Журнал «Здоровье ребенка» Том 18, №3, 2023
Вернуться к номеру
Роль риноманометрії в оцінці ефективності лазерохірургічного лікування в дітей із хронічним гіпертрофічним ринітом
Авторы: D.F. Fuculița
Nicolae Testemițanu State University of Medicine and Pharmacy, Chisinau, Republic of Moldova
Рубрики: Педиатрия/Неонатология
Разделы: Клинические исследования
Версия для печати
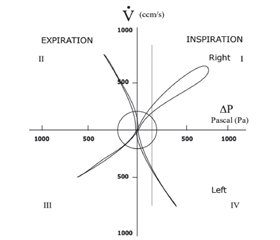
Актуальність. Риноманометрія — об’єктивний спосіб оцінки назальної прохідності. Завдяки розвитку технологій і використанню мікрокомп’ютерів, підключених до вимірювальних приладів, популярність цього методу зросла. За допомогою риноманометрії оцінюють носовий опір шляхом вимірювання потоку повітря та трансназального градієнта тиску, виявляють наявність носової респіраторної обструкції та з’ясовують, яка нозологічна структура постійно її викликає, у цьому випадку гіпертрофія нижніх носових раковин. Мета дослідження: оцінити ефективність функціонального обстеження, такого як передня риноманометрія, у моніторингу результатів лазерохірургічного лікування в дітей із хронічним гіпертрофічним ринітом. Матеріали та методи. Це дослідження було проведено в клініці дитячої оториноларингології Республіканської дитячої клінічної лікарні ім. Е. Коцага. У ньому взяли участь 120 дітей віком 8–17 років із гіпертрофічним хронічним ринітом, розділених на три групи по 40 дітей у кожній, яких лікували 3 методиками: 1-ша група — каутеризація нижніх носових раковин біполярними щипцями, 2-га — шейверна мукотомія та 3-тя група — діодно-лазерна хірургія. Усім хворим проводили риноманометрію як об’єктивне передопераційне та післяопераційне дослідження на 7-му добу, через місяць, рік та через 12 місяців. Результати. Аналіз результатів функціонального обстеження показує, що оперативні втручання були ефективні щодо відновлення просторових параметрів порожнин носа. Визначено більш виражене покращення ендоназальних архітектонічних показників у 3-й групі, де використовували діодно-лазерну оперативну техніку, порівняно з 2-ю (лише шейверна мукотомія) і 1-ю групою, де застосовували стандартну хірургічну техніку каутеризації біполярними щипцями. Висновки. Результати функціональної риноманометрії після хірургічного лікування статистично відрізнялися в усіх групах дослідження, що свідчить про важливу діагностичну цінність цього обстеження в моніторингу післяопераційної динаміки.
Background. Rhinomanometry is an objective way of assessing nasal patency. Due to advances in technology and the use of microcomputers connected to measuring instruments, the use of this approach has increased. Rhinomanometry evaluates nasal resistance by measuring airflow and transnasal pressure gradient. With the help of this examination, the presence of a nasal respiratory obstruction is detected, and it is evaluated which nosological structure continuously causes it, in this case the hypertrophy of the inferior nasal turbinates. The purpose of the research is to evaluate the effectiveness of the functional examination such as the anterior rhinomanometry in monitoring the results of laser surgical treatment in children with chronic hypertrophic rhinitis. Materials and methods. The given study was carried out in the pediatric otorhinolaryngology clinic of the Emilian Coţaga Republican Children’s Clinical Hospital. The research involved a group of 120 children with hypertrophic chronic rhinitis, aged between 8–17 years, divided into three groups of 40 children each, treated surgically by 3 techniques: group 1 — cauterization of the inferior nasal turbinates with bipolar forceps, group 2 — shaver mucotomy and group 3 — diode laser surgery. In all patients, rhinomanometry was performed as an objective preoperative and postoperative examination on the 7th day, after one month, one year and in 12 months. Results. The analysis of the functional examination results demonstrates that the surgical interventions had a beneficial effect in terms of the recovery of the space parameters of the nasal cavities. A more pronounced improvement of the endonasal architectural indices is determined in group 3 where the diode laser surgical technique was used compared to group 2 — only shaver mucotomy and group 1 where the standard surgical technique of cauterization with bipolar forceps was practiced. Conclusions. The functional rhinomanometric results were statistically different after the surgical treatment in all study groups that indicates an important diagnostic value of this examination in the monitoring of postoperative dynamics.
риноманометрія; хронічний гіпертрофічний риніт; назальна прохідність; закладеність носа
rhinomanometry; chronic hypertrophic rhinitis; nasal permeability; nasal obstruction
Для ознакомления с полным содержанием статьи необходимо оформить подписку на журнал.
- Akmenkalne L., Prill M., Vogt K. Nasal valve elastography quatitative determination of the mobility of the nasal valve. Rhinology Online. 2019. 2. 81-86. doi: 10.4193/RHINOL/18.086.
- Clement P.A., Gordts F. Consensus report on acoustic rhinometry and rhinomanometry. Rhinology. 2005. 43. 169-179.
- Gagnieur P., Fieux M., Louis B. Objective diagnosis of internal nasal valve collapse by four-phase-rhinomanometry. Laryngoscope Investig. Otolaryngol. 2022. 7. 388-394. doi: 10.1002/lio2.784.
- Hellings P.W., Klimek L., Cingi C., Agache I., Akdis C., Ba–chert C. et al. Non-allergic rhinitis: position paper of the European Aca–demy of Allergy and Clinical Immunology. Allergy. 2017. 72(11). 1657-1665. doi: 10.1111/ all.13200.
- Komshian S.R., Cohen M.B., Brook C., Levi J.R. Inferior turbinate hypertrophy: a review of the evolution of management in children. Am. J. Rhinol. Allergy. 2019. 33(2). 212-219. doi: 10.1177/1945892418815351.
- Peksis K., Unger J., Paulauska S., Emsina A., Blumbergs M., Vogt K. et al. Relationships among nasal resistance, age and anthropometric parameters of the nose during growth. Rhinology Online. 2018. 1. 112-121. doi: 10.4193/RHINOL/18.032.
- Rüttgers M., Waldmann M., Schroeder W., Lintermann A. Machine Learning-Based Control of Perturbed and Heated Channel Flows. In: Jagode H., Anzt H., Ltaief H., Luszczek P., eds. High Performance Computing. Springer International Publishing, 2021. 7-22. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-90539-2_37.
- Toh S.T., Lin C.H., Guilleminault C. Usage of four-phase high-resolution rhinomanometry and measurement of nasal resistance in sleepdisordered breathing. Laryngoscope. 2012. 122. 2343-2349. doi: 10.1002/lary.23441.
- Vogt K., Wernecke K.-D., Argale M., Kaulina K. Classification of total nasal obstruction in 10,033 cases by 4-phase rhinomanometry. Romanian J. Rhinology. 2016. 6. 149-160. doi: 10.1515/rjr-2016-0017.
- Vogt K., Bachmann-Harildstad G., Lintermann A., Nechyporenko A., Peters F., Wernecke K.D. et al. The new agreement of the International RIGA Consensus conference on nasal airway function tests. Rhinology. 2018. 56. 1-11. doi: 10.4193/Rhin17.084.
- Waldmann M., Grosch A., Witzler C., Vogt K., Kohn C., Schröder W. et al. An effective simulation and measurement-based workflow for enhanced diagnostics in rhinology. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2022. 60. 365-391. doi: 10.1007/s11517-021-02446-3.
- Waldmann M., Rüttgers M., Lintermann A., Schröder W. Virtual Surgeries of Nasal Cavities Using a Coupled Lattice Boltzmann Level-Set Approach. J. Engineering Sci. Med. Diagn. Therapy. 2022. 5. doi: 10.1115/1.4054042.