Международный эндокринологический журнал Том 18, №8, 2022
Вернуться к номеру
Взаємозв’язок між вмістом вітаміну D і розвитком діабетичної ретинопатії у хворих на цукровий діабет 2-го типу
Авторы: V.I. Pankiv (1), T.Yu. Yuzvenko (1), N.V. Pashkovska (2), I.V. Pankiv (2)
(1) — Ukrainian Research and Practical Centre of Endocrine Surgery, Transplantations of Endocrine Organs and Tissues of the Ministry of Health of Ukraine, Kyiv, Ukraine
(2) — Bukovinian State Medical University, Chernivtsi, Ukraine
Рубрики: Эндокринология
Разделы: Клинические исследования
Версия для печати
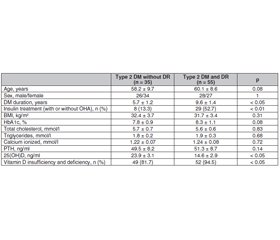
Актуальність. У літературі недостатньо інформації про роль вітаміну D у генезі діабетичної ретинопатії. Активний метаболіт вітаміну D кальцитріол є потужним інгібітором неоваскуляризації сітківки в експериментальній моделі ішемічної ретинопатії. Відсутні дані стосовно можливого взаємозв’язку між вмістом вітаміну D і частотою діабетичної ретинопатії у хворих на цукровий діабет (ЦД) 2-го типу в європейській популяції, у тому числі в Україні. Мета: встановити наявність асоціації між статусом вітаміну D і частотою діабетичної ретинопатії у хворих на ЦД 2-го типу. Матеріали та методи. У спостережному дослідженні типу «випадок — контроль» обстежено дві групи хворих на ЦД 2-го типу: 55 із діабетичною ретинопатією (випадки) і 35 без ретинопатії (контроль). В усіх хворих була нормальна функція нирок (швидкість клубочкової фільтрації > 60 мл/хв, без мікроальбумінурії) за відсутності серцево-судинних ускладнень (інфаркт міокарда, інсульт, ураження периферичних артерій). Пацієнти не отримували препарати кальцію і/або вітаміну D. Результати. Дослідження підтверджує взаємозв’язок між вмістом 25(ОН)D і наявністю діабетичної ретинопатії у хворих на ЦД 2-го типу. У пацієнтів із ретинопатією була вірогідно нижча концентрація 25(ОН)D — 14,6 ± 2,9 нг/мл проти 23,9 ± 3,1 нг/мл в осіб без ретинопатії, р < 0,05. Багатофакторний аналіз підтвердив вірогідний взаємозв’язок між наявністю діабетичної ретинопатії і вмістом 25(OH)D. Висновки. Отримані результати вказують на потенційну роль вітаміну D у патогенезі діабетичної ретинопатії. Необхідні подальші експериментальні й проспективні дослідження, щоб встановити роль статусу вітаміну D у розвитку діабетичної ретинопатії та інших діабетичних мікросудинних уражень.
Background. The literature does not provide enough information about the role of vitamin D in the genesis of diabetic retinopathy. The active metabolite of vitamin D, calcitriol, is a potent retinal neovascularization inhibitor in an experimental model of ischemic retinopathy. There is very few evidence on the possible relationship between the content of vitamin D and the incidence of diabetic retinopathy in type 2 diabetes mellitus (DM) patients in the European population, including Ukraine. The purpose of the study is to establish the association between vitamin D status and the incidence of diabetic retinopathy in patients with type 2 DM. Material and methods. In the case-control observational study, two groups of patients with type 2 DM were examined: 55 with diabetic retinopathy (cases) and 35 without retinopathy (controls). All of them had normal kidney function (glomerular filtration rate > 60 ml/min, without microalbuminuria) in the absence of cardiovascular complications. Patients did not receive calcium and/or vitamin D preparations. Results. The study confirms the relationship between 25(OH)D content and the presence of diabetic retinopathy in patients with type 2 DM. Patients with retinopathy had a significantly lower concentration of 25(OH)D — 14.6 ± 2.9 ng/ml versus 23.9 ± 3.1 ng/ml in patients without retinopathy, p < 0.05. The multivariate analyses demonstrated a significant association of diabetic retinopathy and 25(OH)D. Conclusions. The results indicate the potential role of vitamin D in the pathogenesis of diabetic retinopathy. Further experimental and prospective studies are needed to determine the role of vitamin D status in the development of diabetic retinopathy and other diabetic microvascular complications.
цукровий діабет 2-го типу; діабетична ретинопатія; вітамін D
type 2 diabetes mellitus; diabetic retinopathy; vitamin D
Для ознакомления с полным содержанием статьи необходимо оформить подписку на журнал.
- Mendes M.M., Charlton K., Thakur S., Ribeiro H., Lanham-New S.A. Future perspectives in addressing the global issue of vitamin D deficiency. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2020. 79(2). 246-251. doi: 10.1017/S0029665119001538.
- Charoenngam N., Holick M.F. Immunologic Effects of Vitamin D on Human Health and Disease. Nutrients. 2020. 12(7). 2097. doi: 10.3390/nu12072097.
- Marazziti D., Parra E., Palermo S., Barberi F.M., Buccianelli B., Ricciardulli S., Cappelli A., Mucci F., Dell’Osso L. Vitamin D: A Pleiotropic Hormone with Possible Psychotropic Activities. Curr. Med. Chem. 2021. 28(19). 3843-3864. doi: 10.2174/0929867328666201210104701.
- Ahmed L.H.M., Butler A.E., Dargham S.R., Latif A., Robay A., Chidiac O.M., Jayyousi A., Al Suwaidi J., Crystal R.G., Atkin S.L., Abi Khalil C. Association of vitamin D2 and D3 with type 2 diabetes complications. BMC Endocr. Disord. 2020. 20(1). 65. doi: 10.1186/s12902-020-00549-w.
- Chen J., Gong X., Liu J., Wang T., Shi X., Zhang X., Chen Q. Vitamin D supplementation in the treatment of type 2 diabetic microangiopathy: A protocol for a systematic review and meta-ana–lysis. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020. 99(33). e20978. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000020978.
- Castillo-Otí J.M., Galván-Manso A.I., Callejas-Herrero M.R., Vara-González L.A., Salas-Herrera F., Muñoz-Cacho P. Vitamin D Deficiency Is Significantly Associated with Retinopathy in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Case-Control Study. Nutrients. 2021. 14(1). 84. doi: 10.3390/nu14010084.
- Ashinne B., Rajalakshmi R., Anjana R.M., Narayan K.M.V., Jayashri R., Mohan V., Hendrick A.M. Association of serum vitamin D levels and diabetic retinopathy in Asian Indians with type 2 dia–betes. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2018. 139. 308-313. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2018.02.040.
- Tecilazich F., Formenti A.M., Giustina A. Role of vitamin D in diabetic retinopathy: Pathophysiological and clinical aspects. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2021. 22(4). 715-727. doi: 10.1007/s11154-020-09575-4.
- Luo B.A., Gao F., Qin L.L. The Association between Vitamin D Deficiency and Diabetic Retinopathy in Type 2 Diabetes: A Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies. Nutrients. 2017. 9(3). 307. doi: 10.3390/nu9030307.
- Alcubierre N., Valls J., Rubinat E., Cao G., Esquerda A., Traveset A., Granado-Casas M., Jurjo C., Mauricio D. Vitamin D Deficiency Is Associated with the Presence and Severity of Diabetic Retinopathy in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. J. Diabetes Res. 2015. 2015. 374178. doi: 10.1155/2015/374178.
- Wilkinson C.P., Ferris F.L. III, Klein R.E. et al. Proposed international clinical diabetic retinopathy and diabetic macular edema disease severity scales. Ophthalmology. 2003. 110(9). 1677-1682. doi: 10.1016/S0161-6420(03)00475-5.
- Patrick P.A., Visintainer P.F., Shi Q., Weiss I.A., Brand D.A. Vitamin D and retinopathy in adults with diabetes mellitus. Archives of Ophthalmology. 2012. 130(6). 756-760. doi: 10.1001/archophthalmol.2011.2749.
- Suzuki A., Kotake M., Ono Y. et al. Hypovitaminosis D in type 2 diabetes mellitus: association with microvascular complications and type of treatment. Endocrine Journal. 2006. 53(4). 503-510. doi: 10.1507/endocrj.K06-001.
- Payne J.F., Ray R., Watson D.G., Delille C., Rimler E., Cleveland J. et al. Vitamin D Insufficiency in Diabetic Retinopathy. Endocr. Pract. 2012. 18(2). 185-193. doi: 10.4158/EP11147.OR.
- Aksoy H., Akçay F., Kurtul N., Baykal O., Avci B. Serum 1,25 dihydroxyvitamin D (1,25(OH)2D3), 25 hydroxyvitamin D (25(OH)D) and parathormone levels in diabetic retinopathy. Clinical Biochemistry. 2000. 33(1). 47-51. doi: 10.1016/S0009-9120(99)00085-5.
- Ahmadieh H., Azar S.T., Lakkis N., Arabi A. Hypovitamino–sis D in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a relation to disease control and complications. ISRN Endocrinology. 2013. 2013. Article ID 641098. doi: 10.1155/2013/641098.
- He R., Shen J., Liu F. et al. Vitamin D deficiency increases the risk of retinopathy in Chinese patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetic Medicine. 2014. 31(12). 1657-1664. doi: 10.1111/dme.12581.
- Jee D., Han K.D., Kim E.C., Vavvas D. Inverse association between high blood 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels and diabetic retino–pathy in a representative Korean population. PLoS ONE. 2014. 9(12). Article ID e115199. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0115199.