Международный эндокринологический журнал Том 19, №1, 2023
Вернуться к номеру
Комбінований вплив поліморфізму генів BDNF (rs6265), VDR (rs2228570) та NMDA (rs4880213) на когнітивні порушення у хворих на автоімунний тиреоїдит та гіпотиреоз
Авторы: I. Kamyshna (1), L. Pavlovych (2), I. Pankiv (2), V. Pankiv (3), V. Maslyanko (2), N. Bytsko (2), A. Kamyshnyi (1)
(1) — I. Horbachevsky Ternopil National Medical University, Ternopil, Ukraine
(2) — Bukovinian State Medical University, Chernivtsi, Ukraine
(3) — Ukrainian Research and Practical Center for Endocrine Surgery, Transplantation of Endocrine Organs
and Tissues of the Ministry of Health of Ukraine, Kyiv, Ukraine
Рубрики: Эндокринология
Разделы: Клинические исследования
Версия для печати
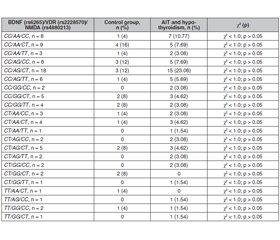
Актуальність. Численні дослідження показали, що захворювання щитоподібної залози можуть впливати на когнітивні функції. Поліморфізм генів, які пов’язані з патологією ендокринної та нервової системи, має етнічну та популяційну специфічність, що визначає необхідність їх вивчення в певному регіоні. Метою дослідження було дослідити комбінований вплив поліморфізму генів BDNF (rs6265), VDR (rs2228570) та NMDA (rs4880213) на когнітивні порушення серед хворих на автоімунний тиреоїдит і гіпотиреоз у популяції західних регіонів України та спрогнозувати виникнення когнітивних розладів. Матеріали та методи. Обстежено 153 особи з автоімунним тиреоїдитом та гіпотиреозом. Генотипування поліморфізму генів VDR (rs2228570), BDNF (rs6265) і NMDA (rs4880213) за допомогою зондів TaqMan і TaqMan Genotyping Master Mix (4371355) виконували в системі CFX96™ Real-Time PCR Detection System (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc., США). Полімеразну ланцюгову реакцію для генотипування TaqMan проводили згідно з інструкцією до набору (Applied Biosystems, США). Когнітивні функції досліджували за допомогою шкали Mini-Mental State Examination. Результати. У носіїв комбінації генотипів CC/AG/CC значно знижений ризик розвитку когнітивних порушень (відношення шансів (ВШ) = 0,1410; 95% довірчий інтервал (ДI) 0,0181–1,0965; p = 0,0416). При цьому носійство комбінації генотипів CT/AG/CT підвищує ризик когнітивних порушень більше ніж у 5 разів (ВШ = 5,1915; 95% ДI 1,2471–21,6107; p = 0,0214), а комбінації генотипів CT/AG/TT (ВШ = 10,1224; 95% ДI 1,1037–92,8401; p = 0,0281) — у 10 разів. Носії комбінації генотипів CT/AA/CT мають в 6,4 раза вищий ризик когнітивних порушень (ВШ = 6,4062; 95% ДI 1,2019–34,1471; p = 0,0253). Висновки. Серед пацієнтів з автоімунним тиреоїдитом і гіпотиреозом носії комбінації генотипів CT/AG/CT, CT/AG/TT і CT/AA/CT мають підвищений ризик розвитку когнітивних порушень, а в носіїв комбінації генотипів СС/АГ/СС генів BDNF (rs6265), VDR (rs2228570) і NMDA (rs4880213) цей ризик знижений.
Background. Numerous studies have demonstrated that thyroid conditions can affect cognitive function. Gene polymorphisms associated with pathology of the endocrine and nervous system have ethnic and population specificity, which determines the need to study them in a certain region. The purpose of the study was to investigate the combined impact of the BDNF (rs6265), VDR (rs2228570), and NMDA (rs4880213) gene polymorphisms on cognitive impairment in patients with autoimmune thyroiditis and hypothyroidism among the population of Western regions of Ukraine, and to predict the onset of cognitive disorders. Materials and methods. The study involved a total of 153 patients with autoimmune thyroiditis and hypothyroidism. Genotyping of the VDR (rs2228570), BDNF (rs6265), and NMDA (rs4880213) gene polymorphism using TaqMan probes and TaqMan Genotyping Master Mix (4371355) was performed on CFX96™ Real-Time PCR Detection System (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc., USA). Polymerase chain reaction for TaqMan genotyping was carried out according to the kit instructions (Applied Biosystems, USA). We detect a decline in cognitive function using the Mini-Mental State Examination. Results. Carrying a combination of CC/AG/CC genotypes significantly reduces the risk of developing cognitive impairment (odds ratio (OR) = 0.1410; 95% confidence interval (CI) 0.0181–1.0965; p = 0.0416). At the same time, carrying a combination of CT/AG/CT genotypes increases the risk of cognitive impairment by more than 5 times (OR = 5.1915; 95% CI 1.2471–21.6107; p = 0.0214) and a combination of CT/AG/TT genotypes — by 10 times (OR = 10.1224; 95% CI 1.1037–92.8401; p = 0.0281). Carriers of the CT/AA/CT genotype combination have a 6.4-fold increased risk of cognitive impairment (OR = 6.4062; 95% CI 1.2019–34.1471; p = 0.0253). Conclusions. Among patients with autoimmune thyroiditis and hypothyroidism, carriers of the CC/AG/CC genotype combination of the BDNF (rs6265), VDR (rs2228570) and NMDA (rs4880213) genes have a reduced risk of developing cognitive disorders, while carriers of the CT/AG/CT, CT/AG/TT and CT/AA/CT have an increased risk of cognitive impairment.
генотип; автоімунний тиреоїдит; гіпотиреоз; когнітивні порушення
genotype; autoimmune thyroiditis; hypothyroidism; cognitive disorders
Для ознакомления с полным содержанием статьи необходимо оформить подписку на журнал.
- Giannocco G., Kizys M.M.L., Maciel R.M., de Souza J.S. Thyroid hormone, gene expression, and central nervous system: where we are. Semin. Cell. Dev. Biol. 2021 Jun. 114. 47-56. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2020.09.007.
- Przybylak M., Grabowski J., Bidzan L. Cognitive functions and thyroid hormones secretion disorders. Psychiatr. Pol. 2021 Apr 30. 55(2). 309-321 (in English, Polish). doi: 10.12740/PP/112470.
- Tang X., Song Z.H., Wang D., Yang J., Augusto Cardoso M., Zhou J.B., Simó R. Spectrum of thyroid dysfunction and dementia: a dose-response meta-analysis of 344,248 individuals from cohort studies. Endocr. Connect. 2021 Apr 22. 10(4). 410-421. doi: 10.1530/EC-21-0047.
- Sydorchuk L., Dzhuryak V., Sydorchuk A., Levytska S., Petrynych V., Knut R., Kshanovska A. et al. The cytochrome 11B2 aldosterone synthase gene rs1799998 single nucleotide polymorphism determines elevated aldosterone, higher blood pressure, and reduced glomerular filtration, especially in diabetic female patients. Endocr. Regul. 2020 Jul 1. 54(3). 217-226. doi: 10.2478/enr-2020-0024.
- Bilous I.I., Pavlovych L.L., Kamyshnyi A.M. Primary hypothyroidism and autoimmune thyroiditis alter the transcriptional activity of genes regulating neurogenesis in the blood of patients. Endocr. Regul. 2021 Jan 29. 55(1). 5-15. doi: 10.2478/enr-2021-0002.
- Garber J.R., Cobin R.H., Gharib H., Hennessey J.V., Klein I., Mechanick J.I., Pessah-Pollack R. et al.; American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists and American Thyroid Association Taskforce on Hypothyroidism in Adults. Clinical practice guidelines for hypothyroidism in adults: cosponsored by the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists and the American Thyroid Association. Endocr. Pract. 2012 Nov-Dec. 18(6). 988-1028. doi: 10.4158/EP12280.GL.
- Arevalo-Rodriguez I., Smailagic N., Roqué-Figuls M., Ciappo–ni A., Sanchez-Perez E., Giannakou A., Pedraza O.L. et al. Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE) for the early detection of dementia in people with mild cognitive impairment (MCI). Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2021 Jul 27. 7(7). CD010783. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010783.pub3.
- Cruz-Flores S. Neurological Complications of Endocrine Emergencies. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 2021 Mar 11. 21(5). 21. doi: 10.1007/s11910-021-01105-2.
- Nicola Marioara O.M., Popescu M., Vlădoianu C.N., Carlig V., Carsote M., Ghenea A.E. Study of Cognitive Disfunctions in Thyroid Pathology. Curr. Health Sci. J. 2021 Apr-Jun. 47(2). 256-262. doi: 10.12865/CHSJ.47.02.16.
- Eslami-Amirabadi M., Sajjadi S.A. The relation between thyroid dysregulation and impaired cognition/behaviour: an integrative review. J. Neuroendocrinol. 2021 Mar. 33(3). e12948. doi: 10.1111/jne.12948.
- Mulat B., Ambelu A., Yitayih S., Gela Y.Y., Adera A., Yeshaw Y., Akalu Y. Cognitive Impairment and Associated Factors Among Adult Hypothyroid Patients in Referral Hospitals, Amhara Region, Ethiopia: Multicenter Cross-Sectional Study. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2021 Mar 25. 17. 935-943. doi: 10.2147/NDT.S299840.
- Khaleghzadeh-Ahangar H., Talebi A., Mohseni-Moghad–dam P. Thyroid Disorders and Development of Cognitive Impairment: A Review Study. Neuroendocrinology. 2022. 112(9). 835-844. doi: 10.1159/000521650.
- Pandey V.P., Singh T., Singh S.K. Verbal Episodic Memory in Young Hypothyroid Patients. Indian J. Endocrinol. Metab. 2017 Nov-Dec. 21(6). 812-814. doi: 10.4103/ijem.IJEM_170_17.
- Notaras M., Hill R., van den Buuse M. The BDNF gene Val66Met polymorphism as a modifier of psychiatric disorder susceptibility: progress and controversy. Mol. Psychiatry. 2015 Aug. 20(8). 916-30. doi: 10.1038/mp.2015.27.
- Gallinat J., Schubert F., Brühl R., Hellweg R., Klär A.A., Kehrer C., Wirth C. et al. Met carriers of BDNF Val66Met genotype show increased N-acetylaspartate concentration in the anterior cingulate cortex. Neuroimage. 2010 Jan 1. 49(1). 767-71. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2009.08.018.
- Mori F., Ribolsi M., Kusayanagi H., Siracusano A., Mantovani V., Marasco E., Bernardi G., Centonze D. Genetic variants of the NMDA receptor influence cortical excitability and plasticity in humans. J. Neurophysiol. 2011 Oct. 106(4). 1637-43. doi: 10.1152/jn.00318.2011.
- Xie X.Q., Cai D.G., Yang Q. Lack of association between BDNF rs6265 polymorphism and risk of type 2 diabetes: a protocol for meta-analysis and trial sequential analysis. Medicine (Baltimore). 2021 Feb 12. 100(6). e23305. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000023305.
- Kamyshna I.I., Pavlovych L.B., Sydorchuk L.P., Malyk I.V., Ka–myshnyi A.M. BDNF blood serum linkage with BDNF gene polymorphism (rs6265) in thyroid pathology patients in the West-Ukrainian population. Endocr. Regul. 2021 Dec 7. 55(4). 193-203. doi: 10.2478/enr-2021-0021.
- Kamyshna I. The role of vitamin D for the management of depression in patients with autoimmune thyroiditis and hypothyroi–dism in the West-Ukrainian population. International Journal of Endocrinology (Ukraine). 2022. 18(4). 208-212. doi: 10.22141/2224-0721.18.4.2022.1173.