Журнал «Медицина неотложных состояний» Том 20, №8, 2024
Вернуться к номеру
Фармакологічна профілактика венозної тромбоемболії у пацієнтів хірургічного профілю
Авторы: Саволюк С.І.1, 2, Бондаренко Л.Б.3
(1) - Національний університет охорони здоров’я України імені П.Л. Шупика, м. Київ, Україна
(2) - КНП «Київська міська клінічна лікарня № 8», м. Київ, Україна
(3) - ДУ «Інститут фармакології і токсикології НАМН України», м. Київ, Україна
Рубрики: Медицина неотложных состояний
Разделы: Справочник специалиста
Версия для печати
Венозна тромбоемболія (ВТЕ) — це третє з найбільш поширених серцево-судинних захворювань після інфаркту міокарда та інсульту, що вражає значний відсоток населення. Хірургічне втручання є добре відомим фактором ризику розвитку венозної тромбоемболії, і чим більш серйозним оперативним втручанням підлягають пацієнти, тим вищим є ступінь ризику її розвитку у них. У цьому огляді наведено аналіз основних факторів ризику виникнення венозної тромбоемболії у пацієнтів, що перенесли хірургічне втручання, ролі оптимізації балансу ризиків тромбоемболії/кровотечі у процесі визначення індивідуальних ризиків пацієнтів хірургічного профілю, а також наведено порівняльний аналіз засобів фармакотерапії венозної тромбоемболії за допомогою лікарських засобів із антиагрегантною та антикоагулянтною активністю. Узагальнення наявних у науковій літературі даних свідчить, що, незважаючи на наявне різноманіття засобів із антиагрегантною та антикоагулянтною активністю, низькомолекулярні гепарини другого покоління, яскравим представником яких може слугувати беміпарин, наразі є препаратами першої лінії фармакопрофілактики венозної тромбоемболії за умов значних хіріргічних втручань, що підтверджено численними клінічними випробуваннями, проведеними по всьому світу. Спеціальними клінічними дослідженнями підтверджено рівнозначність ефективності та безпечності, а у низці випадків — і певні переваги препаратів саме другого покоління (на прикладі беміпарину) порівняно з найпоширенішим зараз у клінічній практиці препаратом першого покоління еноксапарином для пацієнтів хірургічного/онкологічного профілю. Тривалість профілактики кровотеч для пацієнтів хірургічного/онкологічного профілю при застосуванні беміпарину та інших низькомолекулярних гепаринів, відповідно до даних більшості клінічних випробувань із належним рівнем доказовості, може становити залежно від індивідуально оцінюваних балансів ризиків тромбоемболії/кровотеч від 1–2 тижнів аж до 35 діб.
Venous thromboembolism is the third most common cardiovascular disease after myocardial infarction and stroke, affecting a significant percentage of the population. Surgery is a well-known risk factor for venous thromboembolism, and the more serious the surgical procedure, the higher the risk of developing it. This review provides an analysis of the main risk factors for venous thromboembolism in operated patients, the role of optimizing the balance of thromboembolism/bleeding risk in determining the individual risks of surgical patients, and a comparative analysis of therapy for venous thromboembolism using drugs with antiplatelet and anticoagulant activity. A summary of the data available in the scientific literature shows that, despite the existing variety of antiplatelet and anticoagulant drugs, the second-generation low-molecular-weight heparins, with bemiparin as A prominent representative, are currently the first-line drugs for the pharmacoprophylaxis of venous thromboembolism in the context of major surgical interventions, which has been confirmed by numerous clinical trials conducted around the world. Special clinical studies have confirmed the equivalence of efficacy and safety, and in some cases, also certain advantages of second-generation drugs (for example, bemiparin) in comparison with enoxaparin, the most common first-generation drug currently used in clinical practice in surgical/oncological patients. The duration of bleeding prophylaxis with bemiparin and other low-molecular-weight heparins in surgical/oncological patients, according to the data of most clinical trials with an appropriate level of evidence, may range from 1–2 weeks up to 35 days, depending on the individually assessed balance of thromboembolism/bleeding risks.
венозна тромбоемболія; хірургічне втручання; фармакотерапія; беміпарин; еноксапарин; огляд
venous thromboembolism; surgical intervention; pharmacotherapy; bemiparin; enoxaparin; review
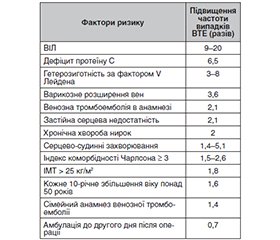
Фактори ризику розвитку венозної тромбоемболії
/11.jpg)
Баланс ризиків тромбоемболії/кровотечі
Фармакопрофілактика тромбоемболії
Низькомолекулярні гепарини
Висновки
- Søgaard KK, Schmidt M, Pedersen L, Horváth-Puhó E, Sørensen HT. 30-year mortality after venous thromboembolism: a population-based cohort study. Circulation. 2014;130(10):829-836.
- Wells PS, Hirsh J, Anderson DR, Lensing AWA, Foster G, Kearon GF, et al. Accuracy of clinical assessment of deep-vein thrombosis. Lancet. 1995;345:1326-1330.
- Hirsh J, Hull RD, Raskob GE. Clinical features and diagnosis of venous thrombosis. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 1986;8:114B-127B.
- Myers D, Farris D, Hawley A, Wrobleski S, Chapman A, Stoolman L, et al. Selectins influence thrombosis in a mouse model of experimental deep venous thrombosis. J. Surg. Res. 2002;108:212-221.
- Righini M, Le Gal G, De Lucia S, et al. Migration of dendritic cells across blood and lymphatic endothelial barriers. Thromb. Haemost. 2006;95:715-719.
- Risk of and prophylaxis for venous thromboembolism in hospital patients. Thromboembolic risk factors (THRIFT) consensus group. BMJ. 1992;305:567-574.
- Agu O, Hamilton G, Baker D. Graduated compression stockings in the prevention of venous thromboembolism. Br. J. Surg. 1999;86:992-1004.
- Snyder MA, Sympson AN, Scheuerman CM, Gregg JL, Hussain LR. Efficacy in deep vein thrombosis prevention with extended mechanical compression device therapy and prophylactic aspirin following total knee arthroplasty: A randomized control trial. J. Arthroplast. 2017;32:1478-1482.
- Nakamura M, Kamei M, Bito S, et al. Spinal anesthesia increases the risk of venous thromboembolism in total arthroplasty: Se-condary analysis of a J-PSVT cohort study on anesthesia. Medicine. 2017;96:e6748.
- Bergen MA, Wall KC, Kim CY, Garrigues GE. Occult left common iliac vein compression increases postoperative venous thromboembolism risk following total hip arthroplasty. J. Arthroplast. 2019;34:375-378.
- Frank B, Maher Z, Hazelton JP, et al. Venous thromboembolism after major venous injuries: Competing priorities. J. Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2017;83:1095-1101.
- Martínez-González J, Vila L, Rodríguez C. Bemiparin: second-generation, low-molecular-weight heparin for treatment and prophylaxis of venous thromboembolism. Expert Rev Cardiovasc Ther. 2008;6(6):793-802.
- Moreno González E, Fontcuberta J, de la Llama F. Prophylaxis of thromboembolic disease with RO-11 (ROVI), during abdominal surgery. Hepato-Gastroenterology. 1996;43:744-47.
- Lyman GH. Venous thromboembolism prophylaxis and treatment in patients with cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology Clinical Practice Guideline. J. Clin Oncol. 2013;31.
- Gould MK, Garcia DA, Wren SM. Prevention of VTE in nonorthopedic surgical patients: antitrombotic therapy and prevention of trombosis, 9th ed: American College of Chest Physicians evidence-based clinical practice guidelines. Chest. 2012;141(2):227-77.
- Roth-Isigkeit A, Borstel TV, Seyfarth M, Schmucker P. Perioperative serum levels of tumour-necrosis-factor alpha (TNF-α), IL-1β, IL-6, IL-10 and soluble IL-2 receptor in patients under-going cardiac surgery with cardiopulmonary bypass without and with correction for haemodilution. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 1999;118:242-246.
- Neumaier M, Metak G, Scherer MA. C-reactive protein as a parameter of surgical trauma: CRP response after different types of surgery in 349 hip fractures. Acta Orthop. 2006;77:788-790.
- Svitina H, Kyryk V, Skrypkina I, et al. Placenta-derived multipotent cells have no effect on the size and number of DMH-induced colon tumors in rats. Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine. 2017;14(3):2135-2147. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2017.4792.
- Grigorieva SM, Starosyla DB, Rybalko SL, Motronenko VV, Lutsenko TM, Galkin OYu. Effect of recombinant human interleukin-7 on Pseudomonas aeruginosa wound infection. Ukr. Biochem. J. 2019;91(5):7-15. https://doi.org/10.15407/ubj91.05.007.
- Galkin OYu, Lutsenko TM, Gorshunov YuV, Motronenko VV. Development of the method for microbiological purity testing of recombinant human interleukin-7-based product. Ukr. Biochem. J. 2017; 89(3):52-59. doi: https://doi.org/10.15407/ubj89.03.052.
- Dahl OE, Harenberg J, Wexels F, Preissner KT. Arterial and venous thrombosis following trauma and major orthopedic surgery: Molecular mechanisms and strategies for intervention. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2015;41:141-145.
- Albayati MA, Grover SP, Saha P, Lwaleed BA, Modarai B, Smith A. Postsurgical inflammation as a causative mechanism of venous thromboembolism. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2015;41:615-620.
- Wanderling C, Liles J, Finkler E, et al. Dysregulation of tissue factor, thrombin-activatable fibrinolysis inhibitor, and fibrinogen in patients undergoing total joint arthroplasty. Clin. Appl. Thromb. 2017;23:967-972.
- Kim Y, Park Y, Joo Y, Kim SY, Kim J. The role of platelet hyperreactivity in venous thromboembolism after total knee arthroplasty in elderly population without pharmacologic prophylaxis: A single-center study. Int. J. Lab. Hematol. 2019;41:102-108.
- Rumbaut RE, Thiagarajan P. Platelet-Vessel Wall Interactions in Hemostasis and Thrombosis; Morgan & Claypool Life Sciences: San Rafael, CA, USA, 2010.
- Olson JJ, Schwab PE, Jackson J, Lange JK, Bedair HS, Abdeen A. HIV-positive patients are at increased risk of venous thromboembolism after total joint replacement. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2021;29(11):479-485.
- Cheung KL, Bouchard BA, Cushman M. Venous thromboembolism, factor VIII and chronic kidney disease. Thromb Res. 2018;170:10-19.
- Koster T, Rosendaal FR, Briët E, et al. Protein C deficiency in a controlled series of unselected outpatients: an infrequent but clear risk factor for venous thrombosis (Leiden Thrombophilia Study). Blood. 1995:5;85(10):2756-2761.
- Kujovich JL. Factor V Leiden thrombophilia. Genet Med. 2011;13(1):1-16.
- White RH, Romano PS, Zhou H, Rodrigo J, Bargar W. Incidence and time course of thromboembolic outcomes following total hip or knee arthroplasty. Arch Intern Med. 1998;158(14):1525-1531.
- Bahl V, Hu HM, Henke PK, Wakefield TW, Campbell DA Jr, Caprini JA. A validation study of a retrospective venous thromboembolism risk scoring method. Ann Surg. 2010;251(2):344-350.
- Ngarmukos S, Kim KI, Wongsak S, et al. Asia-Pacific (AP) region venous thromboembolism (VTE) consensus group. Asia-Pacific venous thromboembolism consensus in knee and hip arthroplasty and hip fracture surgery: Part 1. Diagnosis and risk factors. Knee Surg Relat Res. 2021;19:18.
- Branchford BR, Carpenter SL. The role of inflammation in venous thromboembolism. Front Pediatr. 2018;6(6):142.
- Ogdie A, Kay McGill N, Shin DB, et al. Risk of venous thromboembolism in patients with psoriatic arthritis, psoriasis and rheumatoid arthritis: a general populationbased cohort study. Eur Heart J. 2018;39(39):3608-3614.
- Takemoto CM. Venous thromboembolism in cystic fibrosis. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2012;47(2):105-112.
- Hisada Y, Mackman N. Cancer-associated pathways and biomarkers of venous thrombosis. Blood. 2017;130(13):1499-1506.
- Labunets I, Panteleymonova T, Kyryk V, Toporova O, Pikus P, Litoschenko Z. The effects of human umbilical cord-derived multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells transplantation in mice of different strains with an experimental model of parkinsonism. Cell Organ Transpl. 2023;11(2):96-103. Available from: https://doi.org/10.22494/cot.v11i2.155.
- Konovalov SV, Moroz VM, Yoltukhivskyi MV, Husakova IV, Deryabina OG, Tochilovskyi AA, Kordium VA. Effect of Mesenchymal Stromal Cells of Different Origin on DNA Fragmentation in Rat Hippocampal Neuronal Nuclei After Ischemia-Reperfusion. Innov Biosyst Bioeng. 2024;8(4). DOI: 10.20535/ibb.2024.8.4.315490.
- Nuzhnyi O, Nikolaiev R, Tkachuk Z. Fluorescence-Based Study of Oligonucleotide Interactions with Recombinant Proteins: Insulin, Interferon α2-β, Somatotropin, and Their Receptors. Innovative Biosystems and Bioengineering. 2024;8(3):50-59. https://doi.org/10.20535/ibb.2024.8.3.304238.
- Lizarralde-Iragorri MA, Shet AS. Sickle cell disease: a paradigm for venous thrombosis pathophysiology. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(15):E5279.
- Tormene D, Campello E, Simion C, et al. Incidence of VTE in asymptomatic children with deficiencies of antithrombin, protein C, and protein S: a prospective cohort study. Blood Adv. 2020;4(21):5442-5448.
- Zhang ZH, Shen B, Yang J, Zhou ZK, Kang PD, Pei FX. Risk factors for venous thromboembolism of total hip arthroplasty and total knee arthroplasty: a systematic review of evidences in ten years. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2015;10(1):24.
- Morris GK, Henry APJ, Preston BJ. Prevention of deep-vein thrombosis by low-dose heparin in patients undergoing total hip replacement. Lancet. 1974;304:797-800.
- Chan NC, Siegal D, Lauw MN, et al. A systematic review of contemporary trials of anticoagulants in orthopaedic thromboprophylaxis: suggestions for a radical reappraisal. J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2015;40(2):231-239.
- Prasad N, Padmanabhan V, Mullaji A. Blood loss in total knee arthroplasty: an analysis of risk factors. Int Orthop. 2007;31(1):39-44.
- Frisch NB, Wessell NM, Charters MA, Yu S, Jeffries JJ, Silverton CD. Predictors and complications of blood transfusion in total hip and knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2014;29(9):189-192.
- Pugely AJ, Martin CT, Gao Y, Mendoza-Lattes S, Callaghan JJ. Differences in short-term complications between spinal and general anesthesia for primary total knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2013;95(3):193-199.
- Galkin A, Komar A, Gorshunov Yu, Besarab A, Soloviova V. New monoclonal antibodies to the prostate-specific antigen: obtaining and studying biological properties. The Journal of Microbiology, Biotechnology and Food Sciences. 2019;9(3):573-577. https://doi.org/10.15414/jmbfs.2019/20.9.3.573-577.
- Zufferey PJ, Ollier E, Delavenne X, Laporte S, Mismetti P, Duffull SB. Incidence and risk factors of major bleeding following major orthopaedic surgery with fondaparinux thromboprophylaxis. A time-to-event analysis. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2018;84(10):2242-2251.
- Anderson DR, Dunbar M, Murnaghan J, et al. Aspirin or Rivaroxaban for VTE prophylaxis after hip or knee arthroplasty. N Engl J Med. 2018;378(8):699-707.
- Shohat N, Ludwick L, Goh GS, Streicher S, Chisari E, Parvizi J. Aspirin thromboprophylaxis is associated with less major bleeding events following total joint arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2022;37(2):379-384.e2.
- Ker K, Roberts I, Shakur H, Coats TJ. Antifibrino-lytic drugs for acute traumatic injury. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015;9(5):CD004896.
- Taeuber I, Weibel S, Herrmann E, et al. Association of intravenous tranexamic acid with thromboembolic events and mortality: a systematic review, metaanalysis, and meta-regression. JAMA Surg. 2021;14(6):e210884.
- Porter SB, Spaulding AC, Duncan CM, Wilke BK, Pagnano MW, Abdel MP. Tranexamic acid was not associated with increased complications in high-risk patients with intertrochanteric fracture. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2022;104(13):1138-1147.
- Cionac Florescu S, Anastase DM, Munteanu AM, Stoica IC, Antonescu D. Venous thromboembolism following major orthopedic surgery. Maedica. 2013;8:189-194.
- Deitelzweig SB, McKean SC, Amin AN, Brotman DJ, Jaffe AK, Spyropoulos AC. Prevention of venous thromboembolism in the orthopedic surgery patient. Cleve Clin. J. Med. 2008;75 (Suppl. S3):S27-S36.
- Jenny JY, Bulaid Y, Boisrenoult P, et al. French Society of Orthopaedic Surgery, Traumatology (SofCOT). Bleeding and thromboembolism risk of standard antithrombotic prophylaxis after hip or knee replacement within an enhanced recovery program. Orthop. Traumatol. Surg. Res. 2020;106:1533-1538.
- Alsheikh K, Hilabi A, Aleid A, et al. Efficacy and Safety of Thromboprophylaxis Post-Orthopedic Surgery. Cureus. 2021;13:e19691.
- Etscheidt J, Shahien A, Gainey M, et al. Review of Therapeutic Options for the Prevention of VTE in Total Joint Arthroplasty. Geriatrics. 2020;5:18.
- Mulloy B, Hogwood J, Gray E, Lever R, Page CP. Pharmacology of Heparin and Related Drugs. Pharmacol Rev. 2016 Jan;68(1):76-141.
- Falck-Ytter Y, Francis CW, Johanson NA, et al. Prevention of VTE in orthopedic surgery patients: Antithrombotic Therapy and Prevention of Thrombosis, 9th ed: American College of Chest Physicians Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines. Chest. 2012;141 (Suppl. S2):e278S-e325S.
- Anderson DR, Morgano GP, Bennett C, et al. American Society of Hematology 2019 guidelines for management of venous thromboembolism: Prevention of venous thromboembolism in surgical hospita-lized patients. Blood Adv. 2019;3:3898-3944.
- Guyatt GH, Akl EA, Crowther M, Gutterman D.D, Schuünemann HJ. American College of Chest Physicians Antithrombotic Therapy and Prevention of Thrombosis Panel. Executive summary: Antithrombotic Therapy and Prevention of Thrombosis, 9th ed: American College of Chest Physicians Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines. Chest. 2012;141 (Suppl. S2):7S-47S.
- Douketis JD, Spyropoulos AC, Murad MH, et al. Perioperative Management of Antithrombotic Therapy: An American College of Chest Physicians Clinical Practice Guideline. Chest. 2022;162:e207-e243.
- Douketis JD, Spyropoulos AC, Murad MH, et al. Executive Summary: Perioperative Management of Antithrombotic Therapy: An American College of Chest Physicians Clinical Practice Guideline. Chest. 2022;162:1127-1139.
- Shchokina K, Shtrygol’ S, Shebeko S, Bielik H, Kutsenko T, & Taran A. Study of chondroprotective properties of interleukin-1 receptor antagonist. ScienceRise: Pharmaceutical Science. 2024;1(47):4-11. https://doi.org/10.15587/2519-4852.2024.298740.
- Hull RD, Pineo GF, Francis C, et al. Low-molecular-weight heparin prophylaxis using dalteparin in close proximity to surgery vs warfarin in hip arthroplasty patients: A double-blind, randomized comparison. The North American Fragmin Trial Investigators. Arch. Intern. Med. 2000;160:2199-2207.
- Hull RD, Pineo GF, Stein PD, et al. Timing of initial administration of low-molecular-weight heparin prophylaxis against deep vein thrombosis in patients following elective hip arthroplasty: A systematic review. Arch. Intern. Med. 2001;161:1952-1960.
- Kakkar AK, Brenner B, Dahl OE, et al. Extended duration rivaroxaban versus short-term enoxaparin for the prevention of venous thromboembolism after total hip arthroplasty: A double-blind, randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2008;372:31-39.
- Eriksson BI, Dahl OE, Rosencher N, et al. Dabigatran etexilate versus enoxaparin for prevention of venous thromboembolism after total hip replacement: A randomised, double-blind, non-inferiority trial. Lancet. 2007;370:949-956.
- Lassen MR, Gallus A, Raskob GE, Pineo G, Chen D, Ramirez LM. ADVANCE-3 Investigators. Apixaban versus enoxaparin for thromboprophylaxis after hip replacement. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010;363:2487-2498.
- Anderson DR, Dunbar M, Murnaghan J, et al. Aspirin or Rivaroxaban for VTE Prophylaxis after Hip or Knee Arthroplasty. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018;378:699-707.
- Planes A, Vochelle N, Darmon JY, Fagola M, Bellaud M, Huet Y. Risk of deep-venous thrombosis after hospital discharge in patients having undergone total hip replacement: Double-blind randomised comparison of enoxaparin versus placebo. Lancet. 1996;348:224-228.
- Bergqvist D, Benoni G, Björgell O, et al. Low-molecular-weight heparin (enoxaparin) as prophylaxis against venous thromboembolism after total hip replacement. N. Engl. J. Med. 1996;335:696-700.
- Dahl OE, Andreassen G, Aspelin T, et al. Prolonged thromboprophylaxis following hip replacement surgery — results of a double-blind, prospective, randomised, placebo-controlled study with dalteparin (Fragmin). Thromb. Haemost. 1997;77:26-31.
- Lassen MR, Borris LC, Anderson BS, et al. Efficacy and safety of prolonged thromboprophylaxis with a low molecular weight heparin (dalteparin) after total hip arthroplasty — the Danish Prolonged Prophylaxis (DaPP) Study. Thromb. Res. 1998;89:281-287.
- Comp PC, Spiro TE, Friedman RJ, et al., Enoxaparin Clinical Trial Group. Prolonged enoxaparin therapy to prevent venous thromboembolism after primary hip or knee replacement. Enoxaparin Clinical Trial Group. J. Bone Joint Surg. Am. 2001;83:336-345.
- White RH, Romano PS, Zhou H, Rodrigo J, Bargar W. Incidence and time course of thromboembolic outcomes following total hip or knee arthroplasty. Arch. Intern. Med. 1998;158:1525-1531.
- Eikelboom JW, Quinlan DJ, Douketis JD. Extended-duration prophylaxis against venous thromboembolism after total hip or knee replacement: A meta-analysis of the randomised trials. Lancet. 2001;358:9-15.
- Hull RD, Pineo GF, Stein PD, et al. Extended out-of-hospital low-molecular-weight heparin prophylaxis against deep venous thrombosis in patients after elective hip arthroplasty: A systematic review. Ann. Intern. Med. 2001;135:858-869.
- Sobieraj DM, Lee S, Coleman CI, et al. Prolonged versus standard-duration venous thromboprophylaxis in major orthopedic surgery: A systematic review. Ann. Intern. Med. 2012;156:720-727.
- Fisher WD, Agnelli G, George DJ, et al. Extended venous thromboembolism prophylaxis in patients undergoing hip fracture surgery — the SAVE-HIP3 study. Bone Joint J. 2013;95:459-466.
- O’Donnell M, Linkins LA, Kearon C, Julian J, Hirsh J. Reduction of out-of-hospital symptomatic venous thromboembolism by extended thromboprophylaxis with low-molecular-weight heparin following elective hip arthroplasty: A systematic review. Arch. Intern. Med. 2003;163:1362-1366.
- Forster R, Stewart M. Anticoagulants (extended duration) for prevention of venous thromboembolism following total hip or knee replacement or hip fracture repair. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2016;3:CD004179.
- Heit JA, Elliott CG, Trowbridge AA, Morrey BF, Gent M, Hirsh J. Ardeparin sodium for extended out-of-hospital prophylaxis against venous thromboembolism after total hip or knee replacement. A randomized, double-blind, placebocontrolled trial. Ann. Intern. Med. 2000;132:853-861.
- Eriksson BI, Borris LC, Friedman RJ, et al. Rivaroxaban versus enoxaparin for thromboprophylaxis after hip arthroplasty. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008;358:2765-2775.
- Deitelzweig S, Jaff MR. Medical management of venous thromboembolic disease. Tech. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2004;7:63-67.
- Alur İ, Dodurga Y, Seçme M, et al. Anti-tumor effects of bemiparin in HepG2 and MIA PaCa-2 cells. Gene. 2016 Jul 10;585(2):241-6. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2016.03.044. Epub 2016 Apr 2.
- Hull RD, Pineo GF, Francis C, et al. Low-molecular-weight heparin prophylaxis using dalteparin extended out-of-hospital vs in-hospital warfarin/out-of-hospital placebo in hip arthroplasty patients: A double-blind, randomized comparison. North American Fragmin Trial Investigators. Arch. Intern. Med. 2000;160:2208-2215.
- Mahmoudi M, Sobieraj DM. The cost-effectiveness of oral direct factor Xa inhibitors compared with low-molecular-weight heparin for the prevention of venous thromboembolism prophylaxis in total hip or knee replacement surgery. Pharmacotherapy. 2013;33:1333-1340.
- Goltsev A, Bondarovych M, Gaevska Y, Dubrava T, Babenko N, & Ostankov M. Modern Methods of Obtaining Immune Dendritic Cells with Anti-Tumor Potential. Innovative Biosystems and Bioengineering. 2024;8(1):56-76. https://doi.org/10.20535/ibb.2024.8.1.291879.
- Fuji T, Ochi T, Niwa S, Fujita S. Prevention of postoperative venous thromboembolism in Japanese patients undergoing total hip or knee arthroplasty: Two randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled studies with three dosage regimens of enoxaparin. J Orthop Sci. 2008;13:442-451.
- Leclerc JR, Geerts WH, Desjardins L, et al. Prevention of deep vein thrombosis after major knee surgery — A randomized, double-blind trial comparing a low molecular weight heparin fragment (enoxaparin) to placebo. Thromb. Haemost. 1992;67:417-423.
- Levine MN, Gent M, Hirsh J, et al. Ardeparin (low-mole-cularweight heparin) vs graduated compression stockings for the prevention of venous thromboembolism. A randomized trial in patients undergoing knee surgery. Arch. Intern. Med. 1996;156:851-856.
- Turpie AG, Levine MN, Hirsh J, et al. A randomized controlled trial of a low-molecular-weight heparin (enoxaparin) to prevent deep-vein thrombosis in patients undergoing elective hip surgery. N. Engl. J. Med. 1986;315:925-929.
- Jørgensen PS, Knudsen JB, Broeng L, et al. The thromboprophylactic effect of a low-molecular-weight heparin (Fragmin) in hip fracture surgery. A placebo-controlled study. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1992;278:95-100.
- Kapoor A, Ellis A, Shaffer N, et al. Comparative effectiveness of venous thromboembolism prophylaxis options for the patient undergoing total hip and knee replacement: A network meta-analysis. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2017;15:284-294.
- Hull R, Raskob G, Pineo G, et al. A comparison of subcutaneous low-molecular-weight heparin with warfarin sodium for prophylaxis against deep-vein thrombosis after hip or knee implantation. N. Engl. J. Med. 1993;329:1370-1376.
- Friedman RJ, Davidson BL, Heit J, et al. RD heparin compared with warfarin for prevention of venous thromboembolic disease following total hip or knee arthroplasty. RD Heparin Arthroplasty Group. J. Bone Joint Surg. Am. 1994;76:1174-1185.
- Leclerc JR, Geerts WH, Desjardins L, et al. Prevention of venous thromboembolism after knee arthroplasty. A randomized, double-blind trial comparing enoxaparin with warfarin. Ann. Intern. Med. 1996;124:619-626.
- Fitzgerald RHJr Spiro TE, Trowbridge AA, Gardiner GAJr Whitsett TL, et al. Enoxaparin Clinical Trial Group. Prevention of venous thromboembolic disease following primary total knee arthroplasty. A randomized, multicenter, open-label, parallel-group comparison of enoxaparin and warfarin. J. Bone Joint Surg. Am. 2001;83:900-906.
- Hamulyák K, Lensing AW, van der Meer J, Smid WM, van Ooy A, Hoek JA. Subcutaneous low-molecular weight heparin or oral anticoagulants for the prevention of deep-vein thrombosis in elective hip and knee replacement? Fraxiparine Oral Anticoagulant Study Group. Thromb. Haemost. 1995;74:1428-1431.
- Mismetti P, Laporte S, Zufferey P, Epinat M, Decousus H, Cucherat M. Prevention of venous thromboembolism in orthopedic surgery with vitamin K antagonists: A meta-analysis. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2004;2:1058-1070.
- Raskob GE, Hirsh J. Controversies in timing of the first dose of anticoagulant prophylaxis against venous thromboembolism after major orthopedic surgery. Chest. 2003;124 (Suppl. S6):379S-385S.
- Francis CW, Pellegrini VDJr, Totterman S, Boyd ADJr, Marder VJ, et al. Prevention of deep-vein thrombosis after total hip arthroplasty. Comparison of warfarin and dalteparin. J. Bone Joint Surg. Am. 1997;79:1365-1372.
- Colwell CW, Jr, Collis DK, Paulson R, et al. Comparison of enoxaparin and warfarin for the prevention of venous thromboembolic disease after total hip arthroplasty. Evaluation during hospitalization and three months after discharge. J. Bone Joint Surg. Am. 1999;81:932-940.
- Samama CM, Vray M, Barré J, et al. Extended venous thromboembolism prophylaxis after total hip replacement: A comparison of low-molecular-weight heparin with oral anticoagulant. Arch. Intern. Med. 2002;162:2191-2196.
- Hill J, Treasure T; National Clinical Guideline Centre for Acute and Chronic Conditions. Reducing the risk of venous thromboembolism in patients admitted to hospital: Summary of NICE guidance. BMJ. 2010;340:c95.
- Levine MN, Hirsh J, Gent M, et al. Prevention of deep vein thrombosis after elective hip surgery. A randomized trial comparing low molecular weight heparin with standard unfractionated heparin. Ann. Intern. Med. 1991;114:545-551.
- Karthikeyan G, Eikelboom JW, Turpie AG, Hirsh J. Does acetyl salicylic acid (ASA) have a role in the prevention of venous thromboembolism? Br. J. Haematol. 2009;146:142-149.
- Imperiale TF, Speroff T. A meta-analysis of methods to prevent venous thromboembolism following total hip replacement. JAMA 1994;271:1780-1785.
- Westrich GH, Bottner F, Windsor RE, Laskin RS, Haas SB, Sculco TP. VenaFlow plus Lovenox vs VenaFlow plus aspirin for thromboembolic disease prophylaxis in total knee arthroplasty. J. Arthroplast. 2006;21 (Suppl. S2):139-143.
- Drescher FS, Sirovich BE, Lee A, Morrison DH, Chiang WH, Larson RJ. Aspirin versus anticoagulation for prevention of venous thromboembolism major lower extremity orthopedic surgery: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Hosp. Med. 2014;9:579-585.
- CRISTAL Study Group; Camporese GS, Kelly TL, Pratt N, et al. Effect of Aspirin vs. Enoxaparin on Symptomatic Venous Thromboembolism in Patients Undergoing Hip or Knee Arthroplasty: The CRISTAL Randomized Trial. JAMA. 2022;328:719-727.
- Ozturk PA, Yilmaz T, Ozturk U. Effects of Bemiparin Sodium Versus Dabigatran Etexilate After Anastomosis in Rat Carotid Arteries on the Development of Neointima and Thrombolytic Efficacy. World Neurosurg. 2019 Jun;126:e731-e735. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2019.02.139. Epub 2019 Mar 7.
- Kakkar VV, Howes J, Sharma V, Kadziola Z. A comparative double-blind, randomised trial of a new second generation LMWH (bemiparin) and UFH in the prevention of post-operative venous thromboembolism. The Bemiparin Assessment group. Thromb Haemost. 2000 Apr;83(4):523-9.
- Muñoa L, González AB, Díaz de Rada P, et al. Rivaroxaban is as efficient and safe as bemiparin as thromboprophylaxis in knee arthroscopy. Musculoskelet Surg. 2014 Jun;98(1):21-5. doi: 10.1007/s12306-013-0287-7. Epub 2013 Jul 14.
- Cosmi B, Palareti G. Old and new heparins. Thromb Res. 2012;129:388-91.
- Alalaf SK, Jawad RK, Muhammad PR, et al. Bemiparin versus enoxaparin as thromboprophylaxis following vaginal and abdominal deliveries: a prospective clinical trial. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2015;15:72. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12884-015-0515-2.
- Navarro Quilis A, Castellet E, Rocha E, Paz Jiménez J, Planès A; Bemiparin Study Group in Knee Arthroplasty. Efficacy and safety of bemiparin compared with enoxaparin in the prevention of venous thromboembolism after total knee arthroplasty: A randomized, double blind clinical trial. J Thromb Haemost. 2003;1:425-32.
- Revilla-Peñaloza F, Olsoff-Pagovich PJ, Ochoa-Gomez JR, et al. Randomized Trial of Deep Vein Thrombosis Chemoprophylaxis with Bemiparin and Enoxaparin in Patients with Moderate to High Thrombogenic Risk Undergoing Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery Procedures. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2020 Jun;44(3):820-829. doi: 10.1007/s00266-019-01573-5. Epub 2019 Dec 18.
- Sagüillo K, Pérez-Flecha F, Almeida F, et al. Bemiparin vs enoxaparin in the prevention of thrombosis in microvascular head and neck reconstruction. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2022 Aug;75(8):2831-2870. doi: 10.1016/j.bjps.2022.06.041. Epub 2022 Jun 20.
- Ferriols-Lisart R, Ferriols-Lisart F, Jiménez-Torres V. Effectiveness and safety of bemiparin versus low-molecular weight heparins in orthopaedic surgery. Pharm World Sci. 2002 Jun;24(3):87-94. doi: 10.1023/a:1016187426582.
- Abbas MS. Bemiparin versus enoxaparin in the prevention of venous thromboembolism among Intensive Care Unit patients. Indian J Crit Care Med. 2017;21:419-23.
- Schulman S, Beyth RJ, Kearon C, Levine MN. Hemorrhagic complications of anticoagulant and thrombolytic treatment: American College of Chest Physicians Evidence Based Clinical Practice Guidelines (8th Edition). Chest. 2008;133 (6 Suppl):257S 98S.
- Ciccone MM, Cortese А, Corbo А, et al. Bemiparin, an effective and safe low molecular weight heparin: A review, Vascul Pharmacol. 2014. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.vph.2014.03.001.
- Honorato J, Gómez-Outes A, Navarro-Quilis A, et al. Pharmacoeconomic analysis of bemiparin and enoxaparin as prophylaxis for venous thromboembolism in total knee replacement surgery. Pharmacoeconomics. 2004;22(13):885-94. doi: 10.2165/00019053-200422130-00006.
- Gómez-Outes A, Berto P, Prandoni P. Cost-effectiveness of bemiparin in the prevention and treatment of venous thromboembolism. Expert Rev Pharmacoecon Outcomes Res. 2006 Jun;6(3):249-59. doi: 10.1586/14737167.6.3.249.
- Zierler BK. Ultrasonography and diagnosis of venous thromboembolism. Circulation. 2004;109 (12 Suppl 1):I9-14.
- Desciak MC, Martin DE. Perioperative pulmonary embolism: Diagnosis and anesthetic management. J Clin Anesth 2011;23:153-65.
- Wittram C, Maher MM, Yoo AJ, Kalra MK, Shepard JA, McLoud TC. CT angiography of pulmonary embolism: Diagnostic criteria and causes of misdiagnosis. Radiographics. 2004;24:1219-38.
- Robinson S, Zincuk A, Strøm T, Larsen TB, Rasmussen B, Toft P. Enoxaparin, effective dosage for Intensive Care patients: Double blinded, randomised clinical trial. Crit Care. 2010;14:R41.
- Babenko M, Kosyachenko K. Modern approaches to typologization and modeling in the health technology assessment. ScienceRise: Pharmaceutical Science. 2024;5 (51):78-88. https://doi.org/10.15587/2519-4852.2024.314005.
- Robinson S, Zincuk A, Larsen UL, Ekstrøm C, Nybo M, Rasmussen B, et al. A comparative study of varying doses of enoxaparin for thromboprophylaxis in critically ill patients: A double blinded, randomised controlled trial. Crit Care. 2013;17:R75.
- Kearon C, Akl EA, Comerota AJ, et al. Antithrombotic therapy for VTE disease: Antithrombotic Therapy and Prevention of Thrombosis, 9th ed: American College of Chest Physicians evidence-based clinical practice guidelines. Chest. 2012;141:Suppl:e419S-e494S.
- Zaki HA, Hamdi Alkahlout B, Basharat K, et al. Low-Mole-cular-Weight Heparin Versus Warfarin in Adult Cancer Patients as a Precision Medicine for Thrombosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cureus. 2023 July 01;15(7):e41268. DOI: 10.7759/cureus.41268.
- Gao J-H, Chu X-C, Wang L-L, et al. Effects of different anticoagulant drugs on the prevention of complications in patients after arthroplasty: A network meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017 Oct;96(40):e8059. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000008059.
- Shao J-B, Ni C-F, Duan P-F, Jin Y-H. Preventive Effects of Different Drugs on Asymptomatic Lower Extremities Deep Venous Thrombosis After Artificial Joint Replacement: A Mixed Treatment Comparison. Am J Ther. 2019 Jan/Feb;26(1):e45-e53. doi: 10.1097/MJT.0000000000000438.
- Feng W, Wang X, Huang D, Lu A. Ranking the efficacy of anticoagulants for the prevention of venous thromboembolism after total hip or knee arthroplasty: A systematic review and a network meta-analysis. Pharmacol Res. 2021 Apr;166:105438. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2021.105438. Epub 2021 Feb 1.
- Bajpai V, Patel T, Dwivedi P, et al. Factor Xa Inhibitors and Low Molecular Weight Heparins in Perioperative Surgical Thromboprophylaxis: A Network Meta-Analysis. Cardiovasc Hematol Agents Med Chem. 2024 Oct 2. doi: 10.2174/0118715257331706240919172310. Online ahead of print.