Журнал «Здоровье ребенка» Том 19, №6, 2024
Вернуться к номеру
Проблемні питання орфанних захворювань нервової системи у дітей в умовах воєнного стану
Авторы: Цимбалюк В.І. (1), Антипкін Ю.Г. (2), Кирилова Л.Г. (2), Мірошников О.О. (2)
(1) - Національна академія медичних наук України, м. Київ, Україна
(2) - ДУ «Всеукраїнський центр материнства та дитинства НАМН України», м. Київ, Україна
Рубрики: Педиатрия/Неонатология
Разделы: Справочник специалиста
Версия для печати
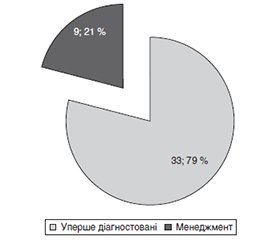
Зростання кількості орфанних (рідкісних) захворювань, більшість з яких мають частоту менше за 1 : 1 000 000, є серйозним викликом для сучасної медицини. У більшості випадків діагноз встановлюється із затримкою, що призводить до необоротних змін в організмі. Відділення психоневрології ДУ «Всеукраїнський центр материнства та дитинства НАМН України» з 2012 року займається діагностикою та лікуванням орфанних захворювань у дітей, 80 % яких супроводжуються ураженням нервової системи. Мета: провести ретроспективний аналіз медичної документації пацієнтів, що проходили лікування у відділенні психоневрології для дітей з перинатальною патологією та орфанними захворюваннями під час війни в Україні. Матеріали та методи. У період повномасштабного вторгнення до відділення було госпіталізовано 42 дитини з орфанними захворюваннями. Ретроспективно проаналізовані медичні карти стаціонарних хворих для виявлення особливостей діагностики, клінічних проявів та лікування. Результати. У 90 % випадків орфанні захворювання мали клінічні маски неврологічних патологій, що ускладнювало ранню діагностику. Найбільший відсоток діагностування (38 %) припадав на дітей віком від 1 до 5 років. Чоловіча стать була більш схильна до орфанних захворювань (співвідношення 1 : 2). Важливим аспектом є лікування: 21 % дітей були направлені до відділення для розробки тактики лікування мультидисциплінарною командою. Висновки. Незважаючи на виклики, відділення психоневрології ДУ «Всеукраїнський центр материнства і дитинства НАМН України» продовжує успішно боротися з орфанними захворюваннями у дітей. Хоча метою є діагностика на першому році життя, це залишається проблемою світової медичної спільноти. У відділенні також впроваджуються ефективні схеми таргетного лікування завдяки мультидисциплінарному підходу.
Background. The increasing number of orphan (rare) diseases, most of which have a prevalence of less than 1 : 1,000,000, poses a serious challenge for modern medicine. In most cases, diagnosis is delayed leading to irreversible changes in the body. The Department of Psychoneurology at the State Institution “Ukrainian Center of Maternity and Childhood of the National Academy of Medical Sciences of Ukraine” has been involved in diagnosing and treating orphan diseases in children since 2012, with 80 % of cases accompanied by nervous system involvement. The purpose was to conduct a retrospective analysis of medical records of patients treated at the Department of Psychoneurology for Children with Perinatal Pathology and Orphan Diseases during the war in Ukraine. Materials and methods. During the full-scale invasion, 42 children with orphan diseases were hospitalized to the department. A retrospective analysis of the medical records of these inpatients was conducted to identify the specifics of diagnosis, clinical manifestations, and treatment. Results. In 90 % of cases, orphan diseases presented with clinical masks of neurological pathologies, complicating early diagnosis. The highest percentage of diagnoses (38 %) occurred in children aged 1 to 5 years. Male children were more susceptible to orphan diseases (ratio 1 : 2). An important aspect of care was treatment: 21 % of children were referred to the department for developing treatment strategies by a multidisciplinary team. Conclusions. Despite the challenges, the Department of Psychoneurology at the State Institution “Ukrainian Center of Maternity and Childhood of the National Academy of Medical Sciences of Ukraine” continues to successfully combat orphan diseases in children. Although the goal is to diagnose these diseases within the first year of life, it remains a challenge for the global medical community. The department also implements effective targeted treatment regimens through a multidisciplinary approach.
орфанні захворювання; перинатальна неврологія; рання діагностика; таргетна терапія; мультидисциплінарна команда; клінічні маски; повне екзомне секвенування; неврологічні розлади
orphan diseases; perinatal neurology; early diagnosis; targeted therapy; multidisciplinary team; clinical masks; whole exome sequencing; neurological disord
Для ознакомления с полным содержанием статьи необходимо оформить подписку на журнал.
- Vickers, P.J. (2013). Challenges and opportunities in the treatment of rare diseases. Drug Discovery World, 14(2), 9-14. Available at: https://www.ddw-online.com/challenges-and-opportunities-in-the-treatment-of-rare-diseases-565-201304/.
- Council of the European Union (2009). Council Recommendation of 8 June 2009 on an action in the field of rare diseases (2009/C 151/02). Official Journal of the European Union, 151, 7-10. Available at: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/LexUriServ/LexUriServ.do?uri=OJ:C:2009:151:0007:0010:EN:PDF.
- Angelis, A., Tordrup, D., Kanavos, P. (2015). Socio-economic burden of rare diseases: A systematic review of cost of illness evidence. Health Policy, 119(7), 964-979. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.healthpol.2014.12.016.
- Rare Diseases UK (n.d.). Key statistics from the RDUK report ‘Experiences of Rare Diseases: An Insight from Patients and Families’. Available at: http://raredisease.org.uk/index.htm.
- Shire (2013). Rare Disease Impact Report: Insights from patients and the medical community. Available at: http://www.geneticalliance.org.uk/docs/e-update/rare-disease-impact-report.pdf.
- European Commission (n.d.). Useful Information on Rare Disea–ses from an EU Perspective. Health & Consumer Protection Directorate-General. Available at: http://ec.europa.eu/health/ph_information/documents/ev20040705_rd05_en.pdf.
- Aronson, J. (2006). Rare diseases and orphan drugs. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology, 61(3), 243-244. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2125.2005.02524.x.
- Bavisetty, S., et al. (2013). Emergence of pediatric rare diseases. Rare Diseases, 1(1), 1-6. https://doi.org/10.4161/rdis.23579.
- Kirilova, L.G., Miroshnikov, O.O., Yuzva, O.O., Kizlyak-Bubryak, M.E. (2017). Perinatal neurology and orphan diseases in Ukraine: Problems and perspectives. Perinatologiya i Pediatriya, 2(70), 126-133. https://doi.org/10.15574/PP.2017.70.126.
- Evtushenko, S.K. (2003). Neordinarnie (raritetnie) syndromy i zabolevaniya detey i vzroslikh: materialy mezhdynarodnoy naychno-prakticheskoy konferentsii. Donetsk-Svyatogorsk.
- Sun, Y., Ruivenkamp, C.A., Hoffer, M.J., et al. (2015). Next-generation diagnostics: Gene panel, exome, or whole genome? Human Mutation, 36(6), 648-655. https://doi.org/10.1002/humu.22783.
- Schwarze, K., Buchanan, J., Taylor, J.C., Wordsworth, S. (2018). Are whole-exome and whole-genome sequencing approaches cost-effective? A systematic review of the literature. Genetics in Medicine, 20(10), 1122-1130. https://doi.org/10.1038/gim.2017.247.
- Richards, S., Aziz, N., Bale, S., et al. (2015). Standards and guidelines for the interpretation of sequence variants: A joint consensus recommendation of the American College of Medical Gene–tics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Genetics in Medicine, 17(5), 405-424. https://doi.org/10.1038/gim.2015.30.
- Kyrylova, L., Miroshnykov, A., Yuzva, A. (2021). Epileptic encephalopathies in children with autistic spectrum disorders: From molecular genetic diagnostics to target therapy. Psychiatry, Psychotherapy and Clinical Psychology, 12(1), 249-259. https://doi.org/10.34883/PI.2021.12.2.006.
- Antipkin, Y.G., Kirilova, L.G., Miroshnikov, A.A., Yuzva, A.A. (2019). Mitochondrial diseases caused by mutations of the POLG gene: Problems of differential diagnosis. Perinatologiya i Pediatriya, 2(78), 58-66. https://doi.org/10.15574/PP.2019.78.58.