Журнал «Здоровье ребенка» Том 20, №5, 2025
Вернуться к номеру
Збереження здоров’я дітей і підлітків: на що звернути увагу педіатру та сімейному лікарю?
Авторы: Бекетова Г.В. (1), Солдатова О.В. (1), Горячева І.П. (1), Шарікадзе О.В. (1), Кундик Р.П. (2)
(1) - Національний університет охорони здоров’я імені П.Л. Шупика, м. Київ, Україна
(2) - Державний науково-контрольний інститут біотехнології і штамів мікроорганізмів, м. Київ, Україна
Рубрики: Педиатрия/Неонатология
Разделы: Справочник специалиста
Версия для печати
Актуальність. У Глобальній програмі Організації Об’єднаних Націй «Цілі сталого розвитку» були ухвалені ключові напрямки розвитку країн світу до 2030 року через ефективне досягнення 17 глобальних цілей. Для реалізації третьої глобальної цілі, що стосується досягнення міцного здоров’я і благополуччя та запобігання найпоширенішим у світі хронічним захворюванням і дефіцитним станам була обґрунтована необхідність забезпечення добробуту людей будь-якого віку та дотримання здорового способу життя. Мета дослідження: здійснити огляд наукових досліджень щодо впливу здорового способу життя на стан здоров’я дітей і підлітків у сучасних умовах та обґрунтувати необхідність усвідомленого дотримання його основних компонентів (збалансованого харчування, повноцінного сну, відповідної віку фізичної активності та відмови від шкідливих звичок (тютюнопаління і вживання алкоголю)) для профілактики розвитку неінфекційних захворювань, ожиріння, гастроезофагеальної рефлюксної хвороби та дефіциту вітаміну D. Матеріали та методи. Огляд літературних джерел базувався на аналізі результатів опублікованих у відкритому доступі наукових досліджень з використанням інформаційно-пошукових систем PubMed, Web of Science, Scopus, Google Scholar та ResearchGate. Ми розглядали наукові дослідження, опубліковані переважно за останні 5 років. Для даної статті було відібрано 137 наукових публікацій. Результати. Виявлено, що недотримання збалансованого харчування, відповідної віку фізичної активності, недостатній сон на фоні вживання тютюну і алкоголю тісно пов’язані з порушеннями здоров’я та супроводжуються високим ризиком розвитку тяжкої соціально значущої неінфекційної патології (цукровий діабет, хронічні обструктивні респіраторні, онкологічні та серцево-судинні захворювання), а також надлишковою масою тіла/ожирінням, гастроезофагеальною рефлюксною хворобою, дефіцитними станами та значним рівнем смертності у дорослих. Результати багатьох досліджень та метааналізів підтвердили, що усвідомлене дотримання основних принципів здорового способу життя (нормалізація харчування і сну, підвищення фізичної активності, відмова від таких шкідливих звичок, як тютюнопаління і вживання алкоголю), контроль маси тіла, скринінг вітамінного та мінерального статусу і раннє консультування родин може поліпшити стан здоров’я та запобігти формуванню низки хронічних захворювань і життєво небезпечних дефіцитних станів. Висновки. Усвідомлене дотримання населенням принципів здорового способу життя з раннього дитинства є основою найбільш ефективних, безпечних та економічно обґрунтованих профілактичних стратегій, реалізація яких повинна здійснюватись спільними зусиллями міжнародних організацій, державних і недержавних структур із залученням громадськості, засобів масової інформації, професійних об’єднань, працівників освіти та медичної спільноти.
Background. The United Nations Global Agenda “Sustainable Development Goals” adopted key directions for the development of the world’s countries by 2030 through the effective achievement of 17 global goals. To implement the third global goal, which concerns the achievement of good health and well-being and the prevention of the most common chronic diseases and deficiencies, the need to ensure the well-being of people of all ages and maintain a healthy lifestyle was substantiated. Objective: to review scientific research on the impact of a healthy lifestyle on the health of children and adolescents in modern conditions and to substantiate the need for conscious adherence to its main components (balanced nutrition, adequate sleep, age-appropriate physical activity, and breaking bad habits (smoking and alcohol consumption)) to prevent the development of non-communicable diseases, obesity, gastroesophageal reflux disease, and vitamin D deficiency. Materials and methods. The literature review was based on the analysis of the results of published open-access scientific studies from PubMed, Web of Science, Scopus, Google Scholar and ResearchGate. We reviewed scientific studies published primarily in the last 5 years. 137 scientific publications were selected for this article. Results. It has been found that failure to maintain a balanced diet, age-appropriate physical activity, and sufficient sleep, combined with tobacco and alcohol use, are closely related to health disorders and are accompanied by a high risk of developing severe socially significant non-communicable diseases (diabetes mellitus, cancer, chronic obstructive respiratory, and cardiovascular diseases), as well as overweight/obesity, gastroesophageal reflux disease, deficiencies and significant mortality in adults. The results of many studies and meta-analyses have confirmed that conscious adherence to the basic principles of a healthy lifestyle (normalization of nutrition and sleep, increased physical activity, breaking bad habits such as smoking and alcohol consumption),weight control, screening for vitamin and mineral status, and early family counseling can improve health and prevent the development of a number of chronic diseases and life-threatening deficiencies. Conclusions. Population’s conscious adherence to the principles of a healthy lifestyle from early childhood is the basis of the most effective, safe and economically sound preventive strategies whose implementation should be carried out by joint efforts of international organizations, state and non-state structures with the involvement of the public, media, professional associations, educators, and the medical community.
здоров’я; здоровий спосіб життя; діти; підлітки; вітамін D; ожиріння; гастроезофагеальна рефлюксна хвороба; харчування; фізична активність; сон; тютюнопаління; алкоголь
health; healthy lifestyle; children; adolescents; vitamin D; obesity; gastroesophageal reflux disease; nutrition; physical activity; sleep, smoking; alcohol
Вступ
Матеріали та методи
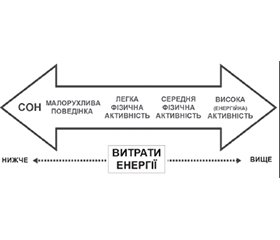
Результати
/88.jpg)
Висновки
- The 17 Goals. Sustainable Development Goals. UN. Retrieved 10 August 2022.
- United Nations Resolution adopted by the General Assembly on 6 July 2017, Work of the Statistical Commission pertaining to the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development (A/RES/71/31).
- Goal 3: Good health and well-being. UNDP. Archived from the original on 30 December 2020. Retrieved 13 April 2017.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Healthy Li–ving. https://www.cdc.gov/healthyweight/healthy_eating/index.html.
- Oster H, Chaves I. Effects of Healthy Lifestyles on Chronic Di–seases: Diet, Sleep and Exercise. Nutrients. 2023 Oct 31;15(21):4627. doi: 10.3390/nu15214627. PMID: 37960280. PMCID: PMC10650398.
- Nutritional health: strategies for disease prevention. Part of the book series: Nutrition and Health (NH). [S.l.]: Humana. Editors: Temple NJ, Wilson T, Jacobs DR, Bray Jr GA. 2023. ISBN 3-031-24662-4. OCLC 13661242497.
- Humphries DL, Scott ME, Vermund SH. Nutrition and infectious diseases: shifting the clinical paradigm. Part of the book series: Nutrition and Health (NH). 2021. Cham. ISBN 978-3-030-56913-6. OCLC 1228650322.
- FAO; IFAD; UNICEF; WFP; WHO. The State of Food Security and Nutrition in the World 2024. doi: 10.4060/cd1254en. ISBN 978-92-5-138882-2.
- Fan H, Han X, Shang X, et al. Fruit and vegetable intake and the risk of cataract: insights from the UK Biobank study. Eye (eng). 2023;1-9. doi: 10.1038/s41433-023-02498-9. ISSN 1476-5454.
- Hustad KS, Rundblad A, Ottestad I, et al. Comprehensive lipid and metabolic profiling in healthy adults with low and high compsumption of fatty fish: a cross-sectional study. British Journal of Nutrition. 2021;125(9):1034-1042. doi: 10.1017/S0007114520002305. ISSN 0007-1145.
- WHO (World Health Organization). Healthy Diet. 29 April 2020.
- Vijay A, Valdes AM. Role of the gut microbiome in chronic diseases: a narrative review. European Journal of Clinical Nutrition. 2022;76(4):489-501. doi: 10.1038/s41430-021-00991-6. ISSN 1476-5640.
- The quest for healthy diets. What are healthy diets? WHO. FAO. 25 October 2024. doi: 10.4060/cd1587en. ISBN 978-92-5-139116-7.
- Tsugane S. Why has Japan become the world’s most long-lived country: insights from a food and nutrition perspective. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2021 Jun;75(6):921-928. doi: 10.1038/s41430-020-0677-5. Epub 2020 Jul 13. PMID: 32661353. PMCID: PMC8189904.
- Rolands MR, Hackl LS, Bochud M, Lê KA. Protein Adequacy, Plant Protein Proportion, and Main Plant Protein Sources Consumed Across Vegan, Vegetarian, Pescovegetarian, and Semivegetarian Diets: A Systematic Review. J Nutr. 2025 Jan;155(1):153-167. doi: 10.1016/j.tjnut.2024.07.033. Epub 2024 Aug 6. PMID: 39117040.
- Sandri E, Cerdá Olmedo G, Piredda M, Werner LU, Dentamaro V. Explanatory AI Predicts the Diet Adopted Based on Nutritional and Lifestyle Habits in the Spanish Population. Eur J Investig Health Psychol Educ. 2025 Jan 24;15(2):11. doi: 10.3390/ejihpe15020011. PMID: 39997075. PMCID: PMC11854735.
- WHO guideline: sugar consumption recommendation. World Health Organization. Retrieved 6 January 2018.
- WHO — Unhealthy diet. who.int.Department of Agriculture and U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. Dietary Guidelines for Americans, 2020-2025. 9th Edition. December 2020. Available at DietaryGuidelines.gov.
- Coconut Oil. The Nutrition Source. The President and Fellows of Harvard College. 24 July 2018. Retrieved 8 August 2022.
- Heart-healthy eating patterns. Heart Foundation. Archived from the original on 28 March 2023.
- Touvier M, da Costa Louzada ML, Mozaffarian D, et al. Ultra-processed foods and cardiometabolic health: public health policies to reduce consumption cannot wait. BMJ. 2023;383:e075294. doi: 10.1136/bmj-2023-075294. PMC 10561017. PMID 37813465.
- Lane MM, Gamage E, Du S, et al. Ultra-processed food exposure and adverse health outcomes: umbrella review of epidemiological meta-analyses. BMJ. 2024 Feb 28;384:e077310. doi: 10.1136/bmj-2023-077310. PMID: 38418082. PMCID: PMC10899807.
- Jennings GL, Audehm R, Bishop W, et al. National Heart Foundation of Australia: position statement on coronary artery calcium scoring for the primary prevention of cardiovascular disease in Australia. Med J Aust. 2021 May;214(9):434-439. doi: 10.5694/mja2.51039. Epub 2021 May 7. PMID: 33960402. PMCID: PMC8252756.
- Riccardi G, Giosuè A, Calabrese I, Vaccaro O. Dietary recommendations for prevention of atherosclerosis. Cardiovascular Research. 2021;118(5):1188-1204. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvab173. PMID: 34229346.
- Dominguez LJ, Di Bella G, Veronese N, Barbagallo M. Impact of Mediterranean Diet on Chronic Non-Communicable Diseases and Longevity. Nutrients. 2021;13(6):2028. doi: 10.3390/nu13062028. PMC 8231595. PMID 34204683.
- Hidalgo-Mora JJ, García-Vigara A, Sánchez-Sánchez ML, et al. The Mediterranean diet: A historical perspective on food for health. Maturitas. 2020;132:65-69. doi: 10.1016/j.maturitas.2019.12.002. PMID 31883665. S2CID 209510802.
- Liska D, Mah E, Brisbois T, et al. Narrative Review of Hydration and Selected Health Outcomes in the General Population. Nutrients. 2019 Jan 1;11(1):70. doi: 10.3390/nu11010070. PMID: 30609670. PMCID: PMC6356561.
- Gropper SS. The Role of Nutrition in Chronic Disease. Nutrients. 2023 Jan 28;15(3):664. doi: 10.3390/nu15030664. PMID: 36771368. PMCID: PMC9921002.
- Li G, Li L, Adachi JD, et al. Relationship between Serum 25-Hydroxyvitamin D Level and Risk of Recurrent Stroke. Nutrients. 2022;14:1908. doi: 10.3390/nu14091908.
- Shah VP, Nayfeh T, Alsawaf Y, et al. A Systematic Review Supporting the Endocrine Society Clinical Practice Guidelines on Vitamin D. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2024 Jul 12;109(8):1961-1974.
- Наказ МОЗ України від 17.04.2023 р. № 730 «Про затвердження Стандартів медичної допомоги «Профілактика та лікування аліментарного рахіту».
- Holick MF, Binkley NC, Bischoff-Ferrari HA, et al. Endocrine Society. Evaluation, treatment, and prevention of vitamin D deficiency: an Endocrine Society clinical practice guideline. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2011 Jul;96(7):1911-30. doi: 10.1210/jc.2011-0385. Epub 2011 Jun 6. Erratum in: J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2011 Dec;96(12):3908. Erratum in: J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2024 Sep 16;109(10):e1991. doi: 10.1210/clinem/dgae373. PMID: 21646368.
- Proia P, Amato A, Drid P, et al. The Impact of Diet and Physical Activity on Bone Health in Children and Adolescents. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021;12:704647. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.704647.
- Rizzoli R. Dairy products and bone health. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2022 Jan;34(1):9-24. doi: 10.1007/s40520-021-01970-4. Epub 2021 Sep 7. PMID: 34494238. PMCID: PMC8794967.
- Scientific Report of the 2025 Dietary Guidelines Advisory Committee. https://www.fmi.org/governmentaffairs/regulatory/comments/view/comments-filed/2025/02/10/hhs-usda--dietary-guidelines-advisorycommittescientific-report-(february-10--2025).
- Mason IC, Grimaldi D, Reid KJ, et al. Light exposure during sleep impairs cardiometabolic function. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2022 Mar 22;119(12):e2113290119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2113290119. Epub 2022 Mar 14. PMID: 35286195. PMCID: PMC8944904.
- Nelson R. The Dichotomy Of Sleep: REM And Non-REM Stages, And Their Impact On Human Health. Quantify Sleep. 2021. Retrieved 15 July 2023.
- Hatori М, Panda S, Hirota T. Circadian Clocks. Neuromethods. Springer US. 2023;429. ISBN 9781071625774.
- Figueiro MG, Pedler D. Red light: A novel, non-pharmacological intervention to promote alertness in shift workers. Journal of Safety Research. 2020;74:169-177. doi: 10.1016/j.jsr.2020.06.003. ISSN 0022-4375.
- Rivera AM, Huberman AD. Neuroscience: A Chromatic Retinal Circuit Encodes Sunrise and Sunset for the Brain. Current bio–logy. 2020;30(7):R316-R318. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2020.02.090. PMCID: PMC8407369. PMID: 32259506.
- Hale L, Troxel W, Buysse DJ. Sleep health: an opportunity for public health to address health equity. Annu Rev Public Health. 2020;41(1):81-99. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-publhealth-040119- 094412.
- Ramar K, Malhotra RK, Carden KA, et al. Sleep is essential to health: an American Academy of Sleep Medicine position statement. J Clin Sleep Med. 2021;17(10):2115-2119. https://doi.org/10.5664/jcsm.9476.
- Lloyd-Jones DM, Allen NB, Anderson CAM, et al. American Heart Association. Life’s essential 8: updating and enhancing the American Heart Association’s construct of cardiovascular health: a presidential advisory from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2022;146(5):e18-e43. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIR.0000000000001078.
- Foster RG. Sleep, circadian rhythms and health. Interface Focus. 2020;10(3):20190098. doi: 10.1098/rsfs.2019.0098.
- McConnell BV, Kronberg E, Medenblik LM, et al. The rise and fall of slow wave tides: vacillations in coupled slow wave/spindle pairing shift the composition of slow wave activity in accordance with depth of sleep. Front Neurosci. 2022;16:915934. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2022.915934.
- Pulver RL, Kronberg E, Medenblik LM, et al. Mapping sleep’s oscillatory events as a biomarker of Alzheimer’s disease. Preprint posted online February 16, 2023. doi: 10.1101/2023.02.15.528725.
- Claussen AH, Dimitrov LV, Bhupalam S, et al. Short sleep duration: children’s mental, behavioral, and developmental disorders and demographic, neighborhood, and family context in a nationally representative sample, 2016-2019. Prev Chronic Dis. 2023;20:E58. doi: 10.5888/pcd20.220408.
- Bird M, Neely KC, Montemurro G, Mellon P, MacNeil M, Brown C, et al. Parental perspectives of sleep in the home: shaping home-school partnerships in school-based sleep promotion initiatives. Prev Chronic Dis. 2023;20:E38. doi: 10.5888/pcd20.22039.
- Milenkova V, Nakova A. Personality Development and Behavior in Adolescence: Characteristics and Dimensions. Societies. 2023;13(6):148. https://doi.org/10.3390/soc13060148.
- Metin Karaaslan M, Basaran B. Dietary Acrylamide Exposure and Its Correlation with Nutrition and Exercise Behaviours Among Tur–kish Adolescents. Nutrients. 2025;7(15):2534. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu17152534.
- Gunderson J, McDaniel K, DiBlanda A. Association between insufficient sleep, depressive symptoms, and suicidality among Florida high school students. Prev Chronic Dis. 2023;20:E59. doi: 10.5888/pcd20.220403.
- Morey BN, Ryu S, Shi Y, Lee S. The mediating role of sleep disturbance on the association between stress and self-rated health among Chinese and Korean immigrant Americans. Prev Chronic Dis. 2023;20:E04. doi: 10.5888/pcd20.220241.
- Ramos AR, Wheaton AG, Johnson DA. Sleep Deprivation, Sleep Disorders, and Chronic Disease. Prev Chronic Dis. 2023 Aug 31;20:E77. doi: 10.5888/pcd20.230197. PMID: 37651644. PMCID: PMC10487788.
- Physiscal activity (eng). World Health Organization (WHO). 2020.
- Yu C, Wang T, Gao Y, et al. Association between physical activity and risk of gastroesophageal reflux disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Sport Health Sci. 2024 Sep;13(5):687-698. doi: 10.1016/j.jshs.2024.03.007. Epub 2024 Mar 27. PMID: 38552714. –PMCID: PMC11282378.
- Costa SA, Willumsen J, Meheus F, et al. The cost of inaction on physical inactivity to public health-care systems: a population-attri–butable fraction analysis. The Lancet Global Health. 2022;11(1):E32-E39. doi: 10.1016/S2214-109X(22)004648. PMID: 36480931. PMCID: PMC9748301.
- Grellier J, White MP, De Bell S, et al. Valuing the health benefits of nature-based recreational physical activity in England. Environment International. 2024;187:108667. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2024.108667. ISSN 0160-4120.
- Costantino A, Pessarelli T, Vecchiato M, Vecchi M, Basilisco G, Ermolao A. A practical guide to the proper prescription of physical activity in patients with irritable bowel syndrome. Dig Liver Dis. 2022 Nov;54(11):1600-1604. doi: 10.1016/j.dld.2022.08.034. Epub 2022 Sep 21. PMID: 36153192.
- Fenech A, Chockalingam N, Formosa C, Gatt A. Longitudinal effects of evidence-based physical education in Maltese children. Child and Adolescent Obesity. 2021;4(1):98-116. doi: 10.1080/2574254X.2021.1915041. S2CID 237846270.
- Milton K, Cavill N, Chalkley A, et al. Eight Investments That Work for Physical Activity. Journal of Physical Activity and Health. 2021;1:625-630. doi: 10.1123/jpah.2021-0112. hdl: 1983/8805dde9-3053-4103-aa70-314da5fd30cc.
- Physical Activity Guidelines for Americans, 2nd Edition. Office of Disease Prevention and Health Promotion. Retrieved 2020-12-04.
- Lin CY, Gentile NL, Bale L, et al. Implementation of a Physical Activity Vital Sigh in Primary Care: Associations Between Physical Activity, Demographic Characteristics, and Chronic Disease Burden. Preventing Chronic Disease. 2022;19:E33. doi: 10.5888/pcd19.210457. PMC11272163. PMID: 35749145. S2CID: 249965817.
- Global Recommendations on Physical Activity for Health, 2009. World Health Organization. Geneva, Switzerland. Accessed 13-07-2018. Available at: http://www.who.int/ncds/prevention/physical-activity/en/.
- World Health Organization. Guidelines on physical acti–vity and sedentary behaviour, 2020. https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240015128.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), Physical Activity Facts, 2022. https://www.cdc.gov/healthyschools/physicalactivity/facts.htm.
- Guthold R, Stevens GA, Riley LM, Bull FC. Global trends in insufficitnt physical activity among adolescents: a pooled analysis of 298 population-based surveys with 1.6 million adolescents. The Lancet Child & Adolescent Health. 2019;4(1):23-35. doi: 10.1016/S2352-4642(19)30323. ISSN 2352-4642. PMC6919336. PMID: 31761562.
- Usmani D, Ganapathy K, Patel D, et al. The role of exercise in preventing chronic diseases: current evidence and recommendations. Georgian Med News. 2023 Jun;339:137-142. PMID: 37522789.
- Cheney MK, Song H, Bhochhibhoya S, Lu Y. Chronic disease as a risk factor for cigarette and e-cigarette use from young adulthood to adulthood. Prev Med Rep. 2023 Oct 14;36:102473. doi: 10.1016/j.pmedr.2023.102473. PMID: 37881176. PMCID: PMC10594544.
- Zhu H, Xu P, Wei Y. et al. Smoking cessation improves health status of patients with chronic diseases: evidence from a longitudinal study of older adults in China. BMC Public Health. 2025;25:957. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-025-22203-7.
- Bryazka D, Reitsma MB, Griswold MG, et al.; GBD 2020 Alcohol Collaboration. Population-level risks of alcohol consumption by amount, geography, age, sex, and year: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2020. The Lancet. 2022;400(10347):185-235. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(22)00847-9. PMC9289789. PMID: 35843246.
- World Health Organization. “Tobacco”. WHO. World Health Organization. Archived from the original on 30 January 2023. Retrieved 30 January 2023.
- Tobacco in China. World Health Organization. Archived from the original on 2022-08-03. Retrieved 2022-09-04.
- Dubey D. Data Dive: Tobacco Kills 3,700 People Every Day, Causes 27 % of Cancer Cases. 2022. Factchecker.in. Retrieved 2022-09-04.
- Tobacco. www.who.int. 2024-07-31. Retrieved 2024-10-04.
- CDCTobaccoFree. 2021-08-16. Global Tobacco Control. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Retrieved 2024-02-24.
- Lay K. Tobacco exposure killed more than 7m people in 2023, study finds. The Guardian. 24 June 2025.
- Harmful Chemicals in Tobacco Products. www.cancer.org. Retrieved 2024-02-23.
- Just one cigarette a day can cause serious heart problems. New Scientist. 3 February 2020. Archived from the original on 22 December 2020. Retrieved 6 May 2020.
- Thomson NC, Polosa R, Sin DD. Cigarette smoking and asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2022;10(11):2783-2797. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaip.2022.04.034.
- Wang Z, Qiu Y, Ji X, Dong L. Effects of smoking cessation on individuals with COPD: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Public Health. 2024;12:1433269. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpubh.2024.1433269.
- Wang S, Shen C, Yang S. Analysis of health-related quality of life in elderly patients with stroke complicated by hypertension in China using the EQ-5D-3L Scale. J Multidiscip Healthc. 2024;17:1981-97. https://doi.org/10.2147/JMDH.S459629.
- Wu AD, Lindson N, Hartmann-Boyce J, et al. Smoking cessation for secondary prevention of cardiovascular disease. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022;2022(8):CD014936. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD014936.pub2.
- Alfredsson L, Klareskog L, Hedström AK. Influence of smoking on disease activity and quality of life in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: results from a Swedish case-control study with longitudinal follow-up. Arthritis Care Res. 2023;75(6):1269-77. https://doi.org/10.1002/acr.25026.
- Anjum F, Zohaib J. Oropharyngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Definitions (Updated ed.). Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing. 2020. doi: 10.32388/G6TG1L. PMID: 33085415. S2CID: 229252540. Bookshelf ID: NBK563268. Archived from the original on 11 June 2021. Retrieved 7 February 2021.
- Gormley M, Creaney G, Schache A, et al. Reviewing the epidemiology of head and neck cancer: definitions, trends and risk factors. British Dental Journal. 2022;233(9):780-786. doi: 10.1038/s41415-022-5166-x. ISSN 0007-0610. PMC9652141. PMID: 36369568.
- Smoking and Diabetes. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 23 April 2018. Archived from the original on 24 August 2019. Retrieved 4 November 2019.
- Shakiba E, Moradinazar M, Rahimi Z, et al. Tobacco smoking and blood parameters in the Kurdish population of Iran. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2023;23(1):401. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12872-023-03433-2.
- Jing Z, Li J, Wang Y, et al. Association of smoking status and health-related quality of life: difference among young, middle-aged, and older adults in Shandong. China Qual Life Res. 2021;30(2):521-30. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11136-020-02645-9.
- Cho ER, Brill IK, Gram IT, et al. Smoking cessation and short- and longer-term mortality. NEJM Evid. 2024;3(3):EVIDoa2300272. https://doi.org/10.1056/EVIDoa2300272.
- Share of deaths from smoking. Our World in Data. Archived from the original on 17 March 2020. Retrieved 5 March 2020.
- Seven out of 10 people protected by at least one tobacco control measure. World Health Organization. Retrieved 2023-08-15.
- Shield K, Manthey J, Rylett M, et al. National, regional, and global burdens of disease from 2000 to 2016 attributable to alcohol use: a comparative risk assessment study. Lancet Public Health. 2020 Jan;5(1):e51-e61. doi: 10.1016/S2468-2667(19)30231-2. PMID: 31910980.www.euro.who.int. Retrieved 8 February 2023.
- Rehm J, Crépault JF, Wettlaufer A, et al. What is the best indicator of the harmful use of alcohol? A narrative review. Drug Alcohol Rev. 2020 Sep;39(6):624-631. doi: 10.1111/dar.13053. Epub 2020 Apr 6. PMID: 32250491.
- The risks of drinking too much. NHS. Retrieved 23 July 2024.Risks of Adolescent Alcohol Use. HHS.gov. 19 January 2018. Archived from the original on 22 March 2019. Retrieved 3 June 2020.
- Management of Substance Abuse Team, World Health Organization (14 February 2019). Global status report on alcohol and health 2018. Geneva: World Health Organization. ISBN 978-92-4-156563-9. OCLC 1089229677.
- Alcohol & Diabetes — ADA. American Diabetes Association. Retrieved 30 November 2022.
- Palzes VA, Parthasarathy S, Chi FW, et al. Associations Between Psychiatric Disorders and Alcohol Consumption Levels in an Adult Primary Care Population. Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research. 2020;44(12):2536-2544. doi: 10.1111/acer.14477. PMC7756330. PMID: 33151592.
- WHO launches SAFER alcohol control initiative to prevent and reduce alcohol-related death and disability. World Health Organization (Press release). Archived from the original on 1 October 2018. Retrieved 21 November 2019.
- van de Luitgaarden IAT, van Oort S, Bouman EJ, et al. Alcohol consumption in relation to cardiovascular diseases and mortality: a systematic review of Mendelian randomization studies. Eur J Epidemiol. 2022 Jul;37(7):655-669. doi: 10.1007/s10654-021-00799-5. Epub 2021 Aug 22. PMID: 34420153. PMCID: PMC9329419.
- Ding C, O’Neill D, Bell S, et al. Association of alcohol consumption with morbidity and mortality in patients with cardiovascular disease: original data and meta-analysis of 48,423 men and women. BMC Med. 2021 Jul 27;19(1):167. doi: 10.1186/s12916-021-02040-2. PMID: 34311738. PMCID: PMC8314518.
- Patra J, Buckley C, Kerr WC, et al. Impact of body mass and alcohol consumption on all-cause and liver mortality in 240,000 adults in the United States. Drug Alcohol Rev. 2021 Sep;40(6):1061-1070. doi: 10.1111/dar.13265. Epub 2021 Mar 8. PMID: 33682957. PMCID: PMC9383267.
- Chrystoja BR, Rehm J, Manthey J, et al. A systematic comparison of the global comparative risk assessments for alcohol. Addiction. 2021 Aug;116(8):2026-2038. doi: 10.1111/add.15413. Epub 2021 Feb 3. PMID: 33449382.
- Chung DD, Pinson MR, Bhenderu LS, et al. Toxic and Teratogenic Effects of Prenatal Alcohol Exposure on Fetal Development, Adolescence, and Adulthood. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021;22(16):8785. doi: 10.3390/ijms22168785. PMC8395909. PMID: 34445488.
- Teen Alcohol Consumption: 5 Dangerous Trends Parents Need to Know. 7 April 2020.
- Alcohol harms the brain in teen years — before and after that, too. 15 January 2021.
- World Health Organization. Obesity and overweight. Geneva: WHO; 2024. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight.
- Оne in eight people are now living with obesity. World Health Organization. 1 March 2024. Retrieved 1 March 2024.
- Prevalence of obesity among children and adolescents, BMI > +2 standard deviations above the median, 2022. World Health Organization. Retrieved 04, February 2025.
- Acceleration plan to support Member States in implementing the recommendations for the prevention and management of obesity over the life course, 2022. World Health Organization A75/10 Add.6. Annex 12-27 April 2022.
- Prieto-Latorre C, Lopez-Agudo LA, Marcenaro-Gutierrez OD. Influence of Body Mass Index on Health Complains and Life Satisfaction. Quality of Life Research. 2024;33(3):705-19. doi: 10.1007/s11136-023-03557-0.
- Lee MJ. Vitamin D Enhancement of Adipose Biology: Implications on Obesity-Associated Cardiometabolic Diseases. Nutrients. 2025;17(3):586. Published 2025 Feb 6. doi: 10.3390/nu170305866.
- Gombart AF, Pierre A, Maggini SA. Review of Micronutrients and the Immune System — Working in Harmony to Reduce the Risk of Infection. Nutrients. 2020;12:236. doi: 10.3390/nu12010236 https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC7019735.
- Kamińska W, Bobrzyk A, Łyko G, et al. Supplementation of vitamin D in children with obesity and vitamin D deficiency — review of outcomes in terms of obesity parameters and comorbidities. Journal of Education, Health and Sport. Online. 2023;44(1):322-332. [Accessed 18 May 2025]. doi: 10.12775/jehs.2023.44.01.021.
- Fiamenghi VI, Mello ED. Vitamin D deficiency in children and adolescents with obesity: a meta-analysis. J Pediatr (Rio J). 2020;97(3):273-279. doi: 10.1016/j.jped.2020.08.0y06 PMID: 33022267. PMCID: PMC9432231.
- Karimian P, Ebrahimi HK, Jafarnejad S, Delavar MA. Effects of vitamin D on bone density in healthy children: A systematic review. J Family Med Prim Care. 2022 Mar;11(3):870-878. doi: 10.4103/jfmpc.jfmpc_2411_20.
- Karlsson MK, Rosengren BE. Exercise and peak bone mass. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2020;18:285-290.
- Wu F, Fuleihan GE, Cai G, et al. Vitamin D supplementation for improving bone density in vitamin D-deficient children and adolescents: systematic review and individual participant data meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Am J Clin Nutr. 2023 Sep;118(3):498-506. doi: 10.1016/j.ajcnut.2023.05.028.
- Van Daal MT, Folkerts G, Garssen J, Braber S. Pharmacological Modulation of Immune Responses by Nutritional Components. Pharmacol Rev. 2021;73:198-232. doi: 10.1124/pharmrev.120.000063.
- Taylor SN. Vitamin D in Toddlers, Preschool Children, and Adolescents. Ann Nutr Metab. 2020;76(2):30-41. doi: 10.1159/000505635.
- National institutes of health. Vitamin D. Fact Sheet for Health Professionals. https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/VitaminD-HealthProfessional/#ref.
- Viraraghavan VR, Seth A, Aneja S, et al. Effect of high dose vitamin D supplementation on vitamin D nutrition status of pre-pubertal children on anti-epileptic drugs — A randomized controlled trial. Clin Nutr ESPEN. 2019 Feb;29:36-40. doi: 10.1016/j.clnesp.2018.11.007. Epub 2018 Nov 23. PMID: 30661698.
- Alzohily B, AlMenhali A, Gariballa S, et al. Unraveling the complex interplay between obesity and vitamin D metabolism. Sci Rep. 2024;14:7583. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-58154-z.
- Hajhashemy Z, Lotfi K, Heidari Z, Saneei P. Serum Vitamin D Levels in Relation to Abdominal Obesity in Children and Adolescents: A Systematic Review and Dose-Response Meta-Analysis. Front Nutr. 2022;9:806459. Published 2022 Feb 16. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.806459.
- Bennour I, Haroun N, Sicard F, et al. Vitamin D and Obesity/Adiposity — A Brief Overview of Recent Studies. Nutrients. 2022;14(10):2049. Published 2022 May 13. doi: 10.3390/nu14102049.
- Lu S, Cao ZB. Interplay between Vitamin D and Adipose Tissue: Implications for Adipogenesis and Adipose Tissue Function. Nutrients. 2023;15(22):4832. Published 2023 Nov 18. doi: 10.3390/nu15224832.
- Park SY, Han SN. Vitamin D and obesity. Advances in Food and Nutrition Research. 2024;109:221-247. doi.org/10.1016/bs.afnr.2023.12.006.
- Corsello A, Macchi M, D’Oria V, et al. Effects of vitamin D supplementation in obese and overweight children and adolescents: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Pharmacological Research. 2023;192:106793. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrs.2023.106793.
- Płudowski P, Kos-Kudła B, Walczak M, et al. Guidelines for Preventing and Treating Vitamin D Deficiency: A 2023 Update in Poland. Nutrients. 2023;15(3):695. Published 2023 Jan 30. doi: 10.3390/nu15030695.
- NHANES 2019-2020. CDC. Atlanta; 2022. https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/nhanes/index.html.
- World Health Organization (WHO). Noncommunicable di–seases. 2023. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/noncommunicable-diseases.
- Mărginean CO, Meliț LE, Borka Balas R, et al. The Crosstalk between Vitamin D and Pediatric Digestive Disorders. Diagnostics (Basel). 2022 Sep 27;12(10):2328. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics12102328. PMID: 36292016. PMCID: PMC9600444.
- Dewa NWI, Wayan WDN. Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease and Obesity [Internet]. Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease — A Growing Concern. IntechOpen. 2023. Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.5772/intechopen.106528.