Журнал "Гастроэнтерология" Том 57, №2, 2023
Вернуться к номеру
Діагностичне значення показників комп’ютерної морфометрії щодо оцінки стеатозу та фіброзу в пацієнтів із хронічними дифузними захворюваннями печінки різної етіології
Авторы: Yu.M. Stepanov, V.I. Didenko, Yu.A. Gaydar, N.Yu. Zavhorodnia, O.P. Petishko
SI “Institute Gastroenterology of the National Academy of the Medical Sciences of Ukraine”, Dnipro, Ukraine
Рубрики: Гастроэнтерология
Разделы: Клинические исследования
Версия для печати
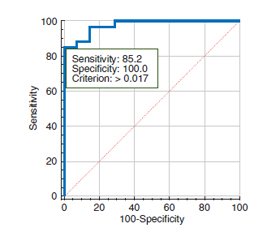
Актуальність. Точна оцінка стадії фіброзу має вирішальне значення для ефективного лікування. Гістологічне дослідження — основний метод, що використовується для оцінки фіброзу печінки, — має певні обмеження через варіації в межах кожної стадії. Комп’ютерна морфометрія пропонує об’єктивний і кількісний підхід для доповнення гістологічного аналізу, надаючи додаткову діагностичну інформацію. Мета дослідження: проаналізувати показники комп’ютерної морфометрії в пацієнтів із хронічними дифузними захворюваннями печінки (ХДЗП) різної етіології та визначити їх діагностичне значення щодо оцінки фіброзу печінки. Матеріали та методи. У дослідження увійшли 75 осіб із ХДЗП, а саме: з неалкогольною жировою хворобою печінки (НАЖХП) — 24 пацієнти; з алкогольною хворобою печінки (АХП) — 8, з токсичним гепатитом — 1, з хронічним гепатитом С (ХГС) — 42. Черезшкірну пункційну біопсію виконували під безперервним ультразвуковим контролем, під місцевою анестезією, напівавтоматичною голкою Colt Shot 16 G. Оцінка стадії фіброзу проводилася за шкалою Metavir. Для комп’ютерної морфометрії біоптати фотографували і здійснювали вимірювання за допомогою програми ImageJ 1.45S (розроблена в National Institutes of Health, USA). Розраховували комп’ютерний індекс фіброзу (КІФ), індекс стеатозу та кількість апоптотично змінених клітин у 5 послідовних полях зору. ROC-аналіз проводили для оцінки діагностичної точності КІФ. Результати. Виражений фіброз печінки (F3-F4) був діагностований у 62,5 % випадків АХП та 31,0 % — ХГС. КІФ печінки є вищим при АХП порівняно як із НАЖХП (у 3,3 раза; р < 0,01), так і з ХГС (у 2 рази; р < 0,05). Водночас індекс стеатозу був найбільший у групі НАЖХП — (0,36 ± 0,11), що в 1,7 раза (р < 0,05) перевищує показники в групах АХП та ХГС. КІФ печінки корелює зі стадією фіброзу (r = 0,71, p < 0,05). Для першої стадії фіброзу печінки за шкалою Metavir характерний КІФ в межах до 0,040, для другої — 0,041–0,130, для третьої — 0,131–0,219, для четвертої стадії — 0,220 і вище. КІФ печінки понад 0,017 підтверджує наявність фіброзу печінки в осіб із ХДЗП незалежно від етіології захворювання (чутливість — 85,2 %, специфічність — 100,0 %). Висновки. Метод комп’ютерної морфометрії біоптатів печінки дозволяє значно підвищити точність та достовірність гістологічного дослідження, об’єктивізувати процес морфологічної оцінки стеатозу та фіброзу, забезпечує тривале зберігання результатів дослідження.
Background. Accurate assessment of the fibrosis stage is crucial for effective treatment. Histological examination, the primary method used for assessing liver fibrosis, has certain limitations due to variation within each stage. Computer morphometry offers an objective and quantitative approach to complement histological analysis, providing additional diagnostic information. The purpose of this study was to analyze the computer morphometry data in patients with chronic liver diseases (CLD) of different etiologies and determine their diagnostic accuracy for liver fibrosis diagnosis. Materials and methods. Seventy-five patients with CLD, namely 24 with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), 8 with alcoholic liver disease (ALD), 1 with toxic hepatitis, and 42 with chronic hepatitis C (CHC), were included in the study. Percutaneous liver biopsy was performed under ultrasound guidance using a semi-automatic needle Colt Shot 16 G. The severity of fibrosis was assessed using the Metavir scale. For computer morphometry, biopsies were photographed and evaluated using the ImageJ 1.45S program (National Institutes of Health, USA). The computerized fibrosis index (CFI), steatosis index, and the number of apoptotic cells in 5 consecutive high-power fields were calculated. Receiver operating characteristic analysis was performed for CFI diagnostic accuracy assessment. Results. Advanced liver fibrosis (F3-F4) was diagnosed in 62.5 % of ALD cases and 31.0 % of CHC. The highest CFI was found in ALD, it exceeded the level of NAFLD and CHC patients by 3.3 (p < 0.01) and 2 times (p < 0.05), respectively. At the same time, people with NAFLD had the highest steatosis index (0.36 ± 0.11), which was 1.7 times higher (p < 0.05) than in ALD and CHC. Moreover, CFI correlated with the fibrosis stage (r = 0.71, p < 0.05). Stage I of liver fibrosis according to the Metavir scale is characterized by CFI up to 0.040, stage II — 0.041–0.130, stage III — 0.131–0.219, and stage IV — more than 0.220. CFI cut-off value was 0.017, which confirms the presence of liver fibrosis in patients with chronic liver diseases regardless of the etiology (sensitivity — 85.2 %, specificity — 100.0 %). Conclusions. Computer morphometry significantly improves the accuracy and reliability of histological examination, and allows to objectify morphological assessment of liver steatosis and fibrosis and to ensure long-term storage of the results.
хронічні дифузні захворювання печінки; комп’ютерна морфометрія; комп’ютерний індекс фіброзу; індекс стеатозу
chronic liver diseases; computer morphometry; computerized fibrosis index; steatosis index
Для ознакомления с полным содержанием статьи необходимо оформить подписку на журнал.
- Parola M., Pinzani M. Liver fibrosis: Pathophysiology, pathogenetic targets and clinical issues. Mol Aspects Med. 2019. Vol. 65. P. 37-55.
- Liver cirrhosis / P. Ginès et al. Lancet. 2021. Vol. 398(10308). P. 1359-1376.
- Roehlen N., Crouchet E., Baumert T.F. Liver Fibrosis: Mechanistic Concepts and Therapeutic Perspectives. Cells. 2020. Vol. 9(4). P. 875.
- Liver fibrogenesis: un update on established and emerging basic concepts / E. Novo et al. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2020. Vol. 689. P. 108445.
- Aydın M.M., Akçalı K.C. Liver fibrosis. Turk J Gastroenterol. 2018. Vol. 29(1). P. 14-21.
- Machine learning liver histology scores correlate with portal hypertension assessments in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis cirrhosis / M. Noureddin et al. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2023. Vol. 57(4). P. 409-417.
- Assessment of fibrosis and cirrhosis in liver biopsies: an update / G. Germani et al. Semin Liver Dis. 2011. Vol. 31(1). P. 82-90.
- Jin S.Y. Role of liver biopsy in the assessment of hepatic fibrosis — its utility and limitations. Korean J Hepatol. 2007. Vol. 13(2). P. 138-145.
- Khalifa A., Rockey D.C. The utility of liver biopsy in 2020. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2020. Vol. 36(3). P. 184-191.
- Hepatopathy of unknown etiology — is liver biopsy a good tool in differential diagnosis? / J. Jabłońska et al. Arch Med Sci. 2019. Vol. 15(6). P. 1462-1467.
- Talwalkar J.A., Sanderson S.O. Role of computerized image morphometry for assessing noninvasive methods to detect hepatic fibrosis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2008. Vol. 6(9). P. 958-959.
- Optical percutaneous needle biopsy of the liver: a pilot animal and clinical study / V. Dremin et al. Sci Rep. 2020. Vol. 10(1). P. 14200.
- Venkatesh S.K., Torbenson M.S. Liver fibrosis quantification. Abdom Radiol (NY). 2022. Vol. 47(3). P. 1032-1052.
- Comparative assessment of liver fibrosis by computerized morphometry in naïve patients with chronic hepatitis B and C / N. Sturm et al. Liver Int. 2013. Vol. 33(3). P. 428-438.
- Ошмянська Н.Ю., Аржанова Г.Ю., Галенко О.П. Сучасні морфологічні методи аналізу прогресування фіброзу при хронічному гепатиті, асоційованому з вірусом С. Сучасна гастроентерологія. 2014. № 4. С. 16-23.