Международный эндокринологический журнал Том 19, №5, 2023
Вернуться к номеру
Глюко- і кардіоцентричний підхід до досягнення компенсації цукрового діабету 2-го типу
Авторы: Паньків В.І.
Український науково-практичний центр ендокринної хірургії, трансплантації ендокринних органів і тканин МОЗ України, м. Київ, Україна
Рубрики: Эндокринология
Разделы: Клинические исследования
Версия для печати
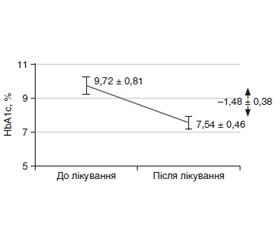
Актуальність. Встановлено, що монотерапія цукрового діабету 2-го типу (ЦД2) ефективна лише обмежений час. При цьому важливою складовою успішного менеджменту ЦД2 залишається раціональність комбінацій лікарських засобів. У цьому контексті, з огляду на складний багатофакторний патогенез ЦД2, оптимальним є вплив на різні механізми виникнення гіперглікемії. Мета дослідження: визначення ефективності й безпеки додаткового призначення комбінації метформіну й глімепіриду в пацієнтів із цукровим діабетом 2-го типу з рівнем глікованого гемоглобіну 8,5–9,5 %, які перебували на монотерапії дапагліфлозином упродовж принаймні трьох місяців. Матеріали та методи. У дослідження було включено 14 чоловіків (середній вік 57,9 ± 8,4 року) і 18 жінок (середній вік 58,2 ± 9,3 року) із ЦД2. Середня тривалість ЦД2 становила 9,7 ± 4,2 року. Хворі перебували в стані декомпенсації ЦД2 (HbA1c понад 8,5 %) на тлі монотерапії дапагліфлозином у максимальній дозі упродовж не менше від трьох попередніх місяців. Пацієнтам додатково до дапагліфлозину (10 мг/добу) було призначено комбінацію метформіну і глімепіриду (Дуглімакс, таблетки по 500 мг/2 мг 1 раз на день) упродовж трьох місяців. Результати. Середній рівень HbA1c у 32 хворих на ЦД2 становив 9,72 ± 0,81 %, глюкози плазми натще (ГПН) — 10,71 ± 1,42 ммоль/л. Через 3 місяці після початку комбінованого лікування рівень HbA1c вірогідно знизився до 7,54 ± 0,46 % (p < 0,05). Середнє зниження HbA1c після переведення на додаткову терапію метформіном з глімепіридом становило 1,48 ± 0,38 %. Частка пацієнтів, які досягли рівня HbA1c < 7,5 %, становила через 3 місяці 34,5 % (p < 0,05). Ефективність додаткового призначення метформіну й глімепіриду підтверджується і високою часткою пацієнтів, які досягли показника HbA1c < 7,0 %, — 12,5 % (p < 0,05). Рівень ГПН знизився в середньому до 7,19 ± 1,06 ммоль/л через 3 місяці. Середнє зниження досягло 3,06 ± 1,08 ммоль/л, що у відносному вираженні становило –31,4 ± 8,7 % від початкового значення. Жодного випадку гіпоглікемії чи інших небажаних явищ упродовж усього періоду дослідження зареєстровано не було. Висновки. Аналіз показників у 32 пацієнтів із ЦД 2-го типу, у яких визначався високий рівень НbА1с (понад 9 %) на тлі монотерапії дапагліфлозином, дозволив дійти висновку, що для досягнення цільових рівнів HbA1c необхідно інтенсифікувати терапію шляхом додаткового призначення комбінації метформіну і глімепіриду. Глюкоцентричні й кардіоцентричні погляди на ЦД2 можуть бути узгоджені й об’єднані шляхом використання комбінованої терапії, зважаючи на різні етіопатологічні особливості захворювання із самого початку лікування.
Background. Monotherapy for type 2 diabetes (T2DM) has been found to be effective only for a limited time. At the same time, the rationality of drug combinations remains an important component of successful management of T2DM. In this context, given the complex multifactorial pathogenesis of T2DM, it is optimal to influence various mechanisms of hyperglycemia. The purpose of the study is to determine the effectiveness and safety of additional administration of a combination of metformin and glimepiride in patients with type 2 diabetes with a glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) level of 8.5–9.5 % who took dapagliflozin alone for at least three months. Materials and methods. Fourteen men (mean age 57.9 ± 8.4 years) and 18 women (mean age 58.2 ± 9.3 years) with T2DM were included in the study. The average duration of T2DM was 9.7 ± 4.2 years. The patients were in a state of decompensation of T2DM (HbA1c over 8.5 %) against the background of dapagliflozin monotherapy in the maximum dose for at least three previous months. In addition to dapagliflozin (10 mg/day), patients were prescribed a combination of metformin and glimepiride (Duglimax tablets, 500 mg/2 mg once a day) for three months. Results. The average level of HbA1c in 32 patients with T2DM was 9.72 ± 0.81 %, fasting plasma glucose was 10.71 ± 1.42 mmol/l. Three months after the start of a combined treatment, the HbA1c level decreased significantly to 7.54 ± 0.46 % (p < 0.05). The average reduction in HbA1c after switching to additional metformin therapy with glimepiride was 1.48 ± 0.38 %. The proportion of patients who achieved HbA1c < 7.5 % was 34.5 % after 3 months (p < 0.05). The effectiveness of the additional administration of metformin and glimepiride is also confirmed by the high percentage of patients (12.5 %) who achieved HbA1c < 7.0 % (p < 0.05). The level of fasting plasma glucose decreased to an average of 7.19 ± 1.06 mmol/l after 3 months. The average decrease reached 3.06 ± 1.08 mmol/l, which in relative terms was 31.4 ± 8.7 % of baseline. No cases of hypoglycemia or other adverse events were registered during the entire study period. Conclusion. The analysis of indicators in 32 patients with type 2 diabetes who had a high level of HbA1c (over 9 %) against the background of dapagliflozin monotherapy allowed us to conclude that it is necessary to intensify the therapy by additionally prescribing a combination of metformin and glimepiride for achieving the target levels of HbA1c. Glucocentric and cardiocentric views on T2DM can be reconciled and integrated by using a combination therapy to address the different etiopathological features of the disease from the very beginning of treatment.
цукровий діабет 2-го типу; лікування; метформін; глімепірид; дапагліфлозин
type 2 diabetes; treatment; metformin; glimepiride; dapagliflozin
Вступ
Матеріали та методи
Результати
Обговорення
Висновки
- Samson S.L., Vellanki P., Blonde L., Christofides E.A., Galindo R.J., Hirsch I.B. et al. American Association of Clinical Endocrinology Consensus Statement: Comprehensive Type 2 Diabetes Management Algorithm — 2023 Update. Endocr. Pract. 2023 May. 29(5). 305-340. doi: 10.1016/j.eprac.2023.02.001. PMID: 37150579.
- Borse S.P., Chhipa A.S., Sharma V., Singh D.P., Nivsarkar M. Management of Type 2 Diabetes: Current Strategies, Unfocussed Aspects, Challenges, and Alternatives. Med. Princ. Pract. 2021. 30(2). 109-121. doi: 10.1159/000511002. Epub 2020 Aug 20. PMID: 32818934; PMCID: PMC8114074.
- Davies M.J., Aroda V.R., Collins B.S., Gabbay R.A., Green J., Maruthur N.M. et al. Management of Hyperglycemia in Type 2 Diabetes, 2022. A Consensus Report by the American Diabetes Association (ADA) and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD). Diabetes Care. 2022 Nov 1. 45(11). 2753-2786. doi: 10.2337/dci22-0034. PMID: 36148880; PMCID: PMC10008140.
- ElSayed N.A., Aleppo G., Aroda V.R., Bannuru R.R., Brown F.M., Bruemmer D. et al., on behalf of the American Diabetes Association. 9. Pharmacologic Approaches to Glycemic Treatment: Standards of Care in Diabetes-2023. Diabetes Care. 2023 Jan 1. 46 (Suppl. 1). S140-S157. doi: 10.2337/dc23-S009. PMID: 36507650; PMCID: PMC9810476.
- Dhillon S. Dapagliflozin: A Review in Type 2 Diabetes. Drugs. 2019 Jul. 79(10). 1135-1146. doi: 10.1007/s40265-019-01148-3. Erratum in: Drugs. 2019 Dec. 79(18). 2013. PMID: 31236801; PMCID: PMC6879440.
- Bailey C.J., Morales Villegas E.C., Woo V., Tang W., Ptaszynska A., List J.F. Efficacy and safety of dapagliflozin monotherapy in people with Type 2 diabetes: a randomized double-blind placebo-controlled 102-week trial. Diabet Med. 2015 Apr. 32(4). 531-41. doi: 10.1111/dme.12624. Epub 2014 Nov 22. PMID: 25381876.
- Zaccardi F., Webb D.R., Htike Z.Z., Youssef D., Khunti K., Davies M.J. Efficacy and safety of sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 inhibitors in type 2 diabetes mellitus: systematic review and network meta-analysis. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2016 Aug. 18(8). 783-94. doi: 10.1111/dom.12670. Epub 2016 May 13. PMID: 27059700.
- Olomu A., Kelly-Blake K., Hart-Davidson W., Gardiner J., Luo Z., Heisler M., Holmes-Rovner M. Improving diabetic patients’ adherence to treatment and prevention of cardiovascular disease (Office Guidelines Applied to Practice-IMPACT Study) — a cluster randomized controlled effectiveness trial. Trials. 2022 Aug 15. 23(1). 659. doi: 10.1186/s13063-022-06581-6. PMID: 35971135; PMCID: PMC9376908.
- Abdul-Ghani M., DeFronzo R.A. Personalized approach for type 2 diabetes pharmacotherapy: where are we and where do we need to be? Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2021 Nov. 22(16). 2113-2125. doi: 10.1080/14656566.2021.1967319. Epub 2021 Aug 26. PMID: 34435523.
- Cai X., Gao X., Yang W., Han X., Ji L. Efficacy and Safety of Initial Combination Therapy in Treatment-Naïve Type 2 Diabetes Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Diabetes Ther. 2018 Oct. 9(5). 1995-2014. doi: 10.1007/s13300-018-0493-2. Epub 2018 Aug 28. PMID: 30155646; PMCID: PMC6167297.
- Pittampalli S., Upadyayula S., Mekala H.M., Lippmann S. Risks vs Benefits for SGLT2 Inhibitor Medications. Fed. Pract. 2018 Jul. 35(7). 45-48. PMID: 30766374; PMCID: PMC6368009.
- Papaetis G.S. Empagliflozin therapy and insulin resistance-associated disorders: effects and promises beyond a diabetic state. Arch. Med. Sci. Atheroscler. Dis. 2021 Apr 12. 6. e57-e78. doi: 10.5114/amsad.2021.105314. PMID: 34027215; PMCID: PMC8117073.
- Phung O.J., Sobieraj D.M., Engel S.S., Rajpathak S.N. Early combination therapy for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus: systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2014 May. 16(5). 410-7. doi: 10.1111/dom.12233. Epub 2013 Dec 16. PMID: 24205921.
- Cai X., Gao X., Yang W., Chen Y., Zhang S., Zhou L., Han X., Ji L. No disparity of the efficacy and all-cause mortality between Asian and non-Asian type 2 diabetes patients with sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors treatment: A meta-analysis. J. Diabetes Investig. 2018 Jul. 9(4). 850-861. doi: 10.1111/jdi.12760. Epub 2017 Nov 13. PMID: 29029369; PMCID: PMC6031489.
- Schnell O., Standl E., Catrinoiu D., Itzhak B., Lalic N., Rahelic D. et al. Report from the 4th Cardiovascular Outcome Trial (CVOT) Summit of the Diabetes & Cardiovascular Disease (D&CVD) EASD Study Group. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2019 Mar 11. 18(1). 30. doi: 10.1186/s12933-019-0822-4. PMID: 30857522; PMCID: PMC6410488.
- Robles N.R., Alvarez A., Fici F. Combination therapy as a first step of treatment in diabetes: Changing the paradigm in KDIGO guidelines? Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2023 May. 111. 21-23. doi: 10.1016/j.ejim.2023.02.024. Epub 2023 Mar 15. PMID: 36931973.

/35.jpg)