 138 дітей віком від 6 місяців до 12 років. Обстеження було анонімним та передбачало використання оригінальної анкети для батьків, у яку увійшло 70 питань. Результати. Під час дослідження оцінено особливості харчової поведінки у дітей різного віку. У періоді новонародженості проаналізовано 5 основних типів харчової поведінки, які відрізнялися за характером смоктання, та простежений зв’язок із подальшим розвитком функціональних розладів травної системи. У дітей раннього віку встановлено 3 основні типи порушення харчової поведінки — режимні порушення, функціональні гастроінтестинальні розлади, раннє припинення грудного вигодовування. Особливості харчування у перші 1000 днів характеризувалися наявністю у третини дітей капризів, використанням розваг під час їжі, відмовою від їжі у належний час. У дітей старшого віку неабиякий вплив на становлення харчової поведінки справляли загальні характеристики раціону, родинні харчові пріоритети та звичаї, а також соціокультурний та освітній рівень сім’ї. Висновки. Виділення сучасних моделей харчування з урахуванням вікового аспекту та сукупності факторів, що впливають на становлення, розвиток та виникнення відхилень харчової поведінки, дозволяє своєчасно запобігти розвитку патологічних станів та визначати подальшу тактику лікаря у формуванні здорових харчових звичок.
Background. Nowadays, increasingly greater attention is paid to the problem of nutrition as a key factor in influencing a child’s health and development. Eating disorders can be observed already in early childhood, from the newborn period. Purpose: to study the modern patterns of eating behavior in children taking into account the age aspect. Material and methods. One hundred and thirty-eight children aged 6 months to 12 years were examined. The examination was anonymous and involved the use of the original questionnaire for parents, which consisted of 70 questions. Results. During the study, the peculiarities of eating behavior in children of different age were evaluated. In the newborn period, 5 main types of eating behavior were analyzed, which differed by the breastfeeding act, and there was a connection with the further development of functional digestive disorders. In infants, 3 main groups of eating disorders have been detected: regime disorders, functional gastrointestinal disorders, early termination of breastfeeding. Eating habits within the first 1,000 days were characterized by naughtiness in a third of children, the use of entertainment during meals, refusal to eat at the proper time. In older children, the general characteristics of the diet, family food habits and taste preferences, as well as the family’s cultural and educational level had a considerable influence on the formation of eating behavior. Conclusions. The identification of modern nutritional patterns, taking into account the age aspect and the set of factors affecting the formation, development and occurrence of eating behavior deviations, allows timely preventing the development of pathological conditions and determining the further approaches to the formation of healthy eating habits.
діти; харчування; харчова поведінка
children; nutrition; eating behavior
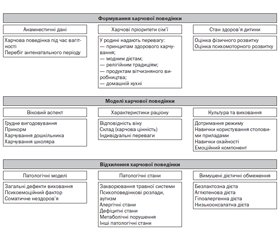
Вступ
Матеріали та методи
Результати та обговорення
/15.jpg)
Висновки
- Niankovskyi S.L., Yatsula M.S., Tytusa A.V. Osoblyvosti kharchovoi povedinky ta kharchuvannia shkoliariv u pochatkovii shkoli. Zdorov’ia Ukrainy. 2020. 2 (53). Tematychnyi nomer. 14–16. https://health-ua.com/article/60215-osoblivost-harchovo-povednki-ta-harchuvannya-shkolyarv-u-pochatkovj-shkol.
- Haines J., Haycraft E., Lytle L., et al. Nurturing Children’s Healthy Eating: Position statement. Appetite. 2019. 137. 124-133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.appet.2019.02.007.
- Martinez-Avila W.D., Sanchez-Delgado G., Acosta F.M., et al. Eating Behavior, Physical Activity and Exercise Training: A Randomized Controlled Trial in Young Healthy Adults. Nutrients. 2020. 12. 3685. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12123685.
- Hughes S.O., Power T.G., O’Connor T.M., Fisher J.O., Micheli N.E., Papaioannou M.A. Maternal feeding style and child weight status among Hispanic families with lowincome levels: a longitudinal study of the direction of effects. The International Journal оf Behavioral Nutrition аnd Physical Activity. 2021. 18 (1). 30. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12966-021-01094-y.
- Kracht C.L., Sisson S.B., Guseman E.H., Hubbs-Tait L., Arnold S.H., Graef J., Knehans A. Family Eating Behavior and Child Eating Patterns Differences Between Children With and Without Siblings. J. Nutr. Educ. Behav. 2019. 51(10). 1188-1193. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jneb.2019.08.004.
- Stoieva T., Scherbak I., Bratkova L., Тitkova O., Soboleva K., Krylov E., Scherbak I. Cerebral intestinal interaction in children with autism spectrum disorder. Child’s Health. 2022. 17(1). 11-17. https://doi.org/10.22141/2224-0551.17.1.2022.1486.
- Dovey T.M., Kumari V., Blissett J., Mealtime Hostage Parent Science Gang. Eating behaviour, behavioural problems and sensory profiles of children with avoidant/restrictive food intake disorder (ARFID), autistic spectrum disorders or picky eating: Same or different? European psychiatry: the journal of the Association of European Psychiatrists. 2019. 61. 56-62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eurpsy.2019.06.008.
- Yap C.X., Henders A.K., Alvares G.A., et al. Autism-related dietary preferences mediate autism-gut microbiome associations. 2021. Cell. 184(24). 5916-5931.e17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2021.10.015.
- Thomas R., Siliquini R., Hillegers M.H., Jansen P.W. The association of adverse life events with children’s emotional overeating and restrained eating in a population based cohort. The International Journal оf Eating Disorders. 2020. 53(10). 1709-1718. https://doi.org/10.1002/eat.23351.
- Frounfelker R.L., Islam N., Falcone J.A., et al. Living through war: Mental health of children and youth in conflict-affected areas. International Review of the Red Cross. 2019. 101, 481-506. https://doi:10.1017/S181638312000017X.
- Di Chio T., Sokollik C., Peroni D.G., Hart L., Simonetti G., Righini-Grunder F., Borrelli O. Nutritional Aspects of Pediatric Gastrointestinal Diseases. Nutrients. 2021. 13(6). 2109. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13062109.
- Person H., Keefer L. Psychological comorbidity in gastrointestinal diseases: Update on the brain-gut-microbiome axis. Progress in Neuro-Psychopharmacology & Biological Psychiatry. 2021. 107. 110209. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pnpbp.2020.110209.
- Baaleman D.F., Velasco-Benítez C.A., Méndez-Guzmán L.M., Benninga M.A., Saps M. Functional gastrointestinal disorders in children: agreement between Rome III and Rome IV diagnoses. European Journal оf Pediatrics. 2021. 180(7). 2297-2303. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00431-021-04013-2.
- Pietrobelli A., Agosti M., MeNu Group. Nutrition in the First 1000 Days: Ten Practices to Minimize Obesity Emerging from Published Science. International Journal оf Environmental Research аnd Public Health. 2017. 14(12). 1491. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph14121491.
- Löffler A., Luck T., Then F.S., et al. Effects of psychological eating behaviour domains on the association between socio-economic status and BMI. Public Health Nutrition. 2017. 20.(15). 2706-2712. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1368980017001653.
- Milano K., Chatoor I., Kerzner B. A Functional Approach to Feeding Difficulties in Children. Curr. Gastroenterol. Rep. 2019. 23. 21(10). 51. doi:10.1007/s11894-019-0719-0.
- Glasper E.A. Promoting Optimum Nutrition During Infancy. Comprehensive child and adolescent nursing. 2019. 42(4). 241-245. doi.org/10.1080/24694193.2019.1683381.
- Lau C. Development of Suck and Swallow Mechanisms in Infants. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2015. 66(5). 7-14. doi: 10.1159/000381361.
- Mizuno K., Fujimaki K., Sawada M. Sucking behavior at breast during the early newborn period affects later breast-feeding rate and duration of breast-feeding. Pediatrics International. 2004. 46. 15-20. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1442-200X.2004.01834.x
- Lutter C.K., Grummer-Strawn L., Rogers L. Complementary feeding of infants and young children 6 to 23 months of age. Nutrition Reviews. 2021. 79(8). 825-846. https://doi.org/10.1093/nutrit/nuaa143.
- Sandhi A., Lee G.T., Chipojola R., Huda M.H., Kuo S.Y. The relationship between perceived milk supply and exclusive breastfeeding during the first six months postpartum: a cross-sectional study. Int. Breastfeed J. 2020. 17. 15(1). 65. doi: 10.1186/s13006-020-00310-y.
- Omar O.M., Massoud M.N., Ibrahim A.G., Khalaf N.A. Effect of early feeding practices and eating behaviors on body composition in primary school children. World J. Pediatr. 2022. 18(9). 613-623. doi: 10.1007/s12519-022-00559-9.
- Lopez N.V., Schembre S., Belcher B.R., et al. Parenting styles, foodrelated parenting practices, and children’s healthy eating: A mediation analysis to examine relationships between parenting and child diet. Appetite. 2018. 128. 205-213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.appet.2018.06.021.
- Mahmood L., Flores-Barrantes P., Moreno L.A., Manios Y., Gonzalez-Gil E.M. The Influence of Parental Dietary Behaviors and Practices on Children’s Eating Habits. Nutrients. 2021. 13. 1138.
- Sorokman T.V., Lozyuk I.Ya. Eating behavior and nutrition characteristics of preschool children. Modern Pediatrics. Ukraine. 2021. 5(117). 2934. doi: 10.15574/SP.2021.117.29.

/16.jpg)