Международный эндокринологический журнал Том 20, №1, 2024
Вернуться к номеру
Взаємозв’язок гіперлептинемії та кардіометаболічного ризику в осіб з ожирінням
Авторы: Чернявська І.В. (1), Кравчун Н.О. (1, 2), Дунаєва І.П. (1), Тиха І.А. (2), Олійникова С.П. (1, 2), Рассолова О.С. (1, 3)
(1) - Харківський національний медичний університет, м. Харків, Україна
(2) - ДУ «Інститут проблем ендокринної патології ім. В.Я. Данилевського НАМН України», м. Харків, Україна
(3) - Комунальне некомерційне підприємство Харківської обласної ради «Обласна клінічна лікарня», м. Харків, Україна
Рубрики: Эндокринология
Разделы: Клинические исследования
Версия для печати
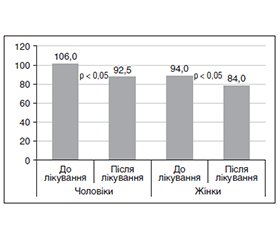
Актуальність. Ожиріння залишається глобальною соціальною та медичною проблемою сучасності. Результати досліджень останніх років демонструють наявність надлишкової маси тіла в 30–70 % та ожиріння в 10–30 % дорослих, при цьому поширеність ожиріння зростає з тривожною швидкістю як в економічно розвинених країнах світу, так і в країнах, що розвиваються. В Україні, за даними Всесвітньої організації охорони здоров’я, надмірну масу тіла або ожиріння мають 41,2 % чоловіків і 58,5 % жінок. Ожиріння є фактором ризику розвитку низки захворювань — цукрового діабету 2-го типу (ЦД2), артеріальної гіпертензії, ішемічної хвороби серця, неалкогольної жирової хвороби печінки, гастроезофагеальної рефлюксної хвороби, синдрому обструктивного апное сну тощо. Наявність гіперлептинемії та стійкість до зменшення маси тіла є загальними характеристиками ожиріння. Мета: встановити взаємозв’язок між рівнем лептину та кардіометаболічним ризиком у хворих на ожиріння. Матеріали та методи. Обстежено 53 пацієнти (43 жінки, 10 чоловіків). ІМТ розраховували як відношення маси тіла (кг) до зросту (м2). Для діагностики надлишкової маси тіла, ожиріння та його ступеня застосовували класифікаційні критерії ВООЗ. Рівень лептину визначали імуноферментним методом на апараті Immunno CHEM 2000. Зв’язок між показниками оцінювали за допомогою коефіцієнта рангової кореляції Спірмана (rs). Результати. Гіперлептинемія у хворих на ожиріння є показником низькоінтенсивного запалення. У хворих на ожиріння відзначається вірогідне підвищення рівня лептину в сироватці крові. Проведений кореляційний аналіз окружності талії з рівнем лептину як у жінок, так і у чоловіків продемонстрував його значущість як до, так і після лікування. В обстеженого контингенту хворих української популяції встановлений значний кардіометаболічний ризик. На тлі комплексного лікування протягом шести місяців відзначається зниження маси тіла, окружності талії (p < 0,05) та зниження рівня лептину (p < 0,05) як у жінок, так і у чоловіків. Висновки. Встановлено взаємозв’язок між рівнем лептину та кардіометаболічним ризиком у хворих на ожиріння.
Background. Obesity remains a global social and medical problem today. The results of recent research demonstrate the presence of overweight in 30–70 % and obesity in 10–30 % of adults, while the prevalence of obesity is increasing at an alarming rate in both economically developed and developing countries of the world. In Ukraine, according to the World Health Organization, 41.2 % of men and 58.5 % of women are overweight or obese. Obesity is a risk factor for the development of a number of diseases — type 2 diabetes, hypertension, coronary heart disease, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, gastroesophageal reflux disease, obstructive sleep apnea syndrome, etc. The presence of hyperleptinemia and weight loss resistance are common characteristics of obesity. The purpose of the study was to reveal the relationship between leptin levels and cardiometabolic risk in obese patients. Materials and methods. Fifty-three patients (43 women, 10 men) were examined. Body mass index was calculated as the ratio of body weight (kg) to height (m2). The classification criteria of the World Health Organization were used to diagnose overweight, obesity, and its degree. The level of leptin was assessed by an enzyme immunoassay on the ImmunnoChem-2000 device. The relationship between indicators was evaluated using the Spearman’s rank correlation coefficient. Results. Hyperleptinemia in obese patients is an indicator of low-grade inflammation. A significant increase in the serum leptin is noted in obese patients. Correlation analysis of waist circumference with leptin level in women and men demonstrated its importance both before and after treatment. A significant cardiometabolic risk was detected in the examined patients from the Ukrainian population. Against the background of a comprehensive treatment for six months, a decrease in body weight, waist circumference (p < 0.05) and in leptin level (p < 0.05) was noted in both women and men. Conclusions. The relationship was found between leptin level and cardiometabolic risk in obese patients.
ожиріння, лептин, інсулінорезистентність, кардіометаболічний ризик
obesity; leptin; insulin resistance; cardiometabolic risk
Вступ
Матеріали та методи
Результати
/61.jpg)
Обговорення
Висновки
- World Health Organization. Obesity and Overweight. Avai–lable from: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight [Accessed 7th November 2020].
- Chooi Y.C., Ding C., Magkos F. The epidemiology of obesity. Metabolism. 2019 Mar. 92. 6-10. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2018.09.005. Epub 2018 Sep 22. PMID: 30253139.
- Dereń K., Nyankovskyy S., Nyankovska O., Łuszczki E., Wyszyńska J., Sobolewski M., Mazur A. The prevalence of underweight, overweight and obesity in children and adolescents from Ukraine. Sci. Rep. 2018 Feb 26. 8(1). 3625. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-21773-4. PMID: 29483604; PMCID: PMC5826931.
- Didushko O.M., Herych P.R., Cherniavska I.V., Yatsyshyn R.I., Pankiv V.I. Influence of the complex treatment of hypothyroidism on the leptin level in patients with primary hypothyroi–dism. World оf Medicine аnd Biology. 2018. 3(65). 59-63. DOI: 10.26724/2079-8334-2018-3-65-59-63.
- Popoviciu M.S., Păduraru L., Yahya G., Metwally K., Cavalu S. Emerging Role of GLP-1 Agonists in Obesity: A Comprehensive Review of Randomised Controlled Trials. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023 Jun 21. 24(13). 10449. doi: 10.3390/ijms241310449. PMID: 37445623; PMCID: PMC10341852.
- Trujillo J.M., Nuffer W., Smith B.A. GLP-1 receptor ago–nists: an updated review of head-to-head clinical studies. Ther. Adv. Endocrinol. Metab. 2021 Mar 9. 12. 2042018821997320. doi: 10.1177/2042018821997320. PMID: 33767808; PMCID: PMC7953228.
- Cornell S. A review of GLP-1 receptor agonists in type 2 diabetes: A focus on the mechanism of action of once-weekly agents. J. Clin. Pharm. Ther. 2020 Sep. 45 (Suppl. 1). 17-27. doi: 10.1111/jcpt.13230. PMID: 32910490; PMCID: PMC7540167.
- Klein S., Gastaldelli A., Yki-Järvinen H., Scherer P.E. Why does obesity cause diabetes? Cell Metab. 2022 Jan 4. 34(1). 11-20. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2021.12.012. PMID: 34986330; PMCID: PMC8740746.
- Rohm T.V., Meier D.T., Olefsky J.M., Donath M.Y. Inflammation in obesity, diabetes, and related disorders. Immunity. 2022 Jan 11. 55(1). 31-55. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2021.12.013. PMID: 35021057; PMCID: PMC8773457.
- Moosaie F., Ghaemi F., Mechanick J.I., Shadnoush M., Firouzabadi F.D., Kermanchi J., et al. Obesity and Diabetic Complications: A Study from the Nationwide Diabetes Report of the Natio–nal Program for Prevention and Control of Diabetes (NPPCD-2021) Implications for Action on Multiple Scales. Prim. Care Diabetes. 2022 Jun. 16(3). 422-429. doi: 10.1016/j.pcd.2022.03.009. Epub 2022 Apr 5. PMID: 35396199.
- Wangnoo S.K., Kumar S., Bhattacharyya A., Tripathi S., Akhtar S., Shetty R., Ghosal S. Liraglutide effect and action in dia–betes-In (LEAD-In): A prospective observational study assessing safety and effectiveness of liraglutide in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus treated under routine clinical practice conditions in India. Indian J. Endocrinol. Metab. 2016 Nov-Dec. 20(6). 838-845. doi: 10.4103/2230-8210.189232. PMID: 27867889; PMCID: PMC5105570.
- Torekov S.S., Madsbad S., Holst J.J. Obesity — an indication for GLP-1 treatment? Obesity pathophysiology and GLP-1 treatment potential. Obes. Rev. 2011 Aug. 12(8). 593-601. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-789X.2011.00860.x. Epub 2011 Mar 15. PMID: 21401851.
- Thon M., Hosoi T., Ozawa K. Possible Integrative Actions of Leptin and Insulin Signaling in the Hypothalamus Targeting Energy Homeostasis. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne). 2016 Oct 20. 7. 138. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2016.00138. PMID: 27812350; PMCID: PMC5071376.
- Mejido D.C.P., Peny J.A., Vieira M.N.N., Ferreira S.T., De Felice F.G. Insulin and leptin as potential cognitive enhancers in metabolic disorders and Alzheimer's disease. Neuropharmacology. 2020 Jul. 171. 108115. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2020.108115. Epub 2020 Apr 25. PMID: 32344008.
- Boucsein A., Kamstra K., Tups A. Central signalling cross-talk between insulin and leptin in glucose and energy homeostasis. J. Neuroendocrinol. 2021 Apr. 33(4). e12944. doi: 10.1111/jne.12944. Epub 2021 Feb 21. PMID: 33615588.
- Myers M.G. Jr, Leibel R.L., Seeley R.J., Schwartz M.W. Obesity and leptin resistance: distinguishing cause from effect. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2010 Nov. 21(11). 643-51. doi: 10.1016/j.tem.2010.08.002. Epub 2010 Sep 16. PMID: 20846876; PMCID: PMC2967652.
- Banks W.A., Farrell C.L. Impaired transport of leptin across the blood-brain barrier in obesity is acquired and reversible. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2003 Jul. 285(1). E10-5. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00468.2002. Epub 2003 Mar 4. PMID: 12618361.
- Izquierdo A.G., Crujeiras A.B., Casanueva F.F., Carreira M.C. Leptin, Obesity, and Leptin Resistance: Where Are We 25 Years Later? Nutrients. 2019 Nov 8. 11(11). 2704. doi: 10.3390/nu11112704. PMID: 31717265; PMCID: PMC6893721.
- Farr O.M., Gavrieli A., Mantzoros C.S. Leptin applications in 2015: what have we learned about leptin and obesity? Curr. Opin. Endocrinol. Diabetes Obes. 2015 Oct. 22(5). 353-9. doi: 10.1097/MED.0000000000000184. PMID: 26313897; PMCID: PMC4610373.
- Ghadge A.A., Khaire A.A. Leptin as a predictive marker for metabolic syndrome. Cytokine. 2019 Sep. 121. 154735. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2019.154735. Epub 2019 May 30. PMID: 31154250.
- Alruwaili H., Dehestani B., le Roux C.W. Clinical Impact of Liraglutide as a Treatment of Obesity. Clin. Pharmacol. 2021 Mar 11. 13. 53-60. doi: 10.2147/CPAA.S276085. PMID: 33732030; PMCID: PMC7958997.
- Konwar M., Bose D., Jaiswal S.K., Maurya M.K., Ravi R. Efficacy and Safety of Liraglutide 3.0 mg in Patients with Overweight and Obese with or without Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2022 Jul 19. 2022. 1201977. doi: 10.1155/2022/1201977. PMID: 35936066; PMCID: PMC9325632.
- Lin Q., Xue Y., Zou H., Ruan Z., Ung C.O.L., Hu H. Efficacy and safety of liraglutide for obesity and people who are overweight: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Expert Rev. Clin. Pharmacol. 2022 Dec. 15(12). 1461-1469. doi: 10.1080/17512433.2022.2130760. Epub 2022 Oct 5. PMID: 36180402.
- Orlenko V.L., Ivaskiva K.Yu., Dobrovynska O.V., Tronko K.M., Bolgarska S.V., Prohorova G.O. Improved methods for treatment of patients with obesity based on the study of some pathogenetic factors of this disease. Endokrynologia. 2023. 28(2). 136-150. DOI: 10.31793/1680-1466.2023.28-2.136.

/61_2.jpg)