Международный эндокринологический журнал Том 19, №3, 2023
Вернуться к номеру
Вплив комплексного застосування міоінозитолу, вітаміну D та селену на цитокіновий статус в жінок репродуктивного віку з автоімунним тиреоїдитом
Авторы: N.V. Pasyechko, V.M. Kulchinska
I. Horbachevsky Ternopil National Medical University, Ternopil, Ukraine
Рубрики: Эндокринология
Разделы: Клинические исследования
Версия для печати
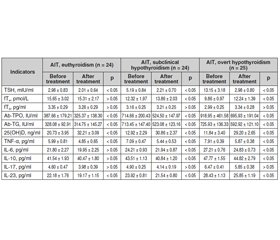
Актуальність. Останніми роками в Україні та інших країнах світу спостерігається збільшення частоти тиреопатій автоімунного генезу. Значну роль у патогенезі автоімунного тиреоїдиту (АІТ) відіграють цитокіни, продукція яких значно підвищується при імунопатологічних реакціях. Мета дослідження: вивчити вплив комплексного застосування міоінозитолу, вітаміну D і селену на цитокіновий статус жінок з еутиреозом, субклінічним гіпотиреозом і явним гіпотиреозом на тлі автоімунного тиреоїдиту. Матеріали та методи. Під спостереженням перебувало 147 жінок віком 18–43 роки з АІТ і 30 жінок контрольної групи. Хворі першої групи (n = 74) додатково до основного лікування отримували міоінозитол у дозі 2000 мг/добу, холекальциферол 2000 МО/добу та селен 100 мкг/добу. Пацієнти другої групи (n = 73) додатково до основного лікування отримували лише холекальциферол у дозі 2000 МО/добу та селен 100 мкг/добу. Функціональний стан щитоподібної залози вивчали шляхом визначення рівнів тиреотропного гормону, вільного тироксину, вільного трийодтироніну, антитіл до тиреоїдної пероксидази (АТ-ТПО) і антитіл до тиреоглобуліну (АТ-ТГ). Стан системного та місцевого запального процесу оцінювали за показниками фактора некрозу пухлини α, інтерлейкінів 6, 10, 17 та 23. Результати. Слід зазначити, що в усіх хворих на АІТ виявлено зміни цитокінового статусу, при цьому певні відмінності спостерігалися залежно від клінічного варіанта автоімунного захворювання щитоподібної залози. Через три місяці лікування хворих першої групи препаратами міоінозитолу в дозі 2000 мг/добу, холекальциферолу 2000 МО/добу та селену 100 мкг/добу, а також пацієнтів другої групи лише препаратами холекальциферолу в дозі 2000 МО/добу та селену 100 мкг/добу виявлено вірогідну різницю між показниками в обох досліджуваних когортах. Висновки. Призначення препаратів міоінозитолу, вітаміну D, селену комплексно впливало на зниження показників цитокінового статусу, рівнів АТ-ТПО та АТ-ТГ, що сприяло компенсації основного захворювання.
Background. In recent years, in Ukraine and other countries of the world, there has been an increase in the frequency of autoimmune thyropathies. A significant role in the pathogenesis of autoimmune thyroiditis (AIT) is played by cytokines whose production is increased significantly during immunopathological reactions. The purpose of study was to investigate the effect of the combined use of myo-inositol, vitamin D and selenium on the cytokine status of women with euthyroidism, subclinical hypothyroidism and overt hypothyroidism against the background of autoimmune thyroiditis. Materials and methods. One hundred and forty-seven women aged 18–43 with AIT and 30 women of the control group were under observation. Patients of first group (n = 74) received myo-inositol at a dose of 2000 mg/day, cholecalciferol 2000 IU/day, and selenium 100 μg/day additionally to the main treatment. Patients of the second group (n = 73) received only cholecalciferol at a dose of 2000 IU/day and selenium 100 μg/day additionally to the main treatment. The functional state of the thyroid gland was studied by determining the levels of thyroid-stimulating hormone, free thyroxine, free triiodothyronine, antibodies to thyroid peroxidase (Ab-TPO) and antibodies to thyroglobulin (Ab-TG). The state of the systemic and local inflammatory process was evaluated according to parameters of tumor necrosis factor α, interleukins 6, 10, 17, and 23. Results. It should be noted all patients with AIT had changes in cytokine status, with some differences depending on the clinical variant of autoimmune thyroid disease. After three months of treatment of patients of the first group with myo-inositol at a dose of 2000 mg/day, cholecalciferol 2000 IU/day and selenium 100 μg/day, and patients of the second group only with cholecalciferol at a dose of 2000 IU/day and selenium at 100 μg /day, a significant difference was found between the indicators in both studied cohorts. Conclusions. The administration of myo-inositol, vitamin D, and selenium had a combination effect on the reduction of cytokine indicators, Ab-TPO and Ab-TG levels, which contributed to the compensation of the underlying disease.
автоімунний тиреоїдит; міоінозитол; вітамін D; селен; цитокіновий статус
autoimmune thyroiditis; myo-inositol; vitamin D; selenium; cytokine status
Для ознакомления с полным содержанием статьи необходимо оформить подписку на журнал.
- Tkachenko V., Maksymets Y., Vydyborets N., Kovalenko O. Analysis of the prevalence and morbidity of thyroid pathology among the population of Kyiv region and Ukraine for 2007–2017. International Journal of Endocrinology (Ukraine). 2018. 14(3). 272-277. doi: 10.22141/2224-0721.14.3.2018.136426 (in Ukrainian).
- Tronko M., Brenner A.V., Bogdanova T., Shpak V., Oliy–nyk V., Cahoon E.K., Drozdovitch V. et al. Thyroid neoplasia risk is increased nearly 30 years after the Chernobyl accident. Int. J. Cancer. 2017 Oct 15. 141(8). 1585-1588. doi: 10.1002/ijc.30857.
- Pankiv V.I., Yuzvenko T.Yu., Pankiv I.V. Type 2 diabetes mellitus and subclinical hypothyroidism: focusing on the role of cholecalciferol. Problems of Endocrine Pathology. 2019. 2. 46-51. doi: 10.21856/j-PEP.2019.2.07.
- Silva J.F., Ocarino N.M., Serakides R. Thyroid hormones and female reproduction. Biol. Reprod. 2018 Nov 1. 99(5). 907-921. doi: 10.1093/biolre/ioy115.
- Taylor P.N., Albrecht D., Scholz A., Gutierrez-Buey G., Lazarus J.H., Dayan C.M., Okosieme O.E. Global epidemiology of hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2018 May. 14(5). 301-316. doi: 10.1038/nrendo.2018.18.
- Jabrocka-Hybel A., Skalniak A., Piątkowski J., Turek-Jabrocka R., Vyhouskaya P., Ludwig-Słomczyńska A., Machlowska J. et al. How much of the predisposition to Hashimoto’s thyroiditis can be explained based on previously reported associations? J. Endocrinol. Invest. 2018 Dec. 41(12). 1409-1416. doi: 10.1007/s40618-018-0910-4.
- Hu X., Chen Y., Shen Y., Tian R., Sheng Y., Que H. Global prevalence and epidemiological trends of Hashimoto’s thyroiditis in adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Public Health. 2022 Oct 13. 10. 1020709. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.1020709.
- Konca Degertekin C., Aktas Yilmaz B., Balos Toruner F., Kalkanci A., Turhan Iyidir O., Fidan I., Yesilyurt E. et al. Circulating Th17 cytokine levels are altered in Hashimoto’s thyroiditis. Cytokine. 2016 Apr. 80. 13-7. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2016.02.011.
- Nordio M., Basciani S. Treatment with Myo-Inositol and Selenium Ensures Euthyroidism in Patients with Autoimmune Thyroiditis. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2017. 2017. 2549491. doi: 10.1155/2017/2549491.
- Pankiv I.V. Impact of vitamin D supplementation on the level of thyroid peroxidase antibodies in patients with autoimmune hypothyroidism. International Journal of Endocrinology. 2016. 5(77). 78-82. doi: 10.22141/2224-0721.5.77.2016.78759 (in Ukrainian).
- Paparo S.R., Ferrari S.M., Patrizio A. Myoinositol in Autoimmune Thyroiditis. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne). 2022. 13. 930756. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.930756.
- Grasberger H., Van Sande J., Hag-Dahood Mahameed A., Tenenbaum-Rakover Y., Refetoff S. A familial thyrotropin (TSH) receptor mutation provides in vivo evidence that the inositol phosphates/Ca2+ cascade mediates TSH action on thyroid hormone synthesis. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2007 Jul. 92(7). 2816-20. doi: 10.1210/jc.2007-0366.
- Frej A.D., Clark J., Le Roy C.I., Lilla S., Thomason P.A., Otto G.P., Churchill G. et al. The Inositol-3-Phosphate Synthase Biosynthetic Enzyme Has Distinct Catalytic and Metabolic Roles. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2016 May 2. 36(10). 1464-79. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00039-16.
- Lee H.J., Li C.W., Hammerstad S.S., Stefan M., Tomer Y. Immunogenetics of autoimmune thyroid diseases: a comprehensive review. J. Autoimmun. 2015 Nov. 64. 82-90. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2015.07.009.
- Luo X., Zheng T., Mao C., Dong X., Mou X., Xu C., Lu Q. et al. Aberrant MRP14 expression in thyroid follicular cells mediates chemokine secretion through the IL-1β/MAPK pathway in Hashimoto’s thyroiditis. Endocr. Connect. 2018 Jun. 7(6). 850-858. doi: 10.1530/EC-18-0019.
- Koehler V.F., Bojunga J. Autoimmune thyroid disease. Dtsch. Med. Wochenschr. 2021 Oct. 146(20). 1329-1336 (in German). doi: 10.1055/a-1258-5674.
- Antonelli A., Ferrari S.M., Corrado A., Ferrannini E., Fallahi P. CXCR3, CXCL10 and type 1 diabetes. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2014. 25. 57-65. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2014.01.006.
- Antonelli A., Ferrari S.M., Corrado A., Di Domenicantonio A., Fallahi P. Autoimmune thyroid disorders. Autoimmun. Rev. 2015 Feb. 14(2). 174-80. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2014.10.016.
- Esfahanian F., Ghelich R., Rashidian H., Jadali Z. Increased Levels of Serum Interleukin-17 in Patients with Hashimoto’s Thyroi–ditis. Indian J. Endocrinol. Metab. 2017 Jul-Aug. 21(4). 551-554. doi: 10.4103/ijem.IJEM_412_16.
- Siemińska L., Wojciechowska C., Walczak K., Borowski A., Marek B., Nowak M., Kajdaniuk D. et al. Associations between meta–bolic syndrome, serum thyrotropin, and thyroid antibodies status in postmenopausal women, and the role of interleukin-6. Endokrynol. Pol. 2015. 66(5). 394-403. doi: 10.5603/EP.2015.0049.
- Marchiori R.C., Pereira L.A., Naujorks A.A., Rovaris D.L., Meinerz D.F., Duarte M.M., Rocha J.B. Improvement of blood inflammatory marker levels in patients with hypothyroidism under levothyroxine treatment. BMC Endocr. Disord. 2015 Jun 23. 15. 32. doi: 10.1186/s12902-015-0032-3.