Журнал «Медицина неотложных состояний» Том 20, №8, 2024
Вернуться к номеру
Застосування ESP-блокади як компонента поєднаної анестезії при абдомінальній гістеректомії
Авторы: A.V. Ryzhkovskyi
Yuri Semenyuk Rivne Regional Clinical Hospital, Rivne, Ukraine
Danylo Halytsky Lviv National Medical University, Lviv, Ukraine
Рубрики: Медицина неотложных состояний
Разделы: Клинические исследования
Версия для печати
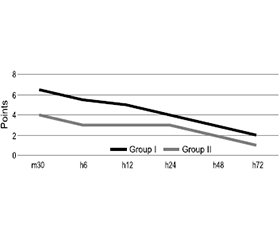
Актуальність. Блокади фасціальних площин можуть забезпечити ефективне знеболювання при операціях на черевній порожнині. Мета: оцінити, чи може додавання блокади erector spinae plane (ESP) зменшити біль після абдомінальної гістеректомії порівняно з відсутністю регіонарної анестезії. Матеріали та методи. Проведено проспективне когортне обсерваційне дослідження, що включало 50 пацієнток віком 40–55 років з ускладненими симптомними фіброміомами матки. Їх було розділено на дві групи, в обох виконували загальну анестезію, а в ІІ групі ще й двосторонню ESP-блокаду. Етапи дослідження: інтраопераційний (h0), 30 хвилин (m30), 6 (h6), 12 (h12), 24 (h24), 48 (h48), 72 години (h72) після операції. Аналізували рівень болю, інтраопераційну потребу у фентанілі, добову потребу в морфіні, частоту серцевих скорочень і середній артеріальний тиск. Результати. Встановлено, що рівень болю за візуальною аналоговою шкалою в І групі сягав максимальних значень на етапах m30 та h6 і становив 6,5 [3,0; 8,5] та 5,5 [3,0; 7,0] бала, тоді як у ІІ групі — 4,0 [3,0; 8,5] та 3,0 [2,0; 8,0] бала відповідно (p < 0,05). Добова потреба в морфіні на стадії h24 становила 7,5 [2,5; 7,0] мг/добу в І групі та 5,0 [2,5; 10,0] мг/добу в ІІ групі (p < 0,05). Зареєстровано відмінності в частоті серцевих скорочень між I та II групами на етапах дослідження m30, h6 та h24 — показники були вищими в І групі (p > 0,05). Висновки. Додавання ESP-блокади асоціювалося з меншою потребою у фентанілі під час втручання, нижчим рівнем болю, меншою потребою в морфіні після операції.
Background. Fascial plane blocks can provide effective analgesia for abdominal surgeries. The purpose of our study was to assess whether adding erector spinae plane (ESP) block preoperatively could reduce pain after abdominal hysterectomy, compared with no regional analgesia. Materials and methods. We conducted a prospective cohort observational study that included 50 patients aged 40–55 years with complicated symptomatic fibroids. They were divided into 2 groups. Both of them underwent general anesthesia, but the group II additio-nally received ESP block bilaterally. Stages of the study: intraoperative stage (h0), 30 minutes (m30), 6 (h6), 12 (h12), 24 (h24), 48 (h48), 72 hours (h72) after the surgery. We analyzed the pain level, intraoperative need for fentanyl, the daily requirement of morphine, heart rate and mean arterial pressure. Results. It was found that the level of pain according to visual analog scale in the group I reached its maximum values at the stages m30 and h6 and was 6.5 [3.0; 8.5] and 5.5 [3.0; 7.0] points, while in the II group — 4.0 [3.0; 8.5] and 3.0 [2.0; 8.0] points, respectively (p < 0.05). The daily requirement of morphine at the h24 stage was 7.5 [2.5; 7.0] mg/day in the group I, and 5.0 [2.5; 10.0] mg/day in the group II (p < 0.05). There were differences in heart rate between the groups I and II at m30, h6 and h24 stage of study — the values were higher in the group I (p > 0.05). Conclusions. Adding ESP block was associated with a lower need for fentanyl during surgery, pain level, and need for morphine after the surgery.
рекомендації ERAS; гістеректомія; регіонарна анестезія; ESP-блокада; мультимодальна аналгезія
ERAS recommendations; hysterectomy; regional anesthesia; ESP block; multimodal analgesia
Для ознакомления с полным содержанием статьи необходимо оформить подписку на журнал.
- Bauchat JR, Habib AS. Evidence-based anesthesia for major gynecologic surgery. Anesthesiol Clin. 2015 Mar;33(1):173-207. doi: 10.1016/j.anclin.2014.11.011.
- Krishnan S, Cascella M. Erector Spinae Plane Block. In: StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024 Jan. Avai-lable from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK545305/.
- Forero M, Adhikary SD, Lopez H, Tsui C, Chin KJ. The Erector Spinae Plane Block: A Novel Analgesic Technique in Thoracic Neuropathic Pain. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2016 Sep-Oct;41(5):621-7. doi: 10.1097/AAP.0000000000000451.
- Altinpulluk EY, Ozdilek A, Colakoglu N, Beyoglu CA, Ertas A, et al. Bilateral postoperative ultrasound-guided erector spinae plane block in open abdominal hysterectomy: a case series and cadaveric investigation. Rom J Anaesth Intensive Care. 2019 Apr;26(1):83-88. doi: 10.2478/rjaic-2019-0013.
- Catarci S, Zanfini BA, Capone E, Vassalli F, Frassanito L, et al. Blended (Combined Spinal and General) vs. General Anesthesia for Abdominal Hysterectomy: A Retrospective Study. J Clin Med. 2023 Jul 19;12(14):4775. doi: 10.3390/jcm12144775.
- Buvanendran A, Kroin JS. Multimodal analgesia for controlling acute postoperative pain. Curr Opin Anaesthesiol. 2009 Oct;22(5):588-93. doi: 10.1097/ACO.0b013e328330373a.
- Nelson G, Bakkum-Gamez J, Kalogera E, Glaser G, Altman A, et al. Guidelines for perioperative care in gynecologic/oncology: Enhanced Recovery After Surgery (ERAS) Society recommendations-2019 update. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 2019 May;29(4):651-668. doi: 10.1136/ijgc-2019-000356.
- Mathew P, Aggarwal N, Kumari K, Gupta A, Panda N, Bagga R. Quality of recovery and analgesia after total abdominal hysterectomy under general anesthesia: A randomized controlled trial of TAP block vs epidural analgesia vs parenteral medications. J Anaesthesiol Clin Pharmacol. 2019 Apr-Jun;35(2):170-175. doi: 10.4103/joacp.JOACP_206_18.
- Kamel AAF, Amin OAI, Ibrahem MAM. Bilateral Ultrasound-Guided Erector Spinae Plane Block Versus Transversus Abdominis Plane Block on Postoperative Analgesia after Total Abdominal Hysterectomy. Pain Physician. 2020 Jul;23(4):375-382.
- Hamed MA, Boules ML, Mahmoud MAEM, Abdelghaffar RA. The effect of erector spinae plane block on fentanyl consumption during open abdominal hysterectomy: a randomised controlled study. BMC Anesthesiol. 2023 Jun 5;23(1):194. doi: 10.1186/s12871-023-02156-3.
- Bai G, Tsai M, Hung T, et al. 198 fascial plane blocks in total abdominal hysterectomy: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. Regional Anesthesia & Pain Medicine. 2021;70:A103.
- Chin KJ, Versyck B, Elsharkawy H, Rojas Gomez MF, Sala-Blanch X, Reina MA. Anatomical basis of fascial plane blocks. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2021 Jul;46(7):581-599. doi: 10.1136/rapm-2021-102506.
- Chin KJ, Malhas L, Perlas A. The Erector Spinae Plane Block Provides Visceral Abdominal Analgesia in Bariatric Surgery: A Report of 3 Cases. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2017 May/Jun;42(3):372-376. doi: 10.1097/AAP.0000000000000581.
- Chin KJ, Adhikary S, Sarwani N, Forero M. The analgesic efficacy of pre-operative bilateral erector spinae plane (ESP) blocks in patients having ventral hernia repair. Anaesthesia. 2017 Apr;72(4):452-460. doi: 10.1111/anae.13814.
- Carugno J, Fatehi M. Abdominal Hysterectomy. In: StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024 Jan. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK564366/.
- Laberge P, Leyland N, Murji A, Fortin C, Martyn P, et al.; Society of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists of Canada. Endometrial ablation in the management of abnormal uterine bleeding. J Obstet Gynaecol Can. 2015 Apr;37(4):362-79. doi: 10.1016/s1701-2163(15)30288-7.
- Marshburn PB, Matthews ML, Hurst BS. Uterine artery embolization as a treatment option for uterine myomas. Obstet Gynecol Clin North Am. 2006 Mar;33(1):125-44. doi: 10.1016/j.ogc.2005.12.009.