Журнал "Гастроэнтерология" Том 57, №1, 2023
Вернуться к номеру
Ендоскопічні особливості слизової оболонки кишечника у хворих на виразковий коліт залежно від рівня IgG4
Авторы: Степанов Ю.М., Стойкевич М.В., Гайдар Ю.А., Тарасова Т.С., Сімонова О.В., Татарчук О.М., Петішко О.П.
ДУ «Інститут гастроентерології НАМН України», м. Дніпро, Україна
Рубрики: Гастроэнтерология
Разделы: Клинические исследования
Версия для печати
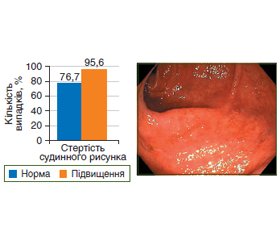
Актуальність. Виразковий коліт має тривалі тяжкі місцеві та системні наслідки, часто рецидивує, що обумовлює актуальність розробки нових діагностичних маркерів скринінгу цієї патології. Мета дослідження: дослідити ендоскопічну картину слизової оболонки товстої кишки при виразковому коліті залежно від вмісту IgG4 у сироватці крові і наявності тканинного IgG4. Матеріали та методи. Обстежено 75 хворих на виразковий коліт, які знаходилися на лікуванні у відділенні захворювань кишечника ДУ «Інститут гастроентерології НАМН України». З них 42 жінки та 33 чоловіки віком від 18 до 69 років, середній вік становив (40,1 ± 1,4) року. Переважна більшість обстежених мали виразковий коліт з перебігом середнього ступеня тяжкості — 54 пацієнти, у 14 хворих було діагностовано тяжкий перебіг і у 7 осіб — легкий перебіг виразкового коліту. Ендоскопічні дослідження товстої кишки проводилися за загальноприйнятими методиками з використанням відеоколоноскопа Olympus EVIS EXERA III (Японія). Усім пацієнтам за допомогою імуноферментного аналізатора Stat Fax 303 Plus (США) визначено рівень IgG4 у сироватці крові згідно з інструкціями для тест-набору реактивів фірми «Хема» (Україна). Контрольну групу становили 15 практично здорових осіб. Наявність IgG4-позитивних плазматичних клітин визначали імуногістохімічним методом, використовували моноклональний кролячий антилюдський IgG4 (Abcam, США). Результати. Підвищення рівня IgG4 понад 1,2 г/л відзначено у 45 пацієнтів. Загалом у хворих на виразковий коліт концентрація IgG4 у сироватці крові була вищою в 2 рази (р < 0,05) порівняно з контрольною групою: 1,50 (0,55; 2,25) г/л проти 0,65 (0,45; 0,80) г/л. У хворих на виразковий коліт підвищення рівня як сироваткового, так і тканинного IgG4 супроводжується збільшенням частоти виявлення ендоскопічних ознак захворювання, у зв’язку з чим ендоскопічна активність 3 ступеня відзначалася в 2 (р < 0,05) та 2,9 раза (р < 0,001) частіше, ніж у хворих з нормальним вмістом IgG4. Висновки. Встановлені кореляційні зв’язки між рівнями сироваткового IgG4 й тканинного IgG4, а також з вираженістю ендоскопічних проявів виразкового коліту обґрунтовують доцільність оцінки рівня IgG4 у крові як неінвазивного маркера прогнозування перебігу цього захворювання.
Background. Ulcerative colitis has long-term severe local and systemic consequences, often recurs which determines the urgency of developing new diagnostic markers for screening this pathology. The purpose of the study: to investigate the endoscopic picture of the colonic mucosa in ulcerative colitis depending on the content of IgG4 in the blood serum and the presence of tissue IgG4. Materials and methods. Seventy-five patients with ulcerative colitis were examined, they were treated at the department of intestinal diseases of the State Institution “Institute of Gastroenterology of the National Academy of Medical Sciences of Ukraine”. Of them, 42 were women and 33 were men aged 18 to 69 years, the average age was (40.1 ± 1.4) years. Most patients (n = 54) had a moderate ulcerative colitis, in 14 patients, the course was severe and 7 people had a mild ulcerative colitis. Endoscopic studies of the colon were performed according to generally accepted methods using the video colonoscope Olympus EVIS EXERA III (Japan). The level of IgG4 in blood serum was evaluated in all patients using the Stat Fax 303 Plus immunoassay analyzer (USA) according to the instructions for the test kit of reagents manufactured by the Xema company (Ukraine). The control group consisted of 15 practically healthy people. The presence of IgG4-positive plasma cells was determined by the immunohistochemical method, using monoclonal rabbit anti-human IgG4 (Abcam, USA). Results. An increase in the level of IgG4 over 1.2 g/l was detected in 45 patients. In general, in patients with ulcerative colitis the concentration of IgG4 in blood serum was 2 times higher (p < 0.05) compared to the control group: 1.50 (0.55; 2.25) g/l versus 0.65 (0.45; 0.80) g/l. Patients with ulcerative colitis had an increase in the level of both serum and tissue IgG4 accompanied by an increase in the frequency of detecting the endoscopic signs of the disease; therefore, endoscopic activity of degree 3 is detected 2 times (p < 0.05) and 2.9 times (p < 0.001) more often than in patients with normal concentration of IgG4. Conclusions. Correlations found between the levels of serum and tissue IgG4, as well as with the severity of endoscopic manifestations of ulcerative colitis substantiate the feasibility of assessing the level of IgG4 in the blood as a non-invasive marker for predicting the course of this disease.
виразковий коліт; діагностика; ендоскопічне дослідження товстої кишки; гуморальний імунітет; IgG4
ulcerative colitis; diagnosis; colon endoscopic examination; humoral immunity; IgG4
Для ознакомления с полным содержанием статьи необходимо оформить подписку на журнал.
- Ulcerative colitis is characterized by a plasmablast-skewed humoral response associated with disease activity / M. Uzzan et al. Nat Med. 2022. Vol. 28. № 4. P. 766-779.
- Integrative computational approach identifies immune-relevant biomarkers in ulcerative colitis / T. He et al. FEBS Open Bio. 2022. Vol. 12. № 2. P. 500-515.
- Lee J.M., Lee K.M. Endoscopic Diagnosis and Differentiation of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Clin Endosc. 2016. Vol. 49. № 4. P. 370-375.
- da Silva B.C., Lyra A.C., Rocha R., Santana G.O. Epidemio–logy, demographic characteristics and prognostic predictors of ulcerative colitis. World J Gastroenterol. 2014. Vol. 20(28). P. 9458-9467.
- Tripathi K., Feuerstein J.D. New developments in ulcerative colitis: latest evidence on management, treatment, and maintenance. Drugs Context. 2019. № 8. P. 212572.
- ECCO-ESGAR Guideline for diagnostic assessment in IBD. Part 2: IBD scores and general principles and technical aspects / A. Sturm et al. J Crohn’s Colitis. 2019. Vol. 13. Issue 3. P. 273-284.
- Vashist M.N., Samaan M., Mosli M.H., Parker C.E. Endoscopic scoring indices for evaluation of disease activity in ulcerative colitis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. 44 р.
- Martín-Nares E., Hernández-Molina G., Baenas D.F., Paira S. IgG4-Related Disease: Mimickers and Diagnostic Pitfalls. J Clin Rheumatol. 2022. Vol. 28. № 2. P. e596-e604.
- Serum IgG4 Subclass Deficiency Defines a Distinct, Commonly Encountered, Severe Inflammatory Bowel Disease Subtype / F. Koutroumpakis et al. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2021. Vol. 27. № 6. P. 855-863.
- Nationwide survey for primary sclerosing cholangitis and IgG4-related sclerosing cholangitis in Japan / A. Tanaka et al. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci. 2014. Vol. 21. № 1. P. 43-50.
- Clinicopathological differential diagnosis of IgG4-related di–sease: A historical overview and a proposal of the criteria for excluding mimickers of IgG4-related disease / A. Satou et al. Pathology International. 2020. Vol. 70. № 7. P. 391-402.
- Comparing the type and severity of inflammatory bowel disease in relation to IgG4 immunohistochemical staining / H.D. Şimşek et al. Acta Gastroenterol Belg. 2016. Vol. 79. № 2. P. 216-221.
- IgG4+ plasma cell infiltration is correlated with the development of inflammatory bowel disease and can be regulated by TLR-4 / X. Chen et al. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2018. Vol. 11. № 9. P. 4537-4544.
- High level of IgG4 as a biomarker for a new subset of inflammatory bowel disease / Z. Wang et al. Sci Rep. 2018. Vol. 8. № 1. P. 10018.
- Serum IgG4 cut-off of 70 mg/dL is associated with a shorter time to cirrhosis decompensation and liver transplantation in primary sclerosing cholangitis patients / F. Peerani et al. Can Liver J. 2022. Vol. 5. № 1. P. 31-42.
- Berberine in the treatment of ulcerative colitis: A possible pathway through Tuft cells / X. Xiong et al. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021. Vol. 134. P. 111129.
- Novel Fecal Biomarkers That Precede Clinical Diagnosis of Ulcerative Colitis / H.J. Galipeau et al. Gastroenterology. 2021. Vol. 160. № 5. P. 1532-1545.
- Rath T., Atreya R., Neurath M.F. Is histological healing a feasible endpoint in ulcerative colitis? Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021. Vol. 15. № 6. P. 665-674.
- Fiorino G., Danese S., Giacobazzi G., Spinelli A. Medical therapy versus surgery in moderate-to-severe ulcerative colitis. Dig Liver Dis. 2021. Vol. 53. № 4. P. 403-408.
- Martínez-Botas J., de la Hoz B. IgE and IgG4 Epitope Mapping of Food Allergens with a Peptide Microarray Immunoassay. Me–thods Mol Biol. 2016. Vol. 1352. P. 235-249.
- Fabián O., Kamaradová K. Morphology of inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD). Cesk Patol. 2022. Vol. 58. № 1. P. 27-37.