Международный эндокринологический журнал Том 21, №4, 2025
Вернуться к номеру
Предиктори змін біомаркерів у патогенезі кардіометаболічних фенотипів при поєднанні артеріальної гіпертензії, цукрового діабету 2-го типу та ожиріння
Авторы: Дунаєва І.П.
Харківський національний медичний університет, м. Харків, Україна
Рубрики: Эндокринология
Разделы: Клинические исследования
Версия для печати
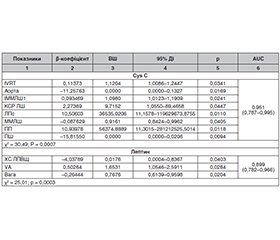
Актуальність. Попри накопичення даних щодо діагностичного значення окремих біомаркерів, існує дефіцит досліджень, які б інтегрували мультифакторний аналіз змін їх рівнів із клінічною оцінкою лікування у пацієнтів із поєднаною артеріальною гіпертензією (АГ), цукровим діабетом 2-го типу (ЦД2) та ожирінням. Особливо мало відомо про предиктори змін цих маркерів під впливом комбінованої фармакотерапії та про їхню взаємодію з гемодинамічними, метаболічними й ренальними параметрами. Мета: оцінити прогностичну роль змін рівнів біомаркерів катестатину, кардіотрофіну-1, β2-мікроглобуліну, цистатину С, ліпокаліну, асоційованого з желатиназою нейтрофілів, N-кінцевого пропептиду натрійуретичного гормону В-типу, лептину та інсуліну у формуванні сприятливого кардіометаболічного фенотипу у пацієнтів з АГ, ЦД2 та ожирінням, а також визначити клініко-функціональні предиктори їх динаміки на тлі цільової фармакотерапії. Матеріали та методи. Досліджено 250 пацієнтів, розподілених на чотири клінічні групи залежно від поєднання супутніх патологій. У межах роботи оцінювалися рівні катестатину, кардіотрофіну-1, β2-мікроглобуліну, цистатину С, NGAL, NT-proBNP, лептину та інсуліну. Результати. Аналіз показав, що зміни рівнів цих біомаркерів мають тісний зв’язок із структурно-функціональними параметрами серця і нирок, вуглеводно-ліпідним обміном, індексом маси тіла, глікемічним контролем, а також залежать від лікування. Найбільш прогностично значущими виявилися CST, CTF-1, Cys C, NT-proBNP, β2-M та лептин. Отримані дані дозволяють розглядати їх як предиктори ремоделювання міокарда, діастолічної дисфункції, порушення ренальної функції, гіпертрофії та дисліпідемії. Висновки. Дослідження підкреслює доцільність інтеграції біомаркерного моніторингу в рутинну практику стратифікації ризику та персоналізації терапевтичного підходу у пацієнтів з АГ, особливо в умовах метаболічної коморбідності.
Background. Despite the accumulation of data on the diagnostic value of individual biomarkers, there is a lack of studies that integrate multivariate analysis of changes in their levels with clinical assessment of treatment in patients with combined hypertension, type 2 diabetes, and obesity. In particular, little is known about predictors of changes in these markers under the influence of combination pharmacotherapy and about their interaction with hemodynamic, metabolic, and renal parameters. The aim of the study was to assess the prognostic role of changes in the levels of biomarkers catestatin, cardiotrophin-1, β2-microglobulin, cystatin C, neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin, N-terminal prohormone of brain natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP), leptin and insulin in the formation of a favorable cardiometabolic phenotype in patients with hypertension, type 2 diabetes and obesity, as well as to identify clinical and functional predictors of their dynamics against the background of targeted pharmacotherapy. Materials and methods. A total of 250 patients were included and classified into four clinical groups based on the combination of comorbidities. The study evaluated the levels of catestatin, cardiotrophin-1, β2-microglobulin, cystatin C, neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin, NT-proBNP, leptin, and insulin. Results. The analysis showed that changes in these biomarkers are closely related to structural and functional parameters of the heart and kidneys, carbohydrate and lipid metabolism, body mass index, glycemic control, and also depend on the treatment. Catestatin, cardiotrophin-1, cystatin C, NT-proBNP, β2-microglobulin, and leptin demonstrated the highest predictive value. The results indicate they may serve as predictors of myocardial remodeling, diastolic dysfunction, renal impairment, hypertrophy, and dyslipidemia. Conclusions. The study emphasizes the feasibility of integrating biomarker monitoring into routine practice for risk stratification and personalization of therapeutic approach in patients with hypertension, especially in metabolic comorbidity.
артеріальна гіпертензія; цукровий діабет 2-го типу; ожиріння; біомаркери; катестатин; кардіотрофін-1; цистатин С; β2-мікроглобулін; NT-proBNP; лептин; предиктори; ремоделювання
hypertension; type 2 diabetes mellitus; obesity; biomarkers; catestatin; cardiotrophin-1; cystatin C; β2-microglobulin; NT-proBNP; leptin; predictors; myocardial remodeling
Для ознакомления с полным содержанием статьи необходимо оформить подписку на журнал.
- Bays HE, Kirkpatrick CF, Maki KC, Toth PP, Morgan RT, Tondt J, Christensen SM, Dixon DL, Jacobson TA. Obesity, dyslipi–demia, and cardiovascular disease: A joint expert review from the Obesity Medicine Association and the National Lipid Association 2024. J Clin Lipidol. 2024 May-Jun;18(3):e320-e350. doi: 10.1016/j.jacl.2024.04.001.
- Einarson TR, Acs A, Ludwig C, Panton UH. Economic Burd of Cardiovascular Disease in Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review. Value Health. 2018 Jul;21(7):881-890. doi: 10.10jval.2017.12.019.
- Koval SM, Yushko KO, Snihurska IO, Starchenko TG, Pankiv VI, Lytvynova OM, Mysnychenko OV. Relations of angiotensin-(1-7) with hemodynamic and cardiac structural and functional parameters in patients with hypertension and type 2 diabetes. Arterial Hypertension. 2019;23(3):183-189. doi: 10.5603/AH.a2019.0012.
- Serhiyenko V, Sehin V, Pankiv V, Serhiyenko A. Post-traumatic stress disorder, dyssomnias, and metabolic syndrome. International Journal of Endocrinology (Ukraine). 2024;20(1):58-67. https://doi.org/10.22141/2224-0721.20.1.2024.1359.
- Davies MJ, Aroda VR, Collins BS, Gabbay RA, Green J, Maruthur NM, Rosas SE, et al. Management of Hyperglycemia in Type 2 Diabetes, 2022. A Consensus Report by the American Diabetes Association (ADA) and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD). Diabetes Care. 2022 Nov 1;45(11):2753-2786. doi: 10.2337/dci22-0034. PMID: 36148880; PMCID: PMC10008140.
- Lauder L, Mahfoud F, Azizi M, Bhatt DL, Ewen S, Kario K, Parati G, et al. Hypertension management in patients with cardiovascular comorbidities. Eur Heart J. 2023 Jun 20;44(23):2066-2077. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehac395. PMID: 36342266.
- Teck J. Diabetes-Associated Comorbidities. Prim Care. 2022 Jun;49(2):275-286. doi: 10.1016/j.pop.2021.11.004. Epub 2022 Apr 22. PMID: 35595482.
- Bozic J, Kumric M, Ticinovic Kurir T, Urlic H, Martinovic D, Vilovic M, Tomasovic Mrcela N, Borovac JA. Catestatin as a Biomar–ker of Cardiovascular Diseases: A Clinical Perspective. Biomedicines. 2021 Nov 25;9(12):1757. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9121757. PMID: 34944578; PMCID: PMC8698910.
- Dejenie TA, Abebe EC, Mengstie MA, Seid MA, Gebeyehu NA, Adella GA, Kassie GA, et al. Dyslipidemia and serum cystatin C levels as biomarker of diabetic nephropathy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Apr 4;14:1124367. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1124367. PMID: 37082121; PMCID: PMC10112538.
- Hogas S, Bilha SC, Branisteanu D, Hogas M, Gaipov A, Kanbay M, Covic A. Potential novel biomarkers of cardiovascular dysfunction and disease: cardiotrophin-1, adipokines and galectin-3. Arch Med Sci. 2017 Jun;13(4):897-913. doi: 10.5114/aoms.2016.58664. Epub 2016 Mar 22. PMID: 28721158; PMCID: PMC5507105.
- Polat U, Aydinlar A, Caliskan S, Boyuk F, Unal O. The correlation between cardiac enzymes and cardiotrophin-1 levels in patients with acute coronary syndrome. Int J Cardiovasc Sci. 2021 Jun 17;34(5 Suppl 1):12-21. doi: https://doi.org/10.36660/ijcs.20210010.
- Shi F, Sun L, Kaptoge S. Association of beta-2-microglo–bulin and cardiovascular events and mortality: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Atherosclerosis. 2021 Mar 1;320:70-78. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2021.01.018.
- Romejko K, Markowska M, Niemczyk S. The Review of Current Knowledge on Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin (NGAL). International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023;24(13):10470. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241310470.
- Poetsch MS, Strano A, Guan K. Role of leptin in cardiovascular diseases. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2020 Jun 16;11:354. doi: https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2020.00354.
- Chi K, Liu J, Li X, Wang H, Li Y, Liu Q, Zhou Y, Ge Y. Biomarkers of heart failure: advances in omics studies. Mol Omics. 2024 Mar 25;20(3):169-183. doi: https://doi.org/10.1039/d3mo00173c.
- Han X, Zhang S, Chen Z, Adhikari BK, Zhang Y, Zhang J, Sun J, Wang Y. Cardiac biomarkers of heart failure in chro–nic kidney disease. Clinica Chimica Acta. 2020;510:298-310. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cca.2020.07.040.
- Castiglione V, Aimo A, Vergaro G, Saccaro L, Passino C, Emdin M. Biomarkers for the diagnosis and management of heart failure. Heart Fail Rev. 2022 Mar;27(2):625-643. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10741-021-10105-w.
- Cao Z, Jia Y, Zhu B. BNP and NT-proBNP as Diagnostic Biomarkers for Cardiac Dysfunction in Both Clinical and Forensic Medicine. Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Apr 12;20(8):1820. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20081820.
- Ianoș RD, Cozma A, Lucaciu RL, Hangan AC, Negrean V, Mercea DC, Ciulei G, Pop C, Procopciuc LM. Role of Circulating Biomarkers in Diabetic Cardiomyopathy. Biomedicines. 2024;12(9). doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12092153.
- Pankiv V, Yuzvenko T, Mykhalchyshyn G. Relationships between diabetes distress and biomarkers in people with type 1 diabetes mellitus. International Journal of Endocrinology (Ukraine). 2025;20(8):639-642. https://doi.org/10.22141/2224-0721.20.8.2024.1472.