Журнал «Медицина неотложных состояний» Том 20, №1, 2024
Вернуться к номеру
Порівняльна характеристика ефективності спінальної анестезії з інтратекальним введенням бупівакаїну і його поєднання з ад’ювантами
Авторы: Щегольков Є.Е.
ДУ «Інститут травматології та ортопедії НАМН України», м. Київ, Україна
Національний університет охорони здоров’я України імені П.Л. Шупика, м. Київ, Україна
Рубрики: Медицина неотложных состояний
Разделы: Клинические исследования
Версия для печати
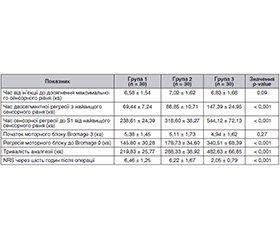
Актуальність. У даний час активно дискутується питання про ефективність використання різних ад’ювантів при проведенні спінальної анестезії. Мета: порівняти ефективність дексмедетомідину і фентанілу, що використовуються як ад’юванти, у поєднанні з інтратекальним введенням бупівакаїну при ендоскопічній біпортальній дискектомії. Матеріали та методи. У дослідження увійшло 150 пацієнтів. За допомогою блокової рандомізації відповідно до розміру вибірки пацієнти були розподілені на такі групи: група 1 — пацієнти отримували 2,5 мл інтратекально гіпербаричного бупівакаїну з 0,5 мл фізіологічного розчину; група 2 — 2,5 мл інтратекально гіпербаричного бупівакаїну з 25 мкг фентанілу; група 3 — 2,5 мл інтратекально гіпербаричного бупівакаїну з 5 мкг дексмедетомідину. Результати. Швидша поява сенсорного блоку до T8 спостерігалася в групі 3 (4,39 ± 0,90 хв), що було на 20,9 ± 1,4 % раніше порівняно з групою 1, де цей показник становив 5,55 ± 1,37 хв (р = 0,00124). При порівнянні аналогічних даних між групами 2 і 3 статистичної різниці не спостерігалося (р = 0,68135). Час двосегментної регресії з найвищого сенсорного рівня був найбільшим у групі бупівакаїну з дексмедетомідином (група 3) і становив 147,39 ± 24,95 хв. Подібна тенденція зберігалася у показниках часу сенсорної регресії до S1 від найвищого сенсорного рівня. Показник часу регресії до Bromage 0 у групі бупівакаїну з дексмедетомідином (група 3) був у середньому на 90,52 ± 3,25 % більше, ніж у групі бупівакаїну з фентанілом, і на 133,55 ± 4,18 % перевищував подібні значення в групі бупівакаїну з фізіологічним розчином (група 1). Загальна тривалість аналгезії була найбільшою в групі 3 і становила 482,63 ± 66,85 хв, що в середньому було на 67,39 ± 2,75 % більше порівняно з групою 2 і на 119,55 ± 4,14 % більше порівняно з групою 1 (p < 0,001). Інтенсивність болю через 6 год після операції була найнижчою в групі з бупівакаїном і дексмедетомідином (група 3) і становила 2,05 ± 0,79, що було на 67,04 ± 2,51 % нижче за аналогічний показник у групі бупівакаїну з фентанілом (група 2) і на 68,27 ± 2,35 % нижче, ніж у групі бупівакаїну з фізіологічним розчином (група 1). Висновки. Інтратекальне застосування гіпербаричного бупівакаїну з 5 мкг дексмедетомідину при проведенні спінальної анестезії дає максимальний ефект щодо розвитку моторного і сенсорного блоків, збільшує час післяопераційного знеболювання і зменшує потребу в післяопераційному використанні наркотичних аналгетиків.
Background. Currently, there is active discussion regarding the effectiveness of different adjuvants in spinal anesthesia. Objective: to compare the effectiveness of dexmedetomidine and fentanyl as adjuvants in combination with intrathecal bupivacaine administration during biportal endoscopic discectomy. Materials and methods. The study included 150 patients. Using block randomization based on a sample size, patients were divided intro the following groups: 1) group 1 — intrathecal hyperbaric bupivacaine 2.5 ml in 0.5 ml of normal saline; 2) group 2 — intrathecal hyperbaric bupivacaine 2.5 ml with fentanyl 25 µg; 3) group 3 — intrathecal hyperbaric bupivacaine with dexmedetomidine 5 µg. Results. A faster onset of a sensory block up to T8 was observed in group 3 (4.39 ± 0.90 minutes), which was 20.9 ± 1.4 % earlier compared to group 1, where this parameter was 5.55 ± 1.37 minutes (p = 0.00124). When comparing similar data between groups 2 and 3, no statistically significant difference was observed (p = 0.68135). The time to two-segment regression from the highest sensory level was highest during the administration of bupivacaine with dexmedetomidine (group 3), 147.39 ± 24.95 minutes. A similar trend was maintained in the time indicators of sensory regression to S1 from the highest sensory level. The time to Bromage 0 regression in the bupivacaine with dexmedetomidine group (group 3) was on average 90.52 ± 3.25 % higher compared to the bupivacaine and fentanyl group and exceeded similar values in the bupivacaine with normal saline group (group 1) by 133.55 ± 4.18 %. The overall duration of analgesia was highest in group 3 — 482.63 ± 66.85 minutes. This was on average 67.39 ± 2.75 % longer compared to group 2 and 119.55 ± ± 4.14 % longer compared to group 1 (p < 0.001). The pain severity 6 hours after surgery was the lowest in the group of bupivacaine and dexmedetomidine (group 3) — 2.05 ± 0.79 that was 67.04 ± 2.51 % lower than the corresponding value in the bupivacaine and fentanyl group (group 2) and 68.27 ± 2.35 % lower than in the bupivacaine with normal saline group (group 1). Conclusions. Intrathecal administration of hyperbaric bupivacaine with dexmedetomidine 5 µg during spinal anesthesia has the maximum effect in terms of deve-loping motor and sensory blocks, prolongs postoperative analgesia, and reduces the need for postoperative use of narcotic analgesics.
інтратекальна анестезія; спінальна аналгезія; ендоскопічна біпортальна дискектомія; інтратекально дексмедетомідин; інтратекально бупівакаїн; інтратекально фентаніл
intrathecal anesthesia; spinal analgesia; biportal endoscopic discectomy; intrathecal dexmedetomidine; intrathecal bupivacaine; intrathecal fentanyl
Вступ
Матеріали та методи
Результати
Обговорення
Висновки
- Jonayed S.А., Alam M.S., Al Mamun Choudhury A., Akter S., Chakraborty S. Efficacy, safety, and reliability of surgery on the lumbar spine under general versus spinal anesthesia — an analysis of 64 cases. J. Clin. Orthop. Trauma. 2021 Jan 8. 16. 176-181. doi: 10.1016/j.jcot.2020.12.032.
- Belgrami S.A.H., Kumar M., Singh D., Priye S. A comparison of fentanyl, dexmedetomidine and combination of fentanyl with dexmedetomidine on the quality of subarachnoid block and postoperative analgesia: A double-blind controlled study. Indian J. Anaesth. 2022 Jun. 66 (Suppl. 4). S220-S224. doi: 10.4103/ija.ija_701_21.
- Pushpanathan E., Setty T., Carvalho B., Sultan P. A Systematic Review of Postoperative Pain Outcome Measurements Utilised in Regional Anesthesia Randomized Controlled Trials. Anesthesiol. Res. Pract. 2018 Jul 29. 2018. 9050239. doi: 10.1155/2018/9050239.
- Derakhshan P., Faiz S.H.R., Rahimzadeh P., Salehi R., Khaef G. A Comparison of the Effect of Fractionated and Bolus Dose Injection on Spinal Anesthesia for Lower Limb Surgery: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Anesth. Pain Med. 2020 Aug 23. 10(5). e102228. doi: 10.5812/aapm.102228. PMID: 34150559.
- Shashikala T.K., Sagar S.S., Ramaliswamy P., Hudgi V.V. Comparing Effects of Intrathecal Adjuvants Fentanyl and Dexmedetomidine with Hyperbaric Ropivacaine in Patients Undergoing Elective Infraumbilical Surgeries: A Prospective, Double-Blind, Clinical Study. Anesth. Essays. Res. 2019 Oct-Dec. 13(4). 654-662. doi: 10.4103/aer.AER_183_18.
- Lee S.C., Kim T.H., Choi S.R., Park S.Y. No Difference between Spinal Anesthesia with Hyperbaric Ropivacaine and Intravenous Dexmedetomidine Sedation with and without Intrathecal Fentanyl: A Randomized Noninferiority Trial. Pain Res. Manag. 2022 Jan 13. 2022. 3395783. doi: 10.1155/2022/3395783.
- Tang Y., Yang M., Fu F., Huang X., Feng Y., Chen X. Comparison of the ED50 of intrathecal hyperbaric ropivacaine co-administered with or without intrathecal dexmedetomidine for cesarean section: A prospective, double-blinded, randomized dose-response trial using up-down sequential allocation method. J. Clin. Anesth. 2020 Jun. 62. 109725. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinane.2020.109725.
- Metcalf T., Sielatycki J.A., Schatzman N., Devin C.J., Goldstein J.A., Hodges S.D. Intrathecal Fentanyl With a Myofascial Plane Block in Open Lumbar Surgeries: A Case Series. Oper. Neurosurg. (Hagerstown). 2022 Jun 1. 22(6). 387-390. doi: 10.1227/ons.0000000000000168.
- Liu M., Wang B., Prudence B., Chen X. Effect of different doses of epidural dexmedetomidine on reducing visceral traction reaction for cesarean section: a double-blind randomized controlled trial. J. Anesth. 2023 Jun. 37(3). 371-378. doi: 10.1007/s00540-023-03166-8.
- Mohamed T., Susheela I., Balakrishnan B.P., Kaniyil S. Dexmedetomidine as Adjuvant to Lower Doses of Intrathecal Bupivacaine for Lower Limb Orthopedic Surgeries. Anesth. Essays. Res. 2017 Jul-Sep. 11(3). 681-685. doi: 10.4103/aer.AER_243_16.
- Nagaraj B., Vinay B.R., Vani N.V., Dayananda V.P. Intrathecal Nalbuphine and Dexmedetomidine as Adjuvants to Bupivacaine versus Plain Bupivacaine for Orthopedic Surgeries under Subarachnoid Block: A Comparative Study. Anesth. Essays. Res. 2022 Jul-Sep. 16(3). 381-385. doi: 10.4103/aer.aer_127_22.
- Kumar S., Choudhury B., Varikasuvu S.R., Singh H., Kumar S., Lahon J., Saikia D. A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Efficacy and Safety of Dexmedetomidine Combined With Intrathecal Bupivacaine Compared to Placebo. Cureus. 2022 Dec 12. 14(12). e32425. doi: 10.7759/cureus.32425.
- Liu S., Zhao P., Cui Y., Lu C., Ji M., Liu W. еt al. Effect of 5-μg Dose of Dexmedetomidine in Combination With Intrathecal Bupivacaine on Spinal Anesthesia: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Clin. Ther. 2020 Apr. 42(4). 676-690.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2020.02.009.
- Uppal V., Retter S., Casey M., Sancheti S., Matheson K., McKeen D.M. Efficacy of Intrathecal Fentanyl for Cesarean Delivery: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials With Trial Sequential Analysis. Anesth. Analg. 2020 Jan. 130(1). 111-125. doi: 10.1213/ANE.0000000000003975.
- Biswas A., Perlas A., Ghosh M., Chin K., Niazi A., Pandher B., Chan V. Relative Contributions of Adductor Canal Block and Intrathecal Morphine to Analgesia and Functional Recovery After Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Reg. Anesth. Pain Med. 2018 Feb. 43(2). 154-160. doi: 10.1097/AAP.0000000000000724. PMID: 29315129.
- Rahimzadeh P., Faiz S.H.R., Imani F., Derakhshan P., Amniati S. Comparative addition of dexmedetomidine and fentanyl to intrathecal bupivacaine in orthopedic procedure in lower limbs. BMC Anesthesiol. 2018 Jun 6. 18(1). 62. doi: 10.1186/s12871-018-0531-7. PMID: 29875020; PMCID: PMC5991430.
- Етичні принципи медичних досліджень за участю людини у якості об'єкта дослідження [Електронний ресурс]: Гельсінська декларація Всесвітньої медичної асоціації. https://zakon.rada.gov.ua/laws/show/990_005#Text (дата звернення: 11.09.2022).
- Загальна декларація про біоетику та права людини [Електронний ресурс]. https://www.un.org/ru/documents/decl_conv/declarations/bioethics_and_hr.shtml (дата звернення: 07.09.2022).
- Конвенція Ради Європи з прав людини та біомедицини [Електронний ресурс]. https://zakon.rada.gov.ua/laws/show/994_334#Text (дата звернення: 07.09.2022).
- Craig D., Carli F. Bromage motor blockade score — a score that has lasted more than a lifetime. Can. J. Anaesth. 2018 Jul. 65(7). 837-838. doi: 10.1007/s12630-018-1101-7.
- Numeric Rating Scale (NRS) [Електронний ресурс] / National Center for Biotechnology Information. 2007. https://www. painscale.com/article/numeric-rating-scale-nrs. (дата звернення: 10.09.2021).
- Mergeay M., Verster A., Van Aken D., Vercauteren M. Regional versus general anesthesia for spine surgery. A comprehensive review. Acta Anaesthesiol. Belg. 2015. 66(1). 1-9.
- Ebert K.M., Jayanthi V.R., Alpert S.A., Ching C.B., DaJusta D.G., Fuchs M.E., McLeod D.J., Whitaker E.E. Benefits of spinal anesthesia for urologic surgery in the youngest of patients. J. Pediatr. Urol. 2019 Feb. 15(1). 49.e1-49.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.jpurol.2018.08.011.
- Shah O.M., Bhat K.M. Comparison of the Efficacy and Safety of Morphine and Fentanyl as Adjuvants to Bupivacaine in Providing Operative Anesthesia and Postoperative Analgesia in Subumblical Surgeries Using Combined Spinal Epidural Technique. Anesth. Essays. Res. 2017 Oct-Dec. 11(4). 913-920. doi: 10.4103/aer.AER_99_17.
- Jagtap S., Chhabra A., Dawoodi S., Jain A. Comparison of intrathecal ropivacaine-fentanyl and bupivacaine-fentanyl for major lower limb orthopaedic surgery: A randomised double-blind study. Indian J. Anaesth. 2014 Jul. 58(4). 442-6. doi: 10.4103/0019-5049.138985.
- Pöpping D.M., Elia N., Marret E., Wenk M., Tramèr M.R. Opioids added to local anesthetics for single-shot intrathecal anesthesia in patients undergoing minor surgery: a meta-analysis of randomized trials. Pain. 2012 Apr. 153(4). 784-793. doi: 10.1016/j.pain.2011.11.028.
- Caballero-Lozada A.F., Gómez J.M., Torres-Mosquera A., González-Carvajal Á., Marín-Prado A., Zorrilla-Vaca A., Zhao X., Li J. Corrected and Republished: Impacts of intrathecal fentanyl on the incidence of postoperative nausea/vomiting: Systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized studies. J. Anaesthesiol. Clin. Pharmacol. 2022 Oct-Dec. 38(4). 529-536. doi: 10.4103/0970-9185.369222.

/57.jpg)
/58.jpg)