Международный эндокринологический журнал Том 18, №8, 2022
Вернуться к номеру
Особливості менеджменту предіабету в підлітків з надмірною масою тіла й ожирінням
Авторы: Паньків В.І.
Український науково-практичний центр ендокринної хірургії, трансплантації ендокринних органів
і тканин МОЗ України, м. Київ, Україна
Рубрики: Эндокринология
Разделы: Клинические исследования
Версия для печати
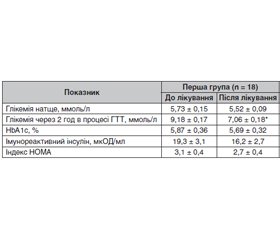
Актуальність. Цукровий діабет 2-го типу (ЦД2) у дитячому й підлітковому віці — відносно нове захворювання. До 1980 р. єдиною формою ЦД у дітей і підлітків вважався ЦД 1-го типу (ЦД1). У даний час кількість дітей, які страждають від ЦД2, у всьому світі щорічно збільшується. Зростання числа підлітків із ЦД2 на тлі надмірної маси тіла й ожиріння зафіксовано і в Україні. Метою дослідження була оцінка ефективності й безпеки дієтичної добавки Сахніл як додаткового комплексу біологічно активних речовин рослинного походження в підлітків з порушенням вуглеводного обміну на тлі надмірної маси тіла й ожиріння. Матеріали та методи. Під спостереженням перебувало 18 підлітків з порушенням толерантності до глюкози (ПТГ) на тлі надмірної маси тіла й ожиріння. Групу контролю становили 20 підлітків з ожирінням, але без порушень вуглеводного обміну. Для пацієнтів із ПТГ критеріями включення до дослідження були: вік на момент встановлення діагнозу 15–18 років, наявність гіперінсулінемії та інсулінорезистентності (за індексом НОМА), надмірної маси тіла й ожиріння. Критерії виключення з дослідження: ЦД1 і моногенні форми ЦД, наявність кетонурії. Результати. У першій і другій групах наприкінці спостереження не відзначалася вірогідного зниження глікемії натще, рівня HbA1c, оскільки ці показники перебували в межах референсних значень. Однак наприкінці лікування в осіб першої групи з ПТГ відзначалося вірогідне зниження рівня глікемії через 2 години після навантаження. Терапія із застосуванням дієтичної добавки Сахніл привела до суттєвого зниження (на 23,1 %; р = 0,01) концентрації глікемії через 2 години після навантаження, що становило 7,06 ± 0,18 ммоль/л. Різниця між групами досягла високої вірогідності (р = 0,01). У процесі спостереження й лікування відзначалася тенденція до зниження рівня імунореактивного інсуліну (з 19,3 ± 3,1 мкОД/мл до 16,2 ± 2,7 мкОД/мл) і величини індексу HOMA (з 3,1 ± 0,4 до 2,7 ± 0,4) у підлітків із ПТГ на тлі надмірної маси тіла й ожиріння. Висновки. Дієтична добавка Сахніл є ефективним засобом для лікування підлітків з порушеною толерантністю до глюкози. Сахніл добре переноситься хворими, не викликає побічних ефектів.
Background. Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) in childhood and adolescence is a relatively new disease. Until 1980, type 1 diabetes was considered the only form of diabetes in children and adolescents. Currently, the number of children suffering from type 2 diabetes is increasing annually worldwide. An increase in the number of adolescents with T2DM against the backdrop of overweight and obesity has also been recorded in Ukraine. The purpose of the study was to evaluate the effectiveness and safety of the dietary supplement Sakhnil as an additional complex of biologically active substances of plant origin in adolescents with impaired carbohydrate metabolism in the presence of overweight and obesity. Materials and methods. Eighteen adolescents with impaired glucose tolerance (IGT) against the background of overweight and obesity were under observation. The control group consisted of 20 obese adolescents without carbohydrate metabolism disorders. For patients with IGT, the criteria for inclusion in the study were: age of 15–18 years at the time of diagnosis, presence of hyperinsulinemia and insulin resistance (according to the Homeostatic Model Assessment for Insulin Resistance (HOMA)), overweight and obesity. Exclusion criteria were: type 1 diabetes and monogenic forms of diabetes, presence of ketonuria. Results. In the first and second groups, by the end of observation, there was no significant decrease in fasting glycemia, HbA1c level, as these indicators were within the reference values. However, at the end of the treatment, the first group with IGT showed a significant decrease in the level of glycemia 2 hours after the load. Therapy with the dietary supplement Sakhnil led to a significant decrease (by 23.1 %, p = 0.01) in glycemia 2 hours after the load, which was 7.06 ± 0.18 mmol/l. The difference between groups reached high reliability (p = 0.01). In the process of observation and treatment, there was a tendency to decrease the level of immunoreactive insulin (from 19.3 ± 3.1 μU/ml to 16.2 ± 2.7) and the value of the HOMA (from 3.1 ± 0.4 to 2.7 ± 0.4) in adolescents with IGT on the background of overweight and obesity. Conclusions. Dietary supplement Sakhnil is an effective remedy for the treatment of adolescents with impaired glucose tolerance. Sakhnil is well tolerated by patients, does not cause side effects.
порушення толерантності до глюкози; ожиріння; підлітки; фітотерапія; Сахніл
impaired glucose tolerance; obesity; adolescents; phytotherapy; Sakhnil
Вступ
Матеріали та методи
Результати
Обговорення
Висновки
- Twig G., Zucker I., Afek A., Cukierman-Yaffe T., Bendor C.D., Derazne E. et al. Adolescent Obesity and Early-Onset Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2020 Jul. 43(7). 1487-1495. doi: 10.2337/dc19-1988. Epub 2020 Apr 22. PMID: 32321731.
- Kumar P., Srivastava S., Mishra P.S., Mooss E.T.K. Prevalence of pre-diabetes/type 2 diabetes among adolescents (10–19 years) and its association with different measures of overweight/obesity in India: a gendered perspective. BMC Endocr. Disord. 2021 Jul 7. 21(1). 146. doi: 10.1186/s12902-021-00802-w. PMID: 34233661; PMCID: PMC8261995.
- Громнацька Н., Лемішко Б., Куля О., Пасічна В. Скринінг метаболічного синдрому в дітей і підлітків. Міжнародний ендокринологічний журнал. 2022. 18(2). 94-99. https://doi.org/10.22141/2224-0721.18.2.2022.1153.
- Serbis A., Giapros V., Kotanidou E.P., Galli-Tsinopoulou A., Siomou E. Diagnosis, treatment and prevention of type 2 diabetes mellitus in children and adolescents. World J. Diabetes. 2021 Apr 15. 12(4). 344-365. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v12.i4.344. PMID: 33889284; PMCID: PMC8040084.
- Kao K.T., Sabin M.A. Type 2 diabetes mellitus in children and adolescents. Aust. Fam. Physician. 2016 Jun. 45(6). 401-6. PMID: 27622231.
- Temneanu O.R., Trandafir L.M., Purcarea M.R. Type 2 dia–betes mellitus in children and adolescents: a relatively new clinical problem within pediatric practice. J. Med. Life. 2016 Jul-Sep. 9(3). 235-239. PMID: 27974926; PMCID: PMC5154306.
- Волошин О., Глубоченко О., Паньків І., Глубоченко В., Малкович Н. Особливості фітотерапії цукрового діабету крізь призму коморбідності й профілактики ускладнень (огляд літератури). Міжнародний ендокринологічний журнал. 2019. 15(3). 258-267. https://doi.org/10.22141/2224-0721.15.3.2019.172113.
- Governa P., Baini G., Borgonetti V., Cettolin G., Giachetti D., Magnano A.R. et al. Phytotherapy in the Management of Diabetes: A Review Molecules. 2018. 23(1). 105. doi: 10.3390/molecules23010105. PMID: 29300317; PMCID: PMC6017385.
- Farzaei F., Morovati M.R., Farjadmand F., Farzaei M.H. A Mechanistic Review on Medicinal Plants Used for Diabetes Mellitus in Traditional Persian Medicine. J. Evid. Based Complementary Altern. Med. 2017. 22(4). 944-955. doi: 10.1177/2156587216686461.
- Di Fabio G., Romanucci V., Zarrelli M., Giordano M., Zarrelli A. C-4 gem-dimethylated oleanes of Gymnema sylvestre and their pharmacological activities. Molecules. 2013. 18(12). 14892-919. doi: 10.3390/molecules181214892. PMID: 24304585; PMCID: PMC6269971.
- Joseph B., Jini D. Antidiabetic effects of Momordica charantia (bitter melon) and its medicinal potency. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Dis. 2013. 3(2). 93-102. doi: 10.1016/S2222-1808(13)60052-3. PMCID: PMC4027280.
- Singh J., Cumming E., Manoharan G., Kalasz H., Adeghate E. Medicinal chemistry of the anti-diabetic effects of momordica charantia: active constituents and modes of actions. Open Med. Chem. J. 2011. 5 (Suppl. 2). 70-7. doi: 10.2174/1874104501105010070.
- Cole T.J., Bellizzi M.C., Flegal K.M., Dietz W.H. Establishing a standard definition for child overweight and obesity worldwide: international survey. BMJ. 2000 May 6. 320(7244). 1240-3. doi: 10.1136/bmj.320.7244.1240. PMID: 10797032; PMCID: PMC27365.
- Baoyi Shao, Saiying Hou, Yuenyan Chan, Changchun Shao, Lixing Lao. Remission of new-onset type 2 diabetes mellitus in an adolescent using an integrative medicine approach: A case report. Journal of Integrative Medicine. 2021. 19(1). 85-88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joim.2020.10.005.
- Bonora E. Postprandial peaks as a risk factor for cardiovascular disease: epidemiological perspectives. Int. J. Clin. Pract. Suppl. 2002. (129). 5-11. PMID: 12166607.
- Pravin Shende, Roma Narvenker. Herbal nanotherapy: A new paradigm over conventional obesity treatment. Journal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology. 2021. 61. 102291. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jddst.2020.102291.

/25.jpg)