Журнал «Здоровье ребенка» Том 18, №3, 2023
Вернуться к номеру
Інфекції, пов’язані з наданням медичної допомоги, у дітей в Україні протягом 2009–2021 років
Авторы: Корнійчук О.П., Тимчук І.В., Павлій С.Й., Конечний Ю.Т.
Львівський національний медичний університет імені Данила Галицького, м. Львів, Україна
Рубрики: Педиатрия/Неонатология
Разделы: Клинические исследования
Версия для печати
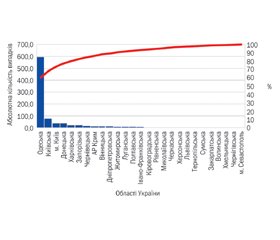
Актуальність. Інфекції, пов’язані з наданням медичної допомоги (ІПНМД): цей термін зараз включає в себе розвиток інфекційних процесів у різних системах органів пацієнтів і у шпиталях різної спеціалізації. Вважається, що ІПНМД — це інфекції, які вперше виникають через 48 годин чи пізніше після госпіталізації або ж через 30 днів після отримання медичної опіки. Мета дослідження: ретроспективний аналіз захворюваності серед дітей в Україні на ІПНМД протягом 2009–2021 рр. Матеріали та методи. Статистичний аналіз поширеності зареєстрованих випадків ІПНМД в Україні у 2009–2021 рр. за даними ЦГЗ МОЗ України. Результати. У середньому щороку в Україні реєстрували 966 ± 489 випадків ІПНМД серед дітей різного віку. За віковим розподілом серед пацієнтів дитячої категорії з ІПНМД в середньому щороку на новонароджених дітей до 1 місяця життя припадало 65,8 %, від 1 місяця до 1 року — 5,9 %, від 1 до 17 років — 28,3 %. За нозологічною структурою ІПНМД у дітей превалювали інфекції окремих станів, що виникають в перинатальному періоді. У середньому відсоток таких хвороб за 2010–2021 рр. становив 49,5 ± 7,5 % (серед дітей 0–17 років) та 13,8 % від загальної кількості випадків ІПНМД в Україні. Висновки. Останніми роками в Україні спостерігався недооблік випадків ІПНМД як серед дорослих пацієнтів, так і серед дітей. Показники, надані установами окремих регіонів (Одеська та Київська області), дають змогу з певною мірою вірогідності отримати уявлення про структуру захворюваності на ІПНМД в цілому у країні. За віковою структурою ІПНМД у дітей (0–17 років) за 2009–2021 рр. становили 22,06 % від загальної кількості ІПНМД. Найбільшу кількість випадків за вказаний період зафіксовано серед новонароджених дітей, що становить 65,8 % від усіх дітей з ІПНМД. Тож основні зусилля повинні бути спрямовані на зниження рівня ІПНМД серед малюків.
Background. Healthcare-associated infections (HCAIs) now include the development of infectious processes in various organ systems of patients and at hospitals of different work directions. It is believed that HCAIs are infections that first occur 48 hours or later after hospitalization or 30 days after receiving medical care. The aim of our research was a retrospective analysis of the incidence of HCAIs among children in Ukraine during 2009–2021. Materials and methods. Statistical analysis of the prevalence of registered cases of HCAIs in Ukraine for 2009–2021, according to the Center for Public Health of the Ministry of Health of Ukraine. Results. On average, 966 ± 489 cases of HCAIs were registered annually in Ukraine among children of various ages. According to the age distribution, the number of annual cases of HCAIs among newborns of up to 1 month of age averaged 65.8 %, for those aged 1 month to 1 year — 5.9 %, from 1 to 17 years — 28.3 %. According to the nosological structure of HCAIs, infections of certain conditions occurring in the perinatal period prevailed among children. On average, the number of such diseases for 2010–2021 was 49.5 ± 7.5 % (among children 0–17 years old) and 13.8 % of the total cases of HCAIs in Ukraine. Conclusions. In recent years, there has been an underestimation of HCAI cases in Ukraine among adult patients and children. Nevertheless, indicators provided by institutions of some regions (Odesa and Kyiv regions) make it possible, with a certain degree of probability, to get an idea of the structure of HCAI incidence in the country. According to the age structure, HCAIs in children (0–17 years) for 2009–2021 accounted for 22.06 % of the total number of HCAIs. Most cases during the specified period were recorded among newborns, 65.8 % of all children with HCAIs. Therefore, the primary efforts should be aimed at reducing HCAIs among newborns.
інфекції, пов’язані з наданням медичної допомоги; нозокоміальні інфекції; діти; перинатальний період
healthcare-associated infections; nosocomial infections; children; perinatal period
Для ознакомления с полным содержанием статьи необходимо оформить подписку на журнал.
- Antipkin Y.G., Marushko R.V., Dudina E.A. Evolution of Infant Mortality in Ukraine. Mod. Pediatr. Ukr. 2021. 6–14. doi: 10.15574/SP.2021.113.6.
- Cassini A., Plachouras D., Eckmanns T., Abu Sin M., Blank H.-P.,
- Ducomble T., Haller S., Harder T., Klingeberg A., Sixtensson M. et al. Burden of Six Healthcare-Associated Infections on European Population Health: Estimating Incidence-Based Disability-Adjusted Life Years through a Population Prevalence-Based Modelling Study. PLоS Med. 2016. 13. e1002150. Doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1002150.
- Vincent J.-L. Nosocomial Infections in Adult Intensive-Care Units. Lancet. 2003. 361. 2068-2077. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(03)13644-6.
- WHO Healthcare-Associated Infections. Fact Sheet. Available online: https://www.who.int/gpsc/country_work/gpsc_ccisc_fact_sheet_en.pdf.
- Konechnyi Y. еt al. Epidemiological and Microbiological Aspects of Healthcare-Associated Infections in Ukraine during the 2009–2019 Period. Przegl. Epidemiol. 2021. 86-95. doi: 10.32394/pe.75.09.
- Konechnyi Y., Skurativskyi Y., Tymchuk I., Pidhirnyi Y., Kornіychuk O. Microbiological Profile of Nosocomial Infections. Proc. Shevchenko Sci. Soc. Med. Sci. 2019. 55. 56-64. doi: 10.25040/ntsh2019.01.05.
- Murni I.K., Duke T., Kinney S., Daley A.J., Wirawan M.T., Soenarto Y. Risk Factors for Healthcare-Associated Infection among Children in a Low-and Middle-Income Country. BMC Infect. Dis. 2022. 22. 406. doi: 10.1186/s12879-022-07387-2.
- Nosocomial Infections in the Pediatric Intensive Care Unit in Children between 1 Month to 12 Years. 2022. 09. 2202-2208.