Международный эндокринологический журнал Том 19, №2, 2023
Вернуться к номеру
Особливості діагностичного пошуку та досвід лікування хронічної кропивниці у хворих на ожиріння з легеневою патологією
Авторы: N.M. Kaspruk, S.O. Batranovska
Bukovinian State Medical University, Chernivtsi, Ukraine
Рубрики: Эндокринология
Разделы: Клинические исследования
Версия для печати
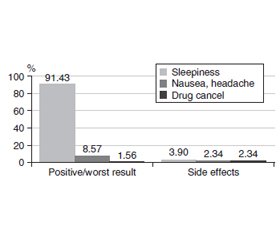
Актуальність. В останні десятиліття поряд із зростанням частоти алергічних захворювань спостерігається прогресуюче збільшення кількості людей із надмірною масою тіла різного ступеня вираженості, про що свідчать численні епідеміологічні дослідження. Тому як алергія, так і ожиріння через їх високу поширеність та медико-соціальну значимість належать до глобальних проблем сучасної охорони здоров’я. Мета: аналіз етіологічних факторів хронічної кропив’янки (ХК) у хворих на ожиріння з легеневою патологією, оптимізація діагностики й лікування ХК для подальшого планування профілактичних заходів. Матеріали та методи. Обстежено 250 пацієнтів, які звернулися за медичною допомогою до обласної клінічної лікарні м. Чернівці з приводу ХК, асоційованої з легеневою патологією та ожирінням. На підставі аналізу отриманих даних сформовано групу зі 140 пацієнтів для подальшого клініко-анамнестичного обстеження: збору анамнезу, визначення ступеня тяжкості кропив’янки, оцінки якості життя, контролю симптомів кропив’янки, загальноклінічних лабораторних досліджень, тестів для верифікації кропив’янки. Алерготестування виконували, коли анамнестичні дані хворого свідчили про його доцільність. Обстеження проводилося протягом одного місяця і включало діагностичний період та 3 консультації кожні 7–10 днів. Результати. Серед причин ХК у пацієнтів пульмонологічного профілю домінують непереносимість лікарських засобів та паразитарна інфекція. Поєднання кількох етіологічних факторів спостерігається в 60 % випадків. Відмінностями ХК у хворих пульмонологічного профілю з ожирінням є тривала персистенція кропив’янки або інших елементів висипки, недостатня ефективність терапії антигістамінними препаратами другого й третього поколінь та глюкокортикостероїдами. Висновки. Отримані результати свідчать про позитивний ефект застосування похідного хінуклідинів хіфенадину при лікуванні ХК у хворих на легеневу патологію та ожиріння. Задовільні ефекти були отримані в 91,43 % пацієнтів. Найгірші результати (8,57 %) зафіксовано в пацієнтів з етіологічним значенням факторів хімічного походження (у тому числі професійних), що пов’язано з більш проблематичним дотриманням режиму елімінації в цієї категорії пацієнтів.
Background. In recent decades, along with the growth of allergic diseases, there has been a progressive increase in the number of people with overweight of varying severity, as evidenced by numerous epidemiological studies. Therefore, both allergies and obesity are among the global problems of modern healthcare due to their high prevalence and medical and social significance. The purpose of the study was analysis of the etiological factors of chronic urticaria (CU) in obese patients with pulmonary pathology, optimization of diagnosis and treatment of CU for further planning of preventive measures. Materials and methods. We examined 250 patients who applied for medical care to the regional clinical hospital in Chernivtsi and had CU associated with pulmonary pathology and obesity. Based on the analysis of the obtained data, a group of 140 patients was formed for further clinical and anamnestic examination: analysis of the anamnesis, determination of the severity of urticaria, assessment of quality of life, control of urticaria symptoms, general clinical laboratory studies, tests for verification of urticaria. Allergy testing was carried out when the patient’s anamnestic data indicated its expediency. The survey was carried out for one month and included a diagnostic period and 3 consultations every 7–10 days. Results. Among the causes of CU in patients with pulmonary disease, drug intolerance and parasitic infection dominate. Polyetiology is observed in 60 % of cases. Differences in CU in obese patients are the long-term persistence of urticaria or other elements of the rash, the lack of effectiveness of therapy with the second- and third-generation antihistamines and glucocorticosteroids. Conclusions. The results obtained indicate a positive effect of the quinuclidine derivative quifenadine for the treatment of CU in patients with pulmonary pathology and obesity. Complete and significant effects were obtained in 91.43 % of patients. The worst results (8.57 %) were demonstrated by patients with the etiological significance of chemical factors (including occupational ones), which is associated with more problematic compliance with the elimination regimen in this category of patients.
легенева патологія; хронічна кропив’янка; ожиріння; хіфенадин
pulmonary pathology; chronic urticaria; obesity; quifenadine
Для ознакомления с полным содержанием статьи необходимо оформить подписку на журнал.
- Gonçalo M., Gimenéz-Arnau A., Al-Ahmad M., Ben-Sho–shan M., Bernstein J.A., Ensina L.F., Fomina D. et al. The global burden of chronic urticaria for the patient and society. Br. J. Dermatol. 2021 Feb. 184(2). 226-236. doi: 10.1111/bjd.19561.
- Radonjic-Hoesli S., Hofmeier K.S., Micaletto S., Schmid-–Grendelmeier P., Bircher A., Simon D. Urticaria and Angioedema: an Update on Classification and Pathogenesis. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2018. 54(1). 88-101. doi: 10.1007/s12016-017-8628-1.
- Duong T.A., Valeyrie-Allanore L., Wolkenstein P., Chosi–dow O. Severe cutaneous adverse reactions to drugs. Lancet. 2017. 390(10106). 1996-2011. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(16)30378-6.
- Foer D., Buchheit K.M., Gargiulo A.R., Lynch D.M., Castells M., Wickner P.G. Progestogen Hypersensitivity in 24 Cases: Diagnosis, Management, and Proposed Renaming and Classification. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2016 Jul-Aug. 4(4). 723-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jaip.2016.03.003.
- Shalom G., Magen E., Babaev M., Tiosano S., Vardy D.A., Linder D., Horev A. et al. Chronic urticaria and the metabolic syndrome: a cross-sectional community-based study of 11 261 patients. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2018 Feb. 32(2). 276-281. doi: 10.1111/jdv.14548.
- Zbiciak-Nylec M., Wcisło-Dziadecka D., Kasprzyk M., Ku–lig A., Laszczak J., Noworyta M., Adamus S. et al. Overweight and obesity may play a role in the pathogenesis of chronic spontaneous urticaria. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2018 Jul. 43(5). 525-528. doi: 10.1111/ced.13368.
- Kaspruk N. Allergic reactions in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus (literature review and own research). International Journal of Endocrinology (Ukraine). 2020. 16(3). 287-291. doi: 10.22141/2224-0721.16.3.2020.205280 (in Ukrainian).
- Peters U., Dixon A.E., Forno E. Obesity and asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018 Apr. 141(4). 1169-1179. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2018.02.004.
- Pedersen H.S.T., Sørensen J.A., Madsen F., Linneberg A., Leth-Møller K.B., Vestergaard C., Thomsen S.F. Prevalence, predictors, and clinical relevance of α-gal sensitization in patients with chronic urticaria. Clin. Transl. Allergy. 2022 Oct. 12(10). e12199. doi: 10.1002/clt2.12199.
- Shahzad Mustafa S., Sánchez-Borges M. Chronic Urticaria: Comparisons of US, European, and Asian Guidelines. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2018 May 24. 18(7). 36. doi: 10.1007/s11882-018-0789-3.
- Dressler C., Werner R.N., Eisert L., Zuberbier T., Nast A., Maurer M. Chronic inducible urticaria: a systematic review of treatment options. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018 May. 141(5). 1726-1734. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2018.01.031.
- Sánchez-Borges M., Capriles-Hulett A., Caballero-Fonseca F., González-Aveledo L. Biomarkers of treatment efficacy in patients with chronic spontaneous urticaria. Eur. Ann. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018 Jan. 50(1). 5-9. doi: 10.23822/eurannaci.1764-1489.24.
- Martina E., Diotallevi F., Bianchelli T., Paolinelli M., Offidani A. Novel Therapeutic Approaches and Targets for Treatment of Chronic Urticaria: New Insights and Promising Targets for a Challen–ging Disease. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2021. 22(1). 32-45. doi: 10.2174/1389201021666200630140137.
- Maurer M., Staubach P., Raap U., Richter-Huhn G., Bauer A., Ruëff F., Jakob T. et al. H1-antihistamine-refractory chro–nic spontaneous urticaria: it’s worse than we thought — first results of the multicenter real-life AWARE study. Clin. Exp. Allergy. 2017 May. 47(5). 684-692. doi: 10.1111/cea.12900.
- Falalyeyeva T., Mamula Y., Scarpellini E., Leshchenko I., Humeniuk A., Pankiv I., Kobyliak N. Probiotics and obesity associated disease: an extended view beyond traditional strains. Minerva Gastroenterol. (Torino). 2021 Dec. 67(4). 348-356. doi: 10.23736/S2724-5985.21.02909-0.